iPhone health apps have become increasingly popular, offering a diverse range of tools to track and improve various aspects of well-being. From meticulously logging workouts to monitoring mental health, these apps are transforming how we manage our health. They provide a wealth of information, allowing users to gain insights into their daily habits and make informed decisions about their health journeys.
This exploration delves into the multifaceted world of iPhone health apps, examining their features, functionality, user experience, data security, and integration with other iPhone features. We’ll analyze the evolution of these apps over time and explore the factors driving their growth. By understanding the various design patterns, best practices, and common user feedback, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current landscape of health apps on the iPhone platform.
User Experience and Interface Design
iPhone health apps are increasingly popular, providing users with a personalized approach to wellness. Effective design is crucial for engaging users and encouraging long-term use. A well-structured interface simplifies data entry and offers clear visualizations of health metrics.
A thoughtful user experience (UX) design enhances the app’s usability, making it easy for users to understand and interact with the app’s features. The interface design should prioritize clarity, consistency, and intuitive navigation to maintain user engagement.
Typical User Interface Elements
Health apps on iPhones often feature similar elements to foster familiarity and ease of use. These include:
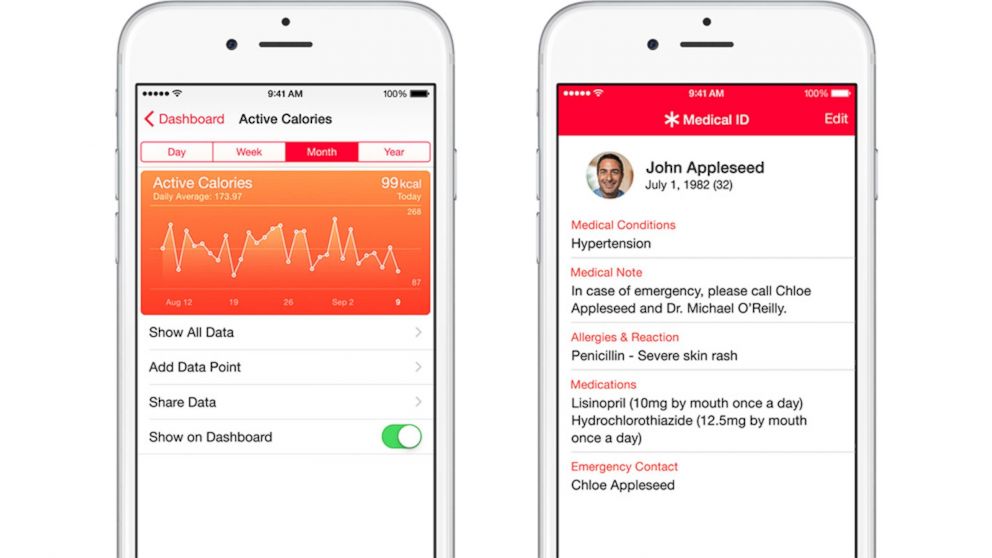
- Dashboard: A central screen displaying key health metrics like steps taken, heart rate, and sleep quality. This visually summarizes current health status and encourages continued monitoring.
- Data Entry Forms: These allow users to log activities, food intake, or record other relevant information. Forms should be concise and easily navigable.
- Charts and Graphs: Visual representations of health data are crucial for understanding trends and progress over time. Charts should be clear, well-labeled, and easily customizable.
- Progress Tracking: Progress bars, milestones, and badges are effective visual cues that motivate users and highlight achievements.
- Notifications: These are essential for reminders, alerts, and important updates related to health goals or progress.
Comparison of Different Health Apps
Comparing different health apps reveals varying approaches to design and user experience. Some apps prioritize visual appeal and a sleek aesthetic, while others emphasize data accuracy and detailed reporting. This variety allows users to select apps tailored to their individual preferences. For example, some apps may focus on providing detailed information about specific metrics, while others offer a more general overview of overall well-being.
Design Considerations for Mobile Health Apps
Several key considerations contribute to the success of a mobile health app. Prioritizing user needs is essential; consider the user’s level of health literacy and their goals when designing the app.
- Intuitive Navigation: Users should be able to easily find and access the information they need. Simple, clear navigation menus and logical screen transitions are vital.
- Accessibility: Designers should consider users with disabilities, ensuring the app is accessible to everyone. This includes sufficient font sizes, color contrast, and keyboard navigation.
- Data Security: Data security and privacy are paramount in health apps. The app should be designed to protect user data and comply with relevant regulations.
- Personalization: Personalized recommendations and tailored content can increase user engagement and encourage adherence to health goals. This involves understanding user preferences and providing tailored feedback.
Best Practices for Intuitive and Engaging Interfaces
To create intuitive and engaging interfaces, consider these best practices:
- Consistency: Maintain consistent design elements across the app, including colors, fonts, and button styles. This creates a familiar and predictable user experience.
- Clear Visualizations: Present data clearly and concisely. Use charts, graphs, and other visualizations to effectively communicate complex information.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Provide immediate feedback to user actions, such as confirming data entry or acknowledging a successful update. This keeps users informed and engaged.
- Simplicity: Avoid unnecessary complexity. Focus on essential features and keep the interface uncluttered.
Design Patterns for iPhone Health Apps
Different design patterns can be applied to enhance the functionality and appeal of health apps.
| Design Pattern | Description | Example Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Navigation | Methods for users to move between screens | Tab bar, swipe navigation, side menus |
| Input Fields | Different ways to input data | Text fields, sliders, date pickers, checkboxes |
| Data Visualization | How to present data clearly | Charts (line, bar, pie), graphs, progress bars, maps |
Features and Functionality
Health apps on iPhones have become increasingly popular tools for managing and improving well-being. These apps offer a wide range of features, catering to diverse needs and preferences. From basic workout tracking to sophisticated personalized nutrition plans, the functionality varies significantly between different applications. This section details the essential features, their varying levels of sophistication, and provides a comparative analysis of leading health apps.
Essential Features
Many health apps share core functionalities that address fundamental aspects of wellness. These features are often crucial for users to establish and maintain healthy habits. A robust foundation of essential features helps users gain a clearer understanding of their health data, allowing for informed decision-making and improved self-care.
- Workout Tracking: This feature allows users to log their exercise routines, monitor progress, and set fitness goals. This includes recording activities like running, cycling, strength training, and more, providing insights into duration, intensity, and calories burned.
- Sleep Monitoring: Tracking sleep patterns helps users understand their sleep quality and identify potential issues. Many apps use sensors or input from users to track sleep duration, sleep stages, and wake-up times, providing valuable insights into their rest.
- Nutrition Tracking: Logging food intake helps users monitor their dietary habits and ensure they’re meeting their nutritional needs. Users input the foods they consume, enabling the app to calculate calories, macronutrients, and micronutrients. This feature is invaluable for managing weight, achieving specific dietary goals, or addressing dietary restrictions.
- Stress Monitoring: Some apps incorporate features that measure stress levels, utilizing various methods like heart rate variability, activity levels, or mood questionnaires. This allows users to understand the potential stressors in their lives and develop coping strategies.
Varying Levels of Functionality
Different health apps offer varying degrees of sophistication in their features. Basic apps often focus on fundamental functionalities, while advanced apps incorporate personalized recommendations, sophisticated algorithms, and extensive data analysis to tailor health plans to the user’s unique needs.
Comparison of Top Health Apps
The table below illustrates the range of features offered by three popular health apps. It highlights the variations in functionality available across different platforms.
| Feature | App A | App B | App C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Workout Tracking | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Sleep Monitoring | No | Yes | Yes |
| Nutrition Tracking | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Stress Monitoring | Yes (basic) | Yes (advanced) | No |
Advanced Functionalities
Some health apps go beyond basic tracking to provide advanced functionalities. These features often utilize machine learning algorithms to analyze user data and offer personalized recommendations.
- Personalized Exercise Plans: Some apps generate customized workout routines based on user preferences, fitness level, and goals. These plans are tailored to address specific needs and limitations.
- Smart Reminders and Notifications: These apps send reminders for workouts, medication, or important health checks. This functionality can help users adhere to their routines and maintain consistency in their health management.
- Integration with Wearable Devices: Many advanced apps can connect to fitness trackers, smartwatches, and other wearable devices. This seamless data integration allows for a more comprehensive and accurate view of health metrics.
- Mental Health Support: Some apps offer resources for managing mental well-being. This might include stress-reduction techniques, meditation guides, or access to mental health professionals.
Data Privacy and Security
Protecting user health data is paramount in any health application. User trust and confidence are essential for successful adoption and long-term use. Robust data security measures are critical to maintaining this trust, ensuring that sensitive information remains confidential and accessible only to authorized individuals.
Data privacy and security in health apps encompass a wide range of considerations, from the collection and storage of personal information to the implementation of security protocols and user controls. Thorough understanding and implementation of these principles are crucial to building a reliable and trustworthy health application.
Data Collection, Storage, and Use
Health apps typically collect a variety of data, including personal health information, medical history, and lifestyle choices. This data is collected via user input, sensors, and potentially, data integration from other sources. Secure storage is essential to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Data is often used for personal health management, providing insights, and supporting decision-making. Aggregated data may also be used for research or to inform public health initiatives. Data anonymization and de-identification procedures are important to maintain user privacy.
Security Measures Implemented by iPhone Health Apps
Apple’s Health app, and other iPhone health apps, often leverage industry-standard security protocols to safeguard user data. This includes encryption of data both in transit and at rest, using strong cryptographic algorithms. Access controls and authentication measures are employed to restrict access to sensitive information. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments help to identify and mitigate potential risks. Data backups and disaster recovery plans are in place to protect against data loss. The implementation of multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security to user accounts.
Best Practices for Ensuring User Data Security
Implementing strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and regularly updating app software are crucial user-centric best practices. Users should also be mindful of phishing attempts and suspicious links. Reviewing app privacy policies and understanding data sharing options is recommended before providing any sensitive information.
Data Sharing and Privacy Policies
Data sharing and privacy policies are crucial elements of health apps. Users should carefully review these policies to understand how their data is collected, used, and shared. Clear and concise language is essential for effectively communicating these policies to users. Transparency is key, as is providing users with explicit choices regarding data sharing. User consent is paramount before any data is shared with third parties.
Data Security Features of Various Health Apps
| App | Data Encryption | Data Sharing Options | User Control |
|---|---|---|---|
| App A | AES-256 | Limited | Yes |
| App B | AES-128 | Extensive | Yes |
Note: The table illustrates a simplified comparison. Actual security features and data sharing policies will vary significantly depending on the specific app and its implementation.
Integration with Other iPhone Features

Seamless integration with other iPhone features, such as Siri and Apple Watch, significantly enhances the user experience of health apps. This interconnectedness allows for a more comprehensive and personalized approach to health management, streamlining data collection and analysis. The integration leverages the power of Apple’s ecosystem to provide a unified platform for health data, making it easier for users to track their progress and achieve their goals.
This integration empowers users to manage their health information across various devices, fostering a more proactive and personalized approach to well-being. It also provides a more convenient and efficient way to access and analyze health data, leading to better insights and improved decision-making.
Siri Integration
Siri integration allows users to access and interact with their health data through voice commands. This feature enables hands-free data retrieval, such as checking recent steps taken, heart rate, or sleep duration. Users can also set reminders for medication or appointments, or receive personalized health recommendations based on their activity level or dietary habits. This hands-free approach enhances convenience and makes it easier to maintain consistent health tracking. For example, a user could ask Siri, “How many steps have I taken today?” and receive the answer immediately.
Apple Watch Integration
Apple Watch integration provides real-time health data capture, allowing users to monitor their activities, heart rate, and sleep patterns continuously. This integration facilitates more accurate and detailed data collection compared to solely relying on iPhone apps. Furthermore, it allows for quick and easy access to health information, such as heart rate variability or workout duration, directly on the watch face. This constant monitoring enables users to react to sudden changes in their health data. For instance, if a user’s heart rate spikes unexpectedly, they can immediately view the data on their Apple Watch and take appropriate action.
Data Management and Analysis
The integration of iPhone health apps with Siri and Apple Watch improves data management and analysis by consolidating data from multiple sources. This consolidated data enables comprehensive insights into user health trends. For example, a user can track their sleep patterns on their Apple Watch and then analyze the data alongside their dietary habits logged in the iPhone app, gaining a more holistic understanding of their overall health. This detailed data also allows for more precise analysis of trends and patterns, which in turn empowers users to make more informed decisions about their health.
Streamlined Data Flow and User Workflow
The integration streamlines data flow and user workflow by automatically syncing data between devices. This seamless synchronization eliminates the need for manual data entry, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Furthermore, the automatic data transfer between the iPhone and Apple Watch enables users to access and interpret their health data in real-time, allowing for immediate feedback and adjustments to their lifestyle choices. For example, a user can track their workout progress on their Apple Watch and immediately see the impact on their daily calorie expenditure in the iPhone app. This continuous synchronization fosters a more proactive approach to health management.
Examples of Integration in Health Apps
Several health apps leverage these integrations effectively. For instance, the Health app, integrated with Siri, enables users to access their health data through voice commands, while other fitness apps utilize Apple Watch to provide real-time feedback during workouts. These features enhance user engagement and foster a more proactive approach to health management.
User Feedback and App Development Trends
User feedback is crucial for the continuous improvement of health apps. Understanding how users interact with and perceive the app is essential for developers to iterate and create a more user-friendly and effective product. Positive feedback highlights areas of success, while negative feedback pinpoints pain points and opportunities for enhancement.
User Feedback Mechanisms
Users provide feedback through various channels, including in-app surveys, ratings, reviews on app stores, and social media discussions. In-app surveys offer direct and targeted insights into user experiences. App store reviews provide a broad overview of user opinions and experiences. Social media interactions allow for real-time feedback and community engagement.
Common User Feedback Patterns
Several common feedback patterns emerge in user interactions with health apps. Users often express concerns about app performance, usability, and data security. Performance issues, such as frequent crashes or slow loading times, can significantly impact user satisfaction. Usability issues include difficulties in navigating the app or understanding features. Data security concerns often relate to the handling and protection of personal health information.
App Development Trends Influencing Health Apps
Several trends in app development influence the design and functionality of health apps. The increasing availability of advanced sensors and wearables drives the integration of real-time data into health apps. The growing emphasis on personalized medicine and preventative care results in more tailored health recommendations. Furthermore, the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) allows for the development of more sophisticated health monitoring and prediction capabilities.
Current and Future Trends in iPhone Health App Development
Current trends include the integration of AI for personalized health insights and the use of augmented reality (AR) for interactive experiences. Future trends might involve the use of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) for real-time health monitoring and the development of more sophisticated personalized fitness programs. Examples of current trends include apps utilizing AR for visualizing exercise techniques or using AI to analyze sleep patterns for personalized recommendations.
How User Feedback Shapes App Development and Evolution
User feedback directly influences the development and evolution of health apps. By analyzing user feedback, developers can identify areas needing improvement and implement changes to enhance the app’s functionality and user experience. Positive feedback reinforces successful features and design choices. Constructive criticism provides valuable insights for improving the app’s performance and user satisfaction. For instance, feedback on slow loading times could lead to code optimization, and feedback about confusing navigation could lead to improved UI design.
Summary of Common User Feedback Categories
| Feedback Category | Example | Suggested Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | App crashes frequently | Optimize code, improve server response time |
| Usability | Difficult to navigate | Improve UI design, add clear instructions |
| Data Security | Concerns about data privacy | Implement robust security measures, provide clear data privacy policies |
| Features | Missing key features | Develop and implement requested features, prioritize user needs |
| Accuracy | Inaccurate measurements | Validate data sources, ensure data accuracy and reliability |
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, iPhone health apps have evolved significantly, offering a wide spectrum of functionalities and features to support diverse health needs. From fitness tracking to nutrition management and mental wellness support, these apps provide powerful tools for users to monitor, analyze, and ultimately improve their health. The seamless integration with other iPhone features, coupled with robust data security measures, underscores the commitment to user experience and data privacy. As the landscape of health apps continues to evolve, user feedback will remain crucial for shaping future development trends, ensuring these apps remain effective and user-friendly tools for enhancing well-being.