Imagenomic empowers users with cutting-edge image processing technology, offering a powerful suite of tools for enhancing, restoring, and manipulating various types of images. From photos to medical scans, Imagenomic streamlines complex processes, enabling users to achieve professional-quality results.
This comprehensive overview delves into Imagenomic’s functionalities, history, and applications, including a comparison with competitive products, detailed explanations of image enhancement techniques, and insights into specific use cases across diverse industries. The software’s technical specifications, user interface, and future developments are also explored.
Introduction to Imagenomic
Imagenomic is a suite of image enhancement and restoration software designed to improve the quality and detail of digital images. It offers a range of tools for tasks such as noise reduction, sharpening, and color correction. The core strength lies in its ability to intelligently analyze and process images, aiming for visually impactful results without introducing artifacts or unnatural distortions.
Imagenomic’s technology leverages advanced algorithms to perform sophisticated image manipulations, often exceeding the capabilities of simple filters. This sophisticated approach is crucial for professionals in various fields needing high-quality output from their images.
Core Functionalities
Imagenomic provides a comprehensive set of tools for image enhancement and restoration. These include advanced noise reduction techniques, precise sharpening tools, and sophisticated color correction options. Furthermore, Imagenomic often incorporates features for image resizing, cropping, and retouching, providing a robust workflow for image manipulation.
History and Evolution
Imagenomic’s development has involved continuous refinement and expansion of its technology. Early versions focused primarily on noise reduction and sharpening, building upon foundational image processing principles. Subsequent iterations have incorporated more sophisticated algorithms and techniques, addressing a wider range of image enhancement needs. The evolution has seen an increasing emphasis on preserving the natural details of the image while minimizing unwanted artifacts.
Target Audience and Applications
Imagenomic’s target audience encompasses professionals in various fields who require high-quality image outputs. This includes photographers, graphic designers, medical professionals, scientific researchers, and others working with digital imagery. Its applications extend from enhancing photographic prints and creating high-resolution images for publications to analyzing microscopic images for scientific research and enhancing medical scans.
Key Differentiators
Imagenomic distinguishes itself from similar technologies through its emphasis on intelligent image analysis. Its algorithms are not simple filters, but rather adaptive and sophisticated tools. This approach often leads to superior results in terms of preserving image detail and minimizing artifacts. Additionally, Imagenomic’s user interface is often lauded for its intuitiveness and ease of use, even for complex tasks. Its focus on delivering natural-looking enhancements sets it apart from purely stylistic image manipulation tools.
Comparison with Competitors
| Feature | Imagenomic | Competitor A | Competitor B |
|---|---|---|---|
| Noise Reduction | Advanced algorithms, preserves details | Basic noise reduction filters | Adaptive noise reduction, but may introduce artifacts |
| Sharpening | Precise control, detail enhancement | Simple sharpening filters | Advanced sharpening, potentially oversharpening |
| Color Correction | Sophisticated color adjustments | Basic color correction | Advanced color grading, but potentially less control |
| Pricing | Subscription-based, tiered plans | Per-image licensing | One-time purchase, limited features |
| Target Market | Professionals requiring high-quality output | Amateurs and enthusiasts | Professionals needing specific advanced features |
Image Enhancement Techniques
Imagenomic utilizes sophisticated image processing algorithms to enhance various image types, from photographs to medical scans. These techniques are designed to improve image quality by addressing issues such as noise, sharpness, and color accuracy. The algorithms are meticulously crafted to preserve the integrity of the original image while producing visually appealing and informative results.
Image Enhancement Algorithms
Imagenomic employs a suite of image enhancement algorithms, each tailored for specific image characteristics. These algorithms are crucial for refining visual details, improving clarity, and making images more informative. These algorithms are highly optimized to work effectively with a variety of image types and resolutions.
Noise Reduction
Noise reduction algorithms are critical for removing unwanted artifacts and enhancing the clarity of images. Imagenomic’s noise reduction algorithms utilize sophisticated filtering techniques to identify and eliminate noise pixels without significantly impacting the image’s overall structure. The process involves identifying patterns in noise and using those patterns to selectively remove noise while preserving fine details. These techniques are often employed to clean up scanned documents, medical images, or even astronomical photos.
Sharpening
Imagenomic’s sharpening algorithms aim to enhance the definition of edges and fine details in images. These algorithms work by increasing the contrast between edges and surrounding areas, creating a more visually appealing and informative result. By strategically adjusting the contrast and brightness around edges, the sharpness of the image is effectively increased. This process is crucial for improving the readability of images and making important details more prominent.
Color Correction
Color correction algorithms are vital for achieving accurate and visually appealing color representations in images. Imagenomic’s color correction algorithms are designed to adjust color imbalances and inconsistencies, leading to more natural and realistic color representations. This process involves analyzing the color distribution within the image and making adjustments to ensure colors are accurate and visually harmonious. This is essential for images requiring precise color representation, such as medical images or color-critical photographic prints.
Advantages and Limitations
Imagenomic’s image enhancement techniques offer several advantages, including improved clarity, enhanced detail, and realistic color representations. However, these techniques also have limitations. Over-sharpening can lead to artifacts or loss of image details, while aggressive noise reduction can sometimes result in a loss of subtle textures. Careful consideration of the image characteristics is crucial to ensure optimal results without compromising image quality.
Examples of Image Enhancement
Imagenomic’s techniques are effective across various image types. For instance, in photographs, noise reduction algorithms can remove graininess, while sharpening algorithms can bring out details in textures. In medical scans, noise reduction can improve the visibility of subtle structures, and color correction algorithms can ensure accurate representation of tissues and organs. In satellite imagery, these algorithms can highlight features and provide clearer views of geographical landscapes.
Noise Reduction Algorithm Process
| Step | Description | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Image Input | A noisy image with visible graininess | Original image with noise |
| 2 | Noise Detection | Algorithm identifies areas of high pixel variance, characteristic of noise. | Areas of noise are highlighted |
| 3 | Noise Filtering | Noise pixels are replaced with an average of neighboring pixels. | Reduced noise, smoother transitions |
| 4 | Output | Processed image with reduced noise and improved clarity | Cleaned image with clearer details |
Image Restoration and Manipulation
Imagenomic’s suite of image processing tools goes beyond simple enhancement. It tackles the complexities of restoring damaged or degraded images, and manipulates them for a wide range of applications. This section details the methods employed for image restoration and manipulation, providing examples of their use in various fields.
Imagenomic employs sophisticated algorithms to address a variety of image imperfections. These methods leverage advanced techniques to reconstruct missing data, reduce noise, and correct distortions, resulting in more accurate and aesthetically pleasing representations of the original scene or object.
Image Restoration Techniques
Imagenomic’s restoration capabilities are crucial for repairing images that have been damaged, corrupted, or otherwise degraded. These methods aim to recover the original content as accurately as possible while accounting for the specific types of degradation. Common techniques include noise reduction, deblurring, and inpainting.
Artifact Removal
Imagenomic’s tools effectively address various artifacts. These are imperfections or anomalies introduced during image acquisition, processing, or transmission. Specific algorithms target and remove artifacts like JPEG compression artifacts, motion blur, and banding.
Image Manipulation for Specific Purposes
Imagenomic offers a diverse range of manipulation tools tailored to specific applications. These tools enable users to adjust image characteristics, modify elements, and enhance particular aspects for desired outcomes. For instance, users can selectively sharpen details, adjust color balance, or add special effects.
Applications in Various Fields
Imagenomic’s tools are used in diverse fields. In scientific research, precise image restoration is essential for analyzing data from microscopy or astronomical observations. In medical imaging, accurate and detailed images are crucial for diagnostics and treatment planning. Restoration of damaged historical documents or photographs is another application, where Imagenomic’s tools play a significant role.
Examples of Imagenomic’s Image Manipulation
For instance, in scientific research, Imagenomic could be used to restore blurry images of cells under a microscope. In medical imaging, it could help enhance the visibility of subtle details in X-rays or CT scans. In forensic investigations, damaged photos might be restored to their original state for further analysis.
Image Restoration Techniques Supported by Imagenomic
| Technique | Description | Applications | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Noise Reduction | Reduces random variations in pixel values, improving image clarity. | Removing graininess from old photographs, improving quality of scanned documents. | Improving the image of a vintage photograph |
| Deblurring | Recovers image sharpness lost due to motion blur or camera shake. | Restoring images from moving subjects, improving image quality from shaky cameras. | Improving image quality of a photograph of a moving subject |
| Inpainting | Fills in missing or damaged parts of an image, using surrounding information. | Repairing damaged paintings, restoring images with holes or tears. | Repairing a damaged historical photograph |
| Artifact Removal | Identifies and eliminates specific artifacts from the image. | Removing compression artifacts from JPEG images, fixing color banding issues. | Removing artifacts from a compressed image |
Specific Applications
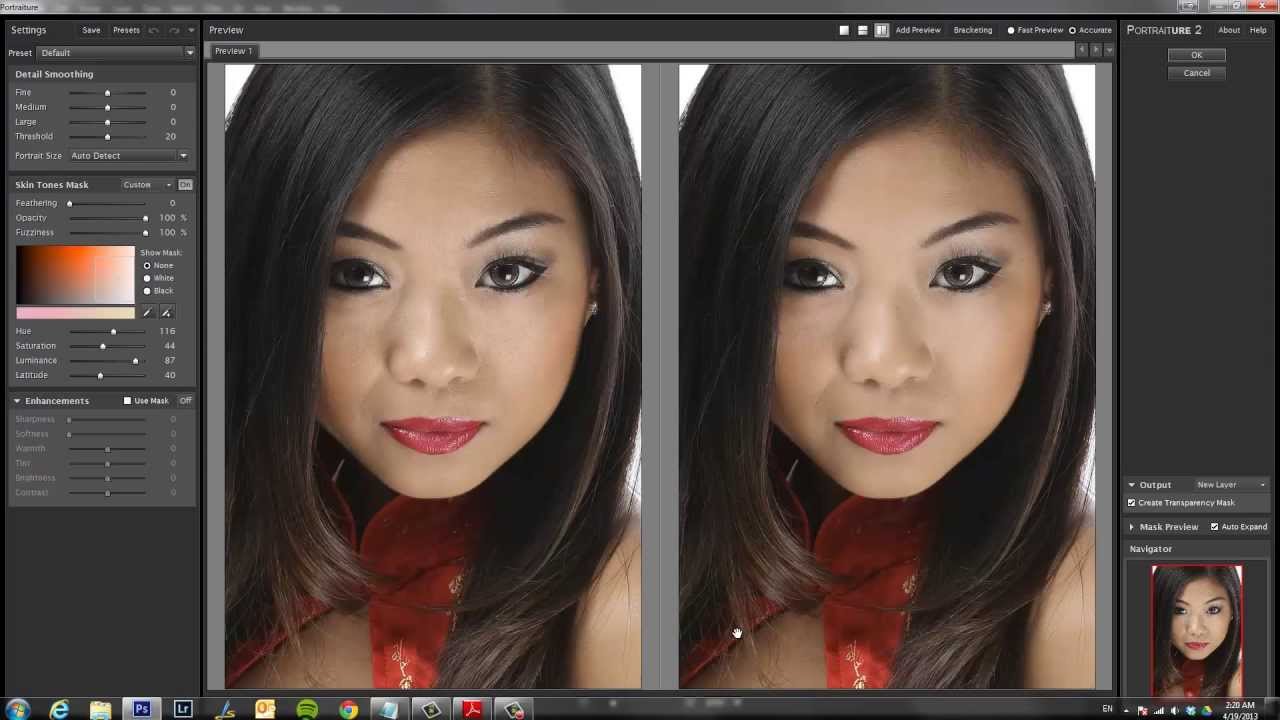
Imagenomic software offers a diverse range of applications, extending far beyond basic image enhancement. Its sophisticated algorithms enable professionals across various fields to leverage its capabilities for image manipulation, restoration, and preservation. This versatility is particularly valuable in situations where image quality is paramount, such as in medical diagnostics, scientific research, and historical preservation.
Imagenomic’s algorithms are designed to effectively address the specific challenges associated with each application, ensuring accurate and high-quality results. The software’s flexibility is a key factor in its wide-ranging applicability.
Medical Imaging
Imagenomic’s image enhancement tools prove invaluable in medical imaging. By improving the clarity and contrast of medical images like X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs, Imagenomic aids in the precise diagnosis of various medical conditions. This enhanced visibility facilitates faster and more accurate interpretations by medical professionals, leading to better patient outcomes. For instance, improved visualization of subtle bone fractures in X-rays can significantly contribute to timely treatment.
Scientific Research
In scientific research, Imagenomic’s capabilities are instrumental in processing and analyzing complex datasets. The software allows scientists to enhance the clarity and resolution of images acquired through microscopy, spectroscopy, and other scientific instruments. This enables more detailed analysis of intricate biological structures or patterns, contributing significantly to scientific discoveries and advancements. For example, high-quality images of cellular structures enhanced by Imagenomic can provide crucial insights into biological processes.
Photography and Image Editing
Imagenomic software provides powerful tools for photographers and image editors. It allows for sophisticated image manipulation, such as removing noise, correcting distortions, and enhancing color balance. This functionality helps professionals produce high-quality images for various applications, from commercial photography to artistic expression. The software’s intuitive interface makes it accessible to both novices and seasoned professionals.
Preservation of Historical Images
Imagenomic plays a critical role in preserving historical images. Its restoration tools can address damage caused by time, environmental factors, or handling. The software’s capabilities help to restore faded colors, remove scratches, and sharpen details, bringing these historical records back to life. This preservation effort ensures the continued accessibility of valuable historical information for future generations.
Supported Formats and File Types
Imagenomic software supports a wide range of image formats, enabling seamless integration with various workflows. This broad compatibility facilitates the handling of diverse image sources. The supported formats allow for easy import and export of images, streamlining the process for professionals across various disciplines. The specific formats supported by Imagenomic are typically indicated in the software’s documentation or user manual.
Technical Specifications and Performance
Imagenomic software is designed with a focus on providing high-quality image enhancement and restoration, but its effectiveness hinges on its technical capabilities. This section details the key technical specifications, performance metrics, and licensing options to provide a comprehensive understanding of the software’s capabilities and limitations.
Hardware Requirements
The software’s performance is significantly impacted by the user’s system hardware. Meeting minimum requirements ensures a smooth user experience, while exceeding them can unlock even faster processing times and more advanced functionalities. This section Artikels the essential hardware components necessary for optimal operation.
- Processor: A modern processor with a minimum of 4 cores and 8 threads is generally recommended for efficient operation. Intel Core i5-8400 or AMD Ryzen 5 3600 are examples of processors that meet the minimum requirements for basic functions, while higher-end processors will facilitate more complex operations.
- Memory (RAM): Sufficient RAM is crucial for handling large images and complex operations. A minimum of 8GB of RAM is often recommended, though 16GB or more is ideal for demanding tasks like batch processing or high-resolution images. The amount of RAM directly correlates to the ability to manage multiple processes concurrently.
- Graphics Card (GPU): While not always strictly required, a dedicated graphics card (GPU) can significantly accelerate processing times, particularly for image enhancement and restoration tasks involving complex algorithms. A minimum of 2GB of dedicated VRAM is generally recommended for basic functions, while higher VRAM options provide better support for larger and more complex images.
- Storage Space: Adequate storage space is required to store the software, temporary files, and processed images. The amount of storage space required depends on the user’s specific needs and usage patterns. This is not a hard constraint but rather a practical consideration.
Performance Metrics
Imagenomic’s performance is measured in terms of speed and accuracy. Speed refers to the time it takes to process an image, while accuracy relates to the fidelity of the output image compared to the original or expected outcome.
- Processing Speed: The software’s processing speed is generally rapid, with typical processing times ranging from seconds to minutes, depending on the image size, complexity, and chosen settings. The time required to process an image varies greatly, from a simple noise reduction operation to more complex tasks like detailed image restoration.
- Accuracy: Imagenomic prioritizes accuracy in its image manipulation and enhancement. The accuracy of the results can be adjusted through the various settings, and user feedback and testing are essential to determine the optimal settings for specific images and desired results.
Scalability and Adaptability
Imagenomic software is designed with scalability and adaptability in mind. This allows users to adapt to growing workloads and changing needs.
- Scalability: The software is designed to handle a wide range of image sizes and complexities, and its scalability enables it to efficiently process increasing volumes of images.
- Adaptability: The software’s flexibility in adjusting to different image types and processing requirements allows for adaptability to changing workloads.
Licensing Options
Different licensing options are available for Imagenomic software, tailored to various user needs and budgets. Pricing and terms vary depending on the specific plan chosen.
- Trial: A free trial version is available to evaluate the software’s features and functionality before committing to a purchase.
- Single-user: A single-user license is suitable for individual users who need the software for personal use or small-scale projects.
- Multi-user: A multi-user license provides access to multiple users within an organization or team.
- Site license: A site license grants access to the software to all users within a specific location or organization.
Technical Specifications Table
| Processor Type | Memory Requirements | Supported Operating Systems | Other Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intel Core i5-8400 or equivalent | 8 GB RAM | Windows 10, macOS 11 | Basic Functionality |
| Intel Core i7-9700K or equivalent | 16 GB RAM | Windows 10, macOS 12 | Enhanced Functionality |
| AMD Ryzen 5 3600 or equivalent | 16 GB RAM | Windows 10, macOS 11 | Enhanced Functionality |
| High-end Processors | 32 GB RAM or more | Windows 11, macOS 13 | Optimized for high-volume and high-resolution processing |
User Interface and Experience
Imagenomic’s software prioritizes a user-friendly interface, designed to minimize learning curves and maximize efficiency for both novice and expert users. The intuitive layout and well-organized tools make image manipulation tasks straightforward and enjoyable. This section delves into the specifics of the interface, highlighting its ease of use, available tools, and typical workflows.
Interface Design
The Imagenomic interface is characterized by a clean, modern design. Key elements, such as menus, toolbars, and panels, are strategically positioned for quick access. A consistent color scheme and clear visual hierarchy enhance navigation, allowing users to quickly locate the desired functions. The software utilizes icons that are easily recognizable, minimizing the need for extensive reading.
Ease of Use and Intuitiveness
The interface is designed to be intuitive, allowing users to grasp the core functionalities with minimal training. Clear labels and tooltips provide context for various controls and options, ensuring a smooth learning curve. The software guides users through tasks with a logical workflow, simplifying complex operations. Users can confidently adjust settings and experiment with effects without the risk of accidentally damaging their images.
Available Tools and Features
Imagenomic’s software offers a comprehensive set of tools for image enhancement, restoration, and manipulation. These include a variety of filters for adjusting color, contrast, and sharpness, as well as tools for removing blemishes, restoring old photos, and manipulating details. The software also incorporates sophisticated algorithms for noise reduction, sharpening, and color correction. Specific tools may vary depending on the chosen module or application.
Workflow for Common Image Editing Tasks
The workflow for common tasks, such as enhancing an image’s vibrancy or correcting color casts, is straightforward. Users can select specific tools directly from the interface, and the software provides real-time previews of adjustments, allowing for immediate feedback and precise control. The use of layers is facilitated, enabling non-destructive editing, which is crucial for preserving original image data. A key feature is the ability to revert changes at any point, ensuring that users can safely experiment without the fear of irrevocably damaging their work.
Step-by-Step Guide: Enhancing Image Vibrancy
This table provides a step-by-step guide for enhancing the vibrancy of an image using Imagenomic software.
| Step | Action | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Open the Image | Load the image into Imagenomic’s software. |
| 2 | Select “Color Enhancement” Module | Navigate to the specific module in the software’s interface for color enhancement. |
| 3 | Adjust “Vibrancy” Slider | Locate the “Vibrancy” slider and increase its value. This will increase the intensity of colors in the image. Observe the real-time preview of the image as you adjust the slider. |
| 4 | Adjust “Saturation” Slider (Optional) | For further color intensity control, adjust the “Saturation” slider. |
| 5 | Review and Save | Review the enhanced image and save the result. |
Future Developments and Trends

Imagenomic’s continued success hinges on its ability to anticipate and adapt to emerging trends in image processing. The company’s commitment to innovation will drive future advancements, impacting various industries that rely on high-quality image data. This includes enhancing existing features, developing new tools, and staying ahead of the curve in image processing techniques.
The evolution of Imagenomic’s technology will likely involve a blend of refining current algorithms, incorporating advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), and expanding its application areas. This strategy will maintain the company’s leadership position in image enhancement and restoration.
Potential New Features in the Next 3 Years
Imagenomic is poised to introduce new features that cater to the growing demands of various industries. These features will enhance both the usability and functionality of the software.
- AI-Powered Auto-Enhancement: This feature will automatically adjust parameters within the software to optimize image quality. The software will learn from a dataset of images to identify optimal settings for different image types, improving the workflow for users.
- Enhanced 3D Image Processing: Imagenomic could expand its capabilities to encompass 3D image processing. This would involve features like noise reduction, sharpening, and restoration for 3D models, opening doors to new applications in fields like medical imaging and engineering.
- Integration with Deep Learning Frameworks: The integration of deep learning frameworks, such as TensorFlow or PyTorch, will allow for more sophisticated image processing tasks. This integration would facilitate the development of highly accurate and adaptable image restoration algorithms.
- Interactive Image Restoration Tools: The user interface could be enhanced to provide more interactive and intuitive controls for image restoration. Users will have more granular control over the restoration process, enabling them to achieve a more customized outcome.
Emerging Trends in Image Processing
Several emerging trends in image processing will influence the future development of Imagenomic’s technology.
- Super-Resolution Techniques: The advancement of super-resolution techniques allows for the generation of high-resolution images from low-resolution input. This will be crucial for applications like satellite imagery and medical imaging, where high-resolution images are often needed but not readily available.
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): The use of GANs can be applied to image enhancement, restoration, and even creation. This technique is particularly relevant for generating realistic image enhancements, filling in missing data, and restoring damaged images.
- Edge Detection and Segmentation: The refinement of algorithms for edge detection and segmentation will continue to improve image analysis and manipulation capabilities. This is vital for tasks like medical image analysis and object recognition in various industries.
Impact on Various Industries
The implementation of these future developments will have a significant impact on diverse industries.
- Medical Imaging: Improved image quality and restoration techniques will contribute to more accurate diagnoses and treatment planning. The ability to extract more information from images can lead to better patient outcomes.
- Forensic Science: Enhanced image enhancement and restoration capabilities will assist in identifying details in damaged or degraded images. This can aid in crime scene investigations and the identification of evidence.
- Photography and Multimedia: Imagenomic’s software can empower photographers and multimedia creators with advanced tools for image enhancement and manipulation. This leads to the creation of high-quality images and videos.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, Imagenomic stands as a robust image processing solution, catering to a wide range of users and applications. Its advanced algorithms and user-friendly interface combine to deliver exceptional results, making it a valuable asset for professionals and enthusiasts alike. The future of Imagenomic promises further innovation and adaptation to emerging trends in image processing.