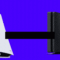
Adobe Lightroom is a powerful photo editing software that empowers users to transform raw images into stunning visuals. From basic adjustments to advanced techniques, Lightroom provides a comprehensive toolkit for photographers of all levels. Its intuitive interface and robust features make it a popular choice for both hobbyists and professionals alike.
This guide delves into the world of Adobe Lightroom, exploring its essential tools, advanced techniques, and integration with other Adobe applications. We’ll also examine the software’s versatility across various photo genres, offering insights into enhancing portraits, landscapes, and more. Furthermore, we’ll discuss modern trends and the future of photo editing in the digital age, emphasizing the role of Lightroom in this evolving landscape.
Introduction to Adobe Lightroom Photo Editor
Adobe Lightroom is a powerful photo editing software widely used by photographers of all levels, from hobbyists to professionals. It’s designed to streamline the entire workflow, from initial image import and organization to final adjustments and export. Lightroom excels at non-destructive editing, allowing users to experiment with various adjustments without permanently altering the original image files.
Lightroom’s core strength lies in its intuitive interface and comprehensive set of tools. It provides a flexible and organized environment for managing and enhancing digital photos. Its features are meticulously crafted to be accessible and efficient, making it a valuable asset for photographers seeking to refine their images and showcase their work effectively.
Overview of Lightroom’s Role in Digital Photography
Lightroom plays a pivotal role in the modern photographer’s workflow. It’s more than just an image editor; it’s a comprehensive system for organizing, processing, and presenting digital photographs. From importing and tagging images to applying sophisticated adjustments and exporting high-quality files, Lightroom offers a streamlined and efficient process.
Key Features and Functionalities of Lightroom
Lightroom offers a robust suite of features for image management and editing. Its core functionalities include:
- Import and Organization: Lightroom facilitates seamless import of images from various sources. It allows for extensive organization using metadata, s, and custom collections, enabling easy retrieval and management of large photo libraries.
- Non-Destructive Editing: Lightroom’s non-destructive editing approach allows photographers to experiment with different adjustments without permanently altering the original image data. This is crucial for iterative refinement and preserving the original image integrity.
- Powerful Adjustment Tools: Lightroom provides a wide array of tools for precise image adjustments, including exposure, contrast, color balance, and sharpness. These tools allow for detailed control over every aspect of an image, enabling photographers to fine-tune their work to perfection.
- Advanced Presets and Styles: Lightroom allows for the creation and application of custom presets, streamlining the editing process and maintaining a consistent aesthetic across a series of images. Presets offer a range of pre-configured adjustments for specific looks and effects.
Target Audience for Lightroom
Lightroom caters to a diverse range of photographers. Its accessibility and versatility make it suitable for hobbyists who want to enhance their images to a professional standard. For professionals, Lightroom’s robust features, speed, and workflow efficiency make it an essential tool for managing large photo libraries and ensuring high-quality outputs.
Different Versions and Pricing Models
Adobe offers various Lightroom versions to suit different needs and budgets. These include:
| Version | Description | Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Lightroom Classic | Focuses on traditional workflow and photo organization. | Subscription-based |
| Lightroom CC (Cloud-based) | Provides cloud-based access and collaboration features. | Subscription-based |
The pricing model typically involves a subscription-based plan for both versions, offering access to the latest features and updates. Different subscription tiers exist, with various options to choose from based on individual needs and usage.
Essential Tools and Techniques
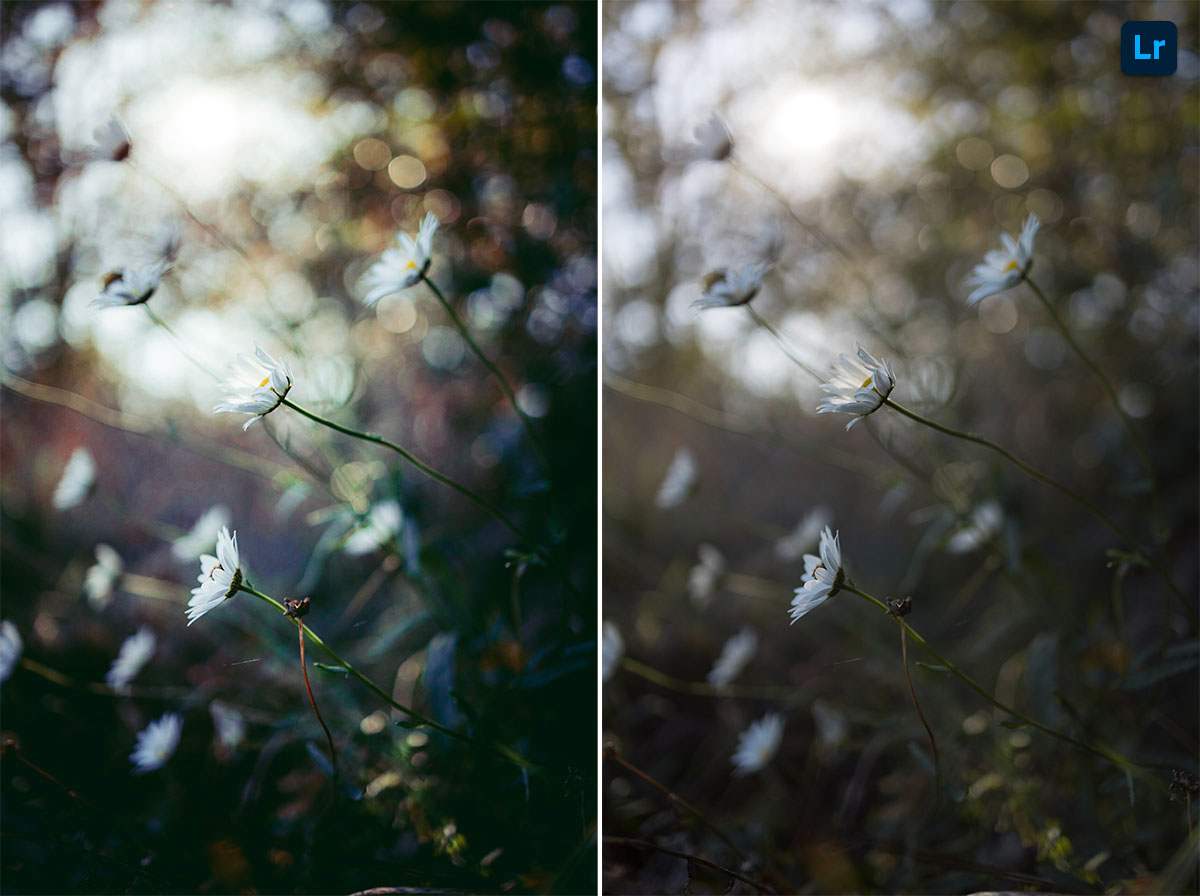

Lightroom’s intuitive interface and powerful tools empower photographers to refine their images efficiently. Mastering these tools unlocks the potential for impactful image editing and organization. This section will delve into the core tools and techniques within Lightroom, from basic adjustments to advanced image correction.
Common Tools and Their Functions
Lightroom offers a diverse set of tools for image manipulation and organization. A comprehensive understanding of these tools is crucial for efficient workflow.
| Tool | Function | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Exposure | Adjusts the overall brightness of the image. | Brightening underexposed shots, darkening overexposed areas. |
| Contrast | Controls the difference between highlights and shadows. | Increasing contrast for more impactful images, reducing contrast for softer looks. |
| Highlights | Adjusts the brightest parts of the image. | Preventing blown-out highlights, recovering details in overexposed areas. |
| Shadows | Adjusts the darkest parts of the image. | Revealing details in shadowed areas, preventing muddy tones. |
| Whites | Adjusts the brightest tones in the image. | Fine-tuning the overall white balance and preventing harsh highlights. |
| Blacks | Adjusts the darkest tones in the image. | Controlling the depth and contrast in dark areas, preventing a washed-out look. |
| Clarity | Adds or reduces sharpness and detail. | Improving image sharpness, softening harsh edges. |
| Vibrance | Adjusts the saturation of colors. | Enhancing color intensity, making colors pop without looking unnatural. |
| Saturation | Adjusts the intensity of all colors. | Increasing color intensity, decreasing it for a more muted effect. |
| Temperature | Adjusts the overall color temperature of the image (warmth/coolness). | Correcting inaccurate color casts, achieving desired color moods. |
| Tint | Adjusts the color balance by adding magenta or green tones. | Correcting color casts, creating specific color palettes. |
Effective Adjustment Tool Usage
Understanding how to utilize adjustment tools effectively is key to achieving desired image transformations. Using the tools with precision and nuance allows photographers to achieve nuanced results.
Applying adjustments strategically, particularly using the graduated filter and radial filter tools, allows for localized adjustments within the image. This localized control allows photographers to maintain the overall image integrity while making selective corrections. For example, a graduated filter can be used to correct exposure differences between the sky and foreground in a landscape photo, while a radial filter can target a specific area of interest for adjustments like sharpening or color correction.
Correcting Common Image Issues
Lightroom provides tools to address common image imperfections. A thorough understanding of these issues and their correction methods is essential for achieving polished results.
Lens distortion, such as barrel or pincushion distortion, can be corrected using Lightroom’s lens correction tools. These tools identify and compensate for the optical characteristics of the lens, resulting in a more accurate and pleasing image. Chromatic aberration, the appearance of color fringes along high-contrast edges, can also be addressed by Lightroom’s lens correction tools. Understanding the nature of these issues is key to achieving the best results.
Organizing and Cataloging Photos
A robust system for organizing and cataloging a large photo collection is vital for efficient retrieval and management. Effective organization saves significant time when searching for specific images later.
Developing a consistent naming convention and using s is paramount to organizing a large collection of photos. This practice allows for fast and precise searching. Creating smart collections based on criteria like date, location, or subject can streamline your workflow, helping you find specific images quickly and easily.
Advanced Editing and Workflow
Mastering advanced techniques in Adobe Lightroom elevates your photo editing from basic adjustments to sophisticated artistry. This section delves into powerful tools like masking, selective adjustments, and exploring diverse editing styles, ultimately equipping you with the skills to manage a large photo workflow efficiently. Understanding preset utilization and creation is also covered, empowering you to streamline your post-processing workflow and achieve personalized results.
Advanced techniques in Lightroom go beyond basic exposure and color corrections. They allow for precise control over specific areas of an image, enabling a high degree of customization and artistic expression. This enhanced level of control is crucial for achieving a desired aesthetic, and managing a large volume of photos effectively.
Advanced Editing Techniques
Advanced editing techniques, such as masking and selective adjustments, provide precise control over specific image elements. Masking allows for targeted adjustments to selected areas, while selective adjustments fine-tune colors, tones, and other parameters within defined regions. This precise control is invaluable for complex edits.
- Masking: Masking in Lightroom allows for isolating specific regions within an image for targeted adjustments. This isolates parts of the image and allows for separate adjustments. It is crucial for retouching, color grading, and removing unwanted elements. For example, using a mask, you can selectively lighten the sky while maintaining the darkness of the foreground.
- Selective Adjustments: Selective adjustments provide a means to fine-tune specific aspects of an image within a selected area. These tools allow for nuanced adjustments like altering highlights, shadows, or color tones in a specific region of the image. For example, you can selectively warm up the colors in the foreground while maintaining the coolness of the background.
Editing Styles
Different editing styles, including black and white, HDR, and others, offer various artistic interpretations. Understanding these styles allows you to choose the approach that best reflects your vision.
- Black and White Conversion: Converting images to black and white involves adjusting the tones to create a dramatic and often artistic effect. This process emphasizes the interplay of light and shadow, allowing you to highlight textures and shapes. The conversion can be a simple process or involve more advanced techniques to fine-tune the tones and contrasts.
- HDR (High Dynamic Range): HDR editing combines multiple exposures to create images with a wider range of tones and details, including highlights and shadows. This is especially beneficial for images with significant differences in lighting conditions, such as landscapes with bright skies and dark shadows. This technique can enhance the overall impact and visual appeal of your images.
Workflow Management
Managing a large workflow involving photo editing and post-processing requires organization and efficient strategies. This is essential to keep track of projects and avoid losing work.
- Organization: Organizing your photos in folders and using metadata are essential to efficiently manage large photo collections. Consistent naming conventions and clear folder structures contribute to easy navigation and retrieval of images.
- Batch Processing: Batch processing tools in Lightroom can streamline the application of edits to multiple images. This can save significant time when dealing with large quantities of photos.
Presets and Customization
Presets streamline your workflow by applying pre-configured adjustments to your photos. Understanding how to utilize and create your own is crucial for consistency and efficiency.
- Utilizing Presets: Presets offer a quick way to apply consistent looks across multiple images. They save time and allow for maintaining a cohesive aesthetic in your photo editing. Presets can be used for color grading, exposure, or other stylistic changes.
- Creating Custom Presets: Creating your own presets allows you to save specific adjustments for later use. You can create personalized presets based on the specific look you’re aiming for in your images. This can significantly increase the speed and efficiency of your workflow.
Integration with Other Adobe Applications
Lightroom excels at its core photo editing and organization function, but its power truly shines when integrated with other Adobe applications. This seamless integration allows for a streamlined workflow, enabling photographers to move effortlessly between applications and maintain a cohesive creative process. This section details how Lightroom interacts with other Adobe products, emphasizing the efficient handling of exported images and their preparation for various platforms.
Comparison with Photoshop
Lightroom and Photoshop, while both powerful Adobe tools, cater to different aspects of the photo editing process. Lightroom focuses on non-destructive editing, utilizing adjustments and presets to refine images quickly and efficiently. Photoshop, on the other hand, offers more granular control over pixel manipulation, allowing for intricate retouching and complex compositing. This difference in approach results in distinct workflows. Photographers often use Lightroom for initial editing and batch processing, then utilize Photoshop for more complex edits and specialized tasks.
Integration with Other Photo Editing and Management Software
Lightroom’s import capabilities are designed for seamless integration with other photo editing and management software. Import features often support various file formats and allow for bulk uploads, streamlining the organization process. This facilitates efficient transitions from external sources, ensuring that files are readily available for further processing within Lightroom’s workflow.
Exporting and Sharing Edited Photos
The export process in Lightroom is straightforward and highly customizable. Lightroom offers a wide array of options for different output formats and resolutions, accommodating various printing and web publishing requirements. These include JPEG, TIFF, and PNG options, allowing for precise control over file sizes and quality. These settings are crucial for ensuring optimal image quality and file size for diverse applications.
Preparing Photos for Printing and Web Purposes
Preparing images for printing or web display requires careful consideration of resolution and file size. Lightroom provides several options to optimize images for these purposes. For print, higher resolutions are needed, often exceeding 300 DPI, while web images benefit from lower resolutions and compressed file sizes to ensure fast loading times. Understanding these parameters allows for the efficient preparation of images for different media. Furthermore, choosing the appropriate color profile (e.g., sRGB for web, Adobe RGB for print) is crucial for maintaining color accuracy across different platforms.
Community and Resources
Leveraging online resources is crucial for maximizing your Lightroom proficiency. Beyond the software’s documentation, a thriving community provides invaluable support, tutorials, and insights from experienced users. This section explores these resources, empowering you to learn and grow your photo editing skills.
Online Learning Resources for Lightroom
Numerous online platforms offer tutorials, courses, and support for Lightroom users. Finding the right resource depends on your learning style and specific needs.
| Resource | Description | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adobe Lightroom Tutorials on Adobe’s Website | Directly from the creators, offering official documentation, tutorials, and often video demonstrations. | High accuracy, comprehensive coverage, official support, often updated. | Can be overwhelming for beginners due to the sheer volume of content. May not offer as much user interaction as community forums. |
| YouTube Channels Dedicated to Lightroom | Abundant channels offer step-by-step tutorials and demonstrations for various techniques, from basic adjustments to advanced compositing. | Accessibility, diverse perspectives, visual learning, often free. | Quality varies significantly, and finding credible and well-structured tutorials can take time. Potential for misinformation. |
| Online Photography Forums (e.g., Reddit, Flickr) | Dedicated photography forums often have sections for Lightroom discussions. | Real-world application, diverse user experiences, ability to ask specific questions and receive quick feedback. | May be less structured and organized than dedicated learning platforms. Potential for irrelevant information. |
| Online Courses (e.g., Skillshare, Udemy) | Structured courses with lessons and projects, often offering a comprehensive learning path. | Structured learning, potential for a deeper understanding of techniques, often with quizzes and assignments. | Can be costly, and the quality of courses varies. |
Popular Lightroom Communities and Forums
Active online communities provide valuable platforms for sharing experiences and troubleshooting issues. Finding and engaging with these groups can accelerate your learning process.
- Reddit’s r/photography subreddit often has dedicated Lightroom discussions. This is a valuable resource for seeking advice, sharing work, and discussing specific techniques.
- Dedicated Lightroom user groups on Facebook or other social media platforms can provide quick answers to specific questions, feedback on your work, and connections to fellow enthusiasts.
- Flickr groups can offer forums for Lightroom-related discussions and support. This often provides feedback on specific images and photo editing challenges.
Utilizing Tutorials
Finding and using tutorials effectively is key to improving your Lightroom skills. Start by identifying specific areas you want to learn.
- Search for tutorials on specific techniques, like adjusting white balance or creating a unique artistic effect. Using precise s is crucial.
- Check the author’s credentials and experience. Consider their portfolio or reputation within the community. A verifiable track record ensures accurate information.
- Practice regularly. Don’t just watch tutorials; actively apply the techniques you learn to your own photos. Consistency is key to mastering any skill.
The Role of Online Communities
Online communities play a vital role in fostering a supportive environment for learning and sharing photo editing skills. They allow users to connect with experienced professionals and fellow enthusiasts.
- Sharing knowledge is a core principle of online communities. Users offer valuable insights and feedback on each other’s work.
- Users can address specific questions and receive tailored solutions. This targeted assistance is a powerful tool for overcoming challenges and learning from others’ experiences.
- Active participation fosters a sense of community and support, which can be highly motivating for learning.
Specific Photo Editing Scenarios
Mastering photo editing in Lightroom goes beyond basic adjustments. Understanding how to tailor techniques to different genres of photography unlocks the full potential of your images. This section delves into practical applications, guiding you through the specific steps needed to enhance portraits, landscapes, wildlife, and architecture.
Enhancing Portraits
Effective portrait enhancement focuses on capturing the subject’s essence while improving skin tone, lighting, and overall mood. Precise adjustments are key to creating a natural and appealing final product.
- Skin Tone Refinement: Use the Brush tool with the Healing Brush, Spot Removal, or the Adjustment Brush to address blemishes and uneven tones without altering the subject’s natural complexion. The Graduated Filter tool is useful for correcting skin tones in large areas, like a whole face. Adjust exposure, contrast, and highlights for a smooth and healthy appearance. Consider using the Clarity slider to add subtle definition and texture.
- Lighting and Color Enhancement: Adjust highlights, shadows, and whites to fine-tune the lighting in the portrait. Use the Tone Curve to make subtle, or more dramatic adjustments. Experiment with the Vibrance and Saturation sliders to enhance colors while maintaining a natural look. Consider the use of split toning for a dramatic effect.
- Eye Enhancement: Carefully adjust the whites of the eyes to ensure a natural reflection of light. Use the Adjustment Brush to add a subtle highlight to the eyes for a more captivating gaze.
- Posing and Composition Adjustments: Subtle adjustments can significantly impact the portrait. Use the crop tool to fine-tune the composition. Ensure the subject is positioned and framed in a way that enhances the overall aesthetic.
Retouching Landscapes
Landscape retouching aims to amplify the natural beauty of the scene. This includes balancing lighting, colors, and details. It’s crucial to preserve the scene’s authenticity while enhancing its visual impact.
- Color Grading: Use the Graduated Filter tool to selectively adjust the color temperature and saturation in specific areas of the image, such as the sky or foreground. This will create a harmonious color balance across the entire landscape.
- Detail Enhancement: Utilize Clarity and Dehaze sliders to sharpen details and reduce haze in the scene. This technique brings out the fine textures and structures of the landscape.
- Highlight and Shadow Adjustments: Adjust the highlights and shadows to recover details in the brightest and darkest parts of the image without creating harsh transitions.
- Noise Reduction: Reduce noise to improve the image’s clarity and sharpness, especially in images taken in low light conditions.
Enhancing Wildlife Photography
Wildlife photography often involves capturing fleeting moments in challenging conditions. Enhancements should highlight the animal’s features and environment without altering the scene’s natural integrity.
- Sharpness and Detail Enhancement: Use the sharpening tools to bring out fine details in the animal’s fur or feathers, while carefully adjusting clarity for optimal detail. Focus on the subject to ensure the subject is sharp.
- Color Correction and Enhancement: Use the color tools to enhance the colors of the wildlife in relation to the environment. Adjust tones for more vibrant, accurate, and appealing results. Ensure that the adjustments do not appear artificial or unnatural.
- Background Adjustments: Adjust the background colors and tones to maintain focus on the subject without making it too distracting.
Editing Architectural Photography
Architectural photography demands precision and attention to detail. The goal is to present the structure’s lines, proportions, and textures accurately.
- Straightening and Perspective Correction: Use the Perspective tool to correct any distortions in the image, ensuring the building’s lines and angles appear accurate and straight. Consider using the crop tool to refine the composition.
- Light and Shadow Adjustment: Correct the light and shadow imbalances in the image, ensuring that the building’s details are visible and accurately represented.
- Color Balance and Saturation: Fine-tune the color balance and saturation to maintain the integrity of the building’s material colors while improving visual appeal.
- Detail Enhancement: Use the sharpening tools to enhance details in the building’s textures and surfaces.
Modern Trends and Future of Photo Editing
The landscape of digital photo editing is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing user preferences. Emerging trends are reshaping how photographers and enthusiasts approach image manipulation, from the tools they use to the desired outcomes. AI and machine learning are significantly impacting this evolution, automating tasks and enhancing creative possibilities.
Photo editing is no longer confined to desktop applications; mobile platforms are gaining prominence, offering accessible and powerful editing capabilities. This shift influences the workflow and expectations of users, leading to new creative avenues and collaboration opportunities. The future of digital photo editing is promising, with potential developments that are poised to revolutionize the way we interact with and manipulate images.
Emerging Trends in Photo Editing
Contemporary photo editing trends reflect a desire for speed, ease of use, and creative expression. Sophisticated tools are designed to streamline complex tasks, offering intuitive interfaces and powerful features. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning is transforming how images are processed and enhanced, enabling faster, more precise results.
Impact of AI and Machine Learning
AI-powered tools are increasingly prevalent in photo editing software. These tools can automatically correct exposure, adjust color balance, remove blemishes, and even generate artistic effects. For instance, AI algorithms can now identify and remove unwanted objects from images with remarkable accuracy. This automation frees up users to focus on creative aspects, such as composition and artistic vision. Furthermore, machine learning is enabling personalized editing recommendations based on user preferences and past edits.
Role of Mobile Photo Editing Apps
Mobile photo editing applications are gaining significant traction, offering convenient access to image manipulation on-the-go. These apps often integrate seamlessly with desktop editing suites, allowing users to start editing on their phones and finish on their computers. This seamless transition enhances the workflow, particularly for photographers who need to process images quickly and efficiently. Many mobile apps leverage AI to perform tasks like automatic retouching and enhancing, making photo editing more accessible and enjoyable for a wider audience.
Potential Future Developments
The future of digital photo editing promises further integration with other creative applications, potentially allowing users to seamlessly transition between different creative mediums. Enhanced photorealistic effects, enabling the creation of hyperrealistic images, are likely to be a focus. Furthermore, advancements in augmented reality (AR) could enable users to overlay digital elements onto their photos, leading to innovative and engaging creative experiences. The integration of blockchain technology may also play a role, offering enhanced security and authenticity verification for digital images. Specific examples include more sophisticated AI-driven tools for complex edits, or enhanced AR filters and overlays for creating personalized imagery.
Example Workflow Processes
Mastering Adobe Lightroom’s workflow is key to efficiently processing images and achieving desired results. Understanding various workflows, from raw file processing to portfolio preparation, streamlines your editing process and enhances your overall productivity. This section details practical steps for diverse photo editing scenarios.
Efficient workflows are crucial for both personal projects and professional endeavors. Whether you’re a hobbyist photographer or a seasoned professional, streamlined processes optimize your time and enhance your creative output.
Processing a Raw Image in Lightroom
A raw image, often captured with a digital camera, offers greater flexibility in post-processing compared to JPEGs. Lightroom’s raw processing capabilities allow for fine-tuning of exposure, white balance, and other crucial aspects of the image without significant loss of quality.
- Import the raw file into Lightroom. This step involves selecting the file location and adding it to the catalog.
- Assess the initial image. Observe the overall exposure, white balance, and potential issues like highlights or shadows. This initial evaluation is crucial for effective adjustments.
- Adjust basic parameters. Begin with exposure, contrast, highlights, and shadows to establish a foundation for further edits. Consider using the “Basic” panel in Lightroom.
- Fine-tune white balance. Accurately adjusting white balance ensures that colors appear natural and consistent. Use the “White Balance” tool, and consider using presets for a quick start.
- Apply lens corrections. Lightroom offers tools for correcting lens distortion, such as vignetting or chromatic aberration. Use the “Lens Corrections” panel for precise adjustments.
- Enhance details and refine. Further adjustments, such as clarity, vibrancy, and other adjustments, may be required to achieve the desired aesthetic. Experiment with these settings for optimal results.
- Export the processed image. Select the desired format (JPEG, TIFF, etc.), resolution, and quality for the final output. This step ensures the processed image is ready for various purposes.
Editing a Series of Photos for a Project
When working with a collection of photos for a project, a consistent workflow ensures a cohesive aesthetic. This systematic approach helps maintain the overall style and quality of the project.
- Establish a consistent style guide. Define the desired look and feel for the project, including color palettes, lighting, and composition. A pre-determined style guide streamlines the editing process.
- Batch process similar adjustments. Use Lightroom’s batch processing features to apply identical edits to multiple images. This approach significantly reduces the time needed to process a large quantity of photos.
- Maintain a detailed record of adjustments. Record all adjustments made to each image for easy referencing and potential future adjustments. This is vital for ensuring consistency and repeatability.
- Establish a review process. Have a review system for each photo to ensure a uniform style and to address any discrepancies in the edited photos. This step is critical for a professional-quality outcome.
- Create a project folder structure. Establish a clear organizational system for files, including folders for different stages of editing and revisions. This system helps avoid confusion and lost files.
Preparing a Portfolio for Submission
A well-prepared portfolio is vital for showcasing your best work. A consistent presentation helps make a lasting impression.
- Select the best images. Choose high-quality images that best represent your skills and style. Focus on images that best showcase your strengths.
- Organize the images. Arrange the images in a logical order that tells a story or demonstrates your growth. Consider the visual flow of the images in your portfolio.
- Edit the images for consistency. Ensure the images have a cohesive style and tone. A uniform aesthetic improves the visual impact of your portfolio.
- Create a professional presentation. Use a visually appealing layout and high-quality images to create a professional-looking portfolio. A compelling layout is crucial for a good impression.
- Ensure high-resolution images. Use high-resolution images to prevent pixelation or loss of detail in your portfolio. High-quality images are essential for a professional look.
Creating and Exporting High-Quality Prints
High-quality prints elevate the impact of your photography. Understanding the printing process enhances the viewer experience.
- Choose the appropriate image size and resolution. Ensure the image resolution meets the print size requirements. This step is essential for print quality.
- Select the right print settings. Choose the appropriate paper type, ink type, and other print settings to achieve the desired print quality. Experiment to find the best print settings for your images.
- Optimize the image for printing. Use Lightroom’s printing tools to fine-tune the image for optimal print quality. This ensures the print quality aligns with the original image.
- Choose a reputable print service. Select a professional printing service with high-quality equipment and expertise. This ensures a professional result.
- Proofread the print. Review the print to ensure the colors, tones, and details meet your expectations. Proofreading helps identify any issues before final printing.
Customization and Preferences
Lightroom’s power stems from its adaptability. Understanding and utilizing its customization options allows photographers to tailor the environment to their specific workflow, ensuring maximum efficiency and comfort. This empowers users to truly personalize their experience and streamline their photo editing process.
Personalizing Lightroom’s interface is a crucial aspect of enhancing your photo editing experience. A well-organized workspace is key to efficient workflow. Customizable interface elements contribute to a more tailored environment, improving the overall editing experience.
Interface Customization
The Lightroom interface offers extensive customization options. These allow you to rearrange panels, adjust panel sizes, and select which tools are visible. This personalized approach streamlines your workflow, placing frequently used tools within easy reach. You can even create custom layouts for different types of projects, allowing for rapid transition between projects.
Custom Presets and Workflows
Creating custom presets is a powerful technique for streamlining your workflow. Presets allow you to save specific adjustments and apply them repeatedly across multiple images. This can significantly reduce the time spent on repetitive tasks, increasing productivity. Furthermore, you can tailor your workflow to specific needs. This allows you to adjust the order in which you apply adjustments, which can be customized for different types of photography.
Personal Preferences in Photo Editing
Personal preferences are integral to effective photo editing. Different photographers have distinct styles and visions. Understanding and implementing these preferences in your editing process will produce results aligned with your unique artistic goals. The process of adjusting Lightroom to your specific workflow and preferences can significantly improve your efficiency and output quality.
Adapting Lightroom to Specific Needs
Adapting Lightroom to your specific needs and style involves thoughtful organization and a well-defined workflow. Understanding the process allows you to move through the editing process efficiently. A well-organized workspace with frequently used tools readily accessible is essential for optimal performance. Experimentation with different layout configurations and tool arrangements can lead to a workflow that truly caters to your style.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, Adobe Lightroom offers a comprehensive and versatile platform for enhancing and managing digital photos. Its intuitive tools and diverse features cater to both beginners and seasoned professionals. We’ve explored its various aspects, from fundamental techniques to advanced editing and workflow strategies. By mastering Lightroom, photographers can elevate their images to new heights, ensuring their creations stand out in the ever-evolving digital realm.