Sage Payroll is a powerful tool designed to streamline the often complex process of managing payroll for businesses, especially small and medium-sized enterprises. It offers a comprehensive suite of features, from basic employee setup to advanced reporting and compliance, making it a popular choice for those seeking a reliable and efficient solution.
This guide explores Sage Payroll in depth, covering everything from its core functionalities and implementation steps to integration options, industry-specific adaptations, security measures, compliance requirements, customer support, and pricing plans. We’ll delve into the nuances of Sage Payroll, highlighting its strengths and providing insights into how it can benefit various businesses.
Introduction to Sage Payroll
Sage Payroll is a comprehensive software solution designed for managing payroll processes, from calculating employee wages and taxes to issuing paychecks and handling administrative tasks. It streamlines the often complex payroll procedures, reducing manual errors and saving businesses valuable time and resources. This is particularly crucial for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) where payroll accuracy and efficiency are paramount.
Sage Payroll offers a wide range of features, allowing businesses to tailor the system to their specific needs. These features range from basic payroll calculations to more advanced functionalities such as benefits administration and reporting. The software’s user-friendly interface and robust functionality make it an attractive option for businesses seeking a reliable and efficient payroll management solution.
Common Use Cases
Sage Payroll is a versatile tool applicable to a variety of business types and sizes. Small businesses, for instance, often find Sage Payroll invaluable for handling their payroll needs. It allows them to process paychecks, calculate taxes, and manage employee information with ease, freeing up valuable time for other critical tasks. Larger organizations, too, may find Sage Payroll beneficial for managing payroll for multiple locations or departments, while also ensuring regulatory compliance.
Key Features Differentiating Sage Payroll
Sage Payroll stands out from other payroll software options through several key features. These include its robust tax calculation engine, ensuring accuracy in complex tax situations. Furthermore, its user-friendly interface and intuitive navigation contribute to its appeal, enabling quick onboarding and easy operation. Integration with other accounting software is another distinguishing feature, providing a seamless workflow for businesses already using Sage accounting solutions. Moreover, Sage Payroll provides comprehensive reporting capabilities, offering valuable insights into payroll data and aiding informed business decisions.
Comparison with Competing Payroll Solutions
The table below compares Sage Payroll with two leading competitors, highlighting differences in pricing, features, and support. This comparison aids in evaluating the most suitable payroll solution for specific business needs.
| Feature | Sage Payroll | QuickBooks Payroll | Xero Payroll |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing | Tiered pricing based on employee count and features. Typically more affordable for small businesses compared to enterprise-level solutions. | Pricing structured similarly to Sage, with tiers based on employee count. Pricing models can be competitive, depending on the chosen features. | Flexible pricing options, with packages tailored to different business sizes. Potential for lower costs in certain circumstances. |
| Features | Comprehensive features including tax calculations, direct deposit, reporting, and integration with other Sage products. | Solid core features covering payroll processing, reporting, and basic compliance. Integration options may be limited. | Focuses on simplicity and ease of use, with core payroll functionalities. May lack advanced features found in other solutions. |
| Support | Offers various support options, including phone, email, and online resources. Extensive documentation and knowledge base available. | Provides support through phone, email, and online resources. Availability and responsiveness may vary. | Online resources, including FAQs and help articles, are commonly accessible. Support options may vary depending on the chosen package. |
Sage Payroll Features
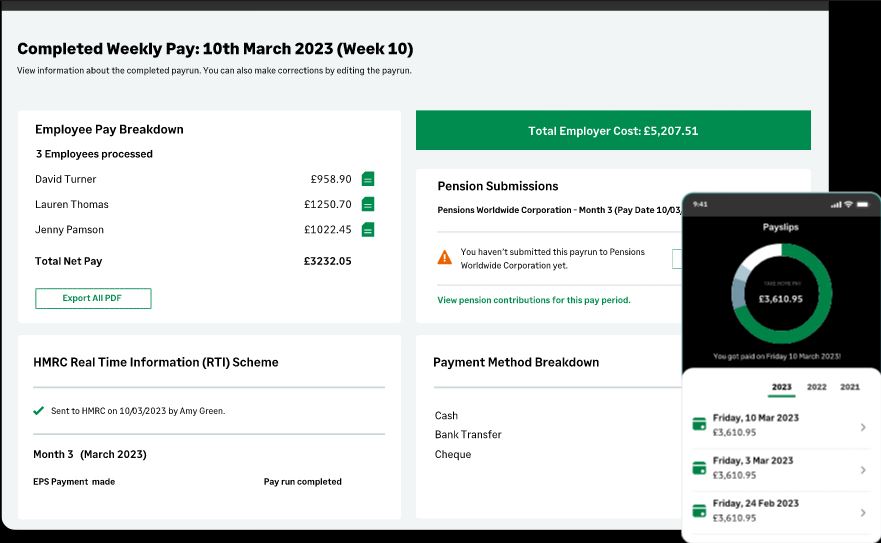
Sage Payroll is a comprehensive software solution designed to streamline payroll processes for businesses of all sizes. It offers a suite of features to manage employees, calculate pay accurately, and ensure compliance with tax regulations. Understanding these features is crucial for businesses to optimize their payroll operations and avoid potential errors or penalties.
The core functionality of Sage Payroll encompasses employee setup, pay calculation, tax reporting, and compliance. Advanced features extend to benefits administration, time and attendance tracking, and comprehensive reporting tools, providing a holistic view of payroll data. Different versions of Sage Payroll cater to diverse business needs, each offering varying levels of functionalities.
Core Payroll Functions
Sage Payroll’s fundamental functions cover the essential aspects of payroll management. These functions are crucial for efficient and accurate processing of employee compensation and related tax obligations. Employee setup, pay calculation, tax reporting, and compliance form the backbone of the software’s core functionality.
- Employee Setup: This function allows for the creation and maintenance of employee records, including personal details, contact information, employment dates, and tax information. Accurate employee setup is essential to ensure proper calculation of salaries and deductions.
- Pay Calculation: Sage Payroll automates the calculation of gross pay, deductions (such as taxes, health insurance, and retirement contributions), and net pay for each employee. This automated process minimizes errors and ensures timely payment to employees.
- Tax Reporting: The software generates and submits required tax reports, including payroll tax returns (e.g., income tax, social security tax, Medicare tax) to the relevant authorities. Accurate and timely tax reporting is vital for compliance and avoiding penalties.
- Compliance: Sage Payroll ensures compliance with local, state, and federal labor laws and tax regulations. This includes adhering to requirements for minimum wage, overtime pay, and other employment regulations. Compliance is crucial to avoid legal issues.
Advanced Features
Beyond the core functions, Sage Payroll offers advanced features to enhance efficiency and provide a more comprehensive payroll management solution. These features provide greater control and insights into payroll data.
- Benefits Administration: Sage Payroll can manage various employee benefits, such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off. This allows for streamlined administration of benefits and accurate tracking of benefit-related costs.
- Time and Attendance Tracking: The software can track employee time worked, including hours, overtime, and absences. This feature enables accurate pay calculations based on actual work hours and helps to prevent errors.
- Reporting Tools: Sage Payroll offers various reporting tools to analyze payroll data, providing insights into employee compensation, costs, and trends. These tools can help businesses identify potential issues or areas for improvement.
Different Versions and Functionalities
Sage Payroll is available in various versions or editions to cater to different business needs and sizes. Each version often offers different functionalities, features, and pricing structures.
- Sage Payroll Standard: This version usually includes the core payroll functions for basic needs and a limited number of advanced features. It is often a suitable choice for small businesses.
- Sage Payroll Premium: This edition typically encompasses all core functions, along with advanced features such as benefit administration and more extensive reporting capabilities. It’s often suitable for mid-sized companies.
- Sage Payroll Enterprise: The Enterprise version usually provides the most comprehensive functionalities, including advanced features, customization options, and support for larger companies with complex payroll requirements.
New Employee Setup
Setting up a new employee in Sage Payroll involves several steps to ensure accurate data entry and compliance. This detailed process helps to streamline the onboarding process for new hires.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Enter Employee Details: Input the employee’s personal information, such as name, address, and contact details. |
| 2 | Employment Information: Specify employment start date, job title, and department. |
| 3 | Tax Information: Enter tax details, including tax ID and applicable tax rates. |
| 4 | Pay Rate and Deductions: Define the employee’s pay rate, including any applicable deductions. |
| 5 | Review and Confirm: Review all entered data for accuracy and completeness. |
Sage Payroll Implementation
Implementing Sage Payroll effectively is crucial for businesses seeking a streamlined payroll process. A well-executed implementation ensures accurate payments, compliance with regulations, and efficient management of employee data. This involves careful planning, thorough preparation, and a clear understanding of the system’s capabilities.
Typical Implementation Steps
The process of implementing Sage Payroll typically involves several key steps. Initial setup includes system configuration, data migration, and user training. Configuring the system involves setting up company details, employee information, tax rates, and payment methods. Data migration ensures the transfer of existing payroll data from the previous system, while user training equips personnel with the necessary skills to operate the new system effectively. Post-implementation, ongoing monitoring and adjustments are necessary to ensure smooth operations and continued compliance.
Factors to Consider Before Implementation
Several factors are critical to evaluate before committing to Sage Payroll. A thorough assessment of the company’s payroll needs is essential. This includes evaluating the current payroll processes, identifying pain points, and determining the specific features required. The existing infrastructure, including hardware and software compatibility, must be considered to ensure a smooth transition. The financial implications, such as the cost of the software, implementation fees, and ongoing maintenance, should also be carefully assessed. The company’s specific industry regulations and compliance requirements are another crucial consideration. Evaluating the company’s internal resources and capabilities, such as the availability of trained personnel, is essential. Finally, the anticipated return on investment (ROI) and potential benefits from using Sage Payroll must be thoroughly considered.
Support Options for Sage Payroll Users
Sage Payroll offers a range of support options to assist users during and after implementation. These options include online resources such as FAQs, tutorials, and online help documentation. Sage provides dedicated customer support teams via phone and email. Expert consultations are also available for complex or specialized needs. These support avenues aim to address user queries, resolve technical issues, and provide guidance throughout the implementation and ongoing use of the system.
Potential Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Implementing Sage Payroll can present certain challenges. One common issue is data migration, which may involve errors or discrepancies. Solutions include meticulous data validation and verification procedures. Ensuring all data is accurately mapped and transferred can minimize errors. Another challenge is user resistance to change. Solutions include comprehensive user training and clear communication about the benefits of the new system. A well-structured training program, demonstrating how the new system simplifies and streamlines processes, can improve user adoption. Integration issues with existing systems can also arise. Addressing these requires careful planning, thorough testing, and clear communication between different departments. These steps can reduce the chance of unexpected problems. Technical glitches can also occur. Regular system maintenance and proactive monitoring can prevent and resolve these issues quickly. In summary, careful planning, preparation, and consistent support can significantly mitigate these challenges.
Sage Payroll Integration
Sage Payroll’s power extends beyond its core functionality. Seamless integration with other business software is crucial for streamlined operations and data consistency. This integration allows for real-time data flow, reducing manual entry and enhancing overall efficiency. By connecting Sage Payroll to accounting and CRM systems, businesses can achieve a holistic view of their financial and customer data.
Integration Capabilities with Other Business Software
Sage Payroll offers a variety of integration options to connect with various business applications. This enables the transfer of crucial data like employee information, payroll details, and deductions to other systems, automating processes and reducing errors. The integration capabilities often include APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) for customized data exchange.
Advantages of Integrating Sage Payroll
Integrating Sage Payroll with other systems provides numerous benefits. Reduced data entry errors are a key advantage, minimizing the risk of costly mistakes. Improved data accuracy leads to more reliable financial reporting. Automation of tasks such as data transfer frees up valuable employee time, allowing them to focus on more strategic initiatives. Real-time data visibility across systems enhances decision-making capabilities.
Specific Integration Examples and Benefits
Sage Payroll integrates with accounting software like QuickBooks and Xero, facilitating the automatic transfer of payroll data to financial statements. This eliminates manual data entry, improving accuracy and reducing processing time. Integration with CRM systems like Salesforce allows for a comprehensive view of employee information, enabling personalized communication and targeted marketing strategies. For example, payroll deductions can be directly linked to employee’s account details within the CRM system, simplifying the process.
Data Flow Illustration
| Data Source | Sage Payroll | Integrated System (e.g., Accounting Software) |
|---|---|---|
| Employee Information | Stores employee details (name, address, tax information) | Receives employee data for accounting records and reporting. |
| Payroll Deductions | Calculates and records payroll deductions (taxes, insurance, etc.) | Imports deductions for financial reporting and compliance. |
| Gross Pay | Calculates gross pay | Records gross pay as an income source in the accounting system. |
| Net Pay | Calculates net pay after deductions | Used for expense and cost accounting, balancing the income and expenditure. |
| Payment Information | Manages payment methods (direct deposit, checks) | Integrates payment information for reconciliation and expense management. |
Sage Payroll for Specific Industries
Sage Payroll’s flexibility extends beyond general payroll functionalities, adapting to the unique needs of various industries. This tailored approach ensures accurate and compliant payroll processing while minimizing administrative burdens specific to each sector. Understanding the specific payroll considerations for each industry allows for optimal use of Sage Payroll’s features and tools.
Industry-specific configurations and features within Sage Payroll streamline tasks, reduce errors, and ensure compliance with regulations. This tailored approach enhances efficiency and accuracy in payroll management. Examples include handling commission structures in retail, complex benefits packages in healthcare, and intricate overtime calculations in manufacturing.
Retail Industry Payroll Considerations
Retail businesses often face fluctuating employee schedules and variable sales. Sage Payroll accommodates these by allowing flexible pay structures, enabling the calculation of commissions based on sales targets. The system facilitates accurate tracking of hours worked, especially for part-time and temporary employees common in retail. Further, the system can handle discounts and bonuses directly within the payroll processing.
Manufacturing Industry Payroll Considerations
Manufacturing environments often involve complex production schedules, overtime requirements, and unique benefits packages. Sage Payroll handles these by providing features for calculating overtime pay based on pre-defined rules or agreements. The system can manage multiple pay rates for different shifts or job roles. It allows for detailed tracking of employee hours worked, which is crucial for payroll accuracy and compliance in manufacturing settings.
Healthcare Industry Payroll Considerations
Healthcare payroll often includes intricate considerations like varying shift patterns, complex benefits, and compliance with specific regulations. Sage Payroll can accommodate these requirements through specific configurations for calculating overtime and handling different pay rates for various shifts. Furthermore, the system can handle the diverse benefits packages common in the healthcare industry, such as health insurance premiums and retirement contributions.
Comparison of Sage Payroll’s Adaptability Across Industries
| Industry | Key Payroll Considerations | Sage Payroll Features/Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Retail | Commission calculations, fluctuating schedules, part-time employees | Flexible pay structures, commission-based calculations, detailed time tracking |
| Manufacturing | Overtime calculations, multiple pay rates, production-based schedules | Overtime calculations based on pre-defined rules, multiple pay rates, detailed time tracking |
| Healthcare | Shift-based pay, complex benefits, regulatory compliance | Shift-based pay calculations, handling of diverse benefits packages, regulatory compliance tools |
Sage Payroll Security
Sage Payroll prioritizes the security of employee data, recognizing its sensitive nature. Robust security measures are implemented to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and other threats. This ensures the confidentiality and integrity of payroll information, safeguarding both employees and the organization.
Security Measures in Sage Payroll
Sage Payroll employs a multi-layered approach to security, encompassing data encryption, access controls, and user authentication. These measures are designed to deter unauthorized access and maintain the confidentiality of payroll data.
Data Encryption
Protecting sensitive data is crucial in payroll processing. Sage Payroll utilizes industry-standard encryption techniques to safeguard employee data during transmission and storage. This ensures that even if a breach occurs, the data remains unreadable to unauthorized individuals. For example, data is encrypted using Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) algorithms to protect data at rest and in transit.
Access Controls
Sage Payroll implements granular access controls, restricting access to payroll data based on user roles and responsibilities. Only authorized personnel can view and modify specific payroll records, preventing unauthorized changes and maintaining data integrity. This minimizes the potential impact of any security breaches by limiting the scope of access.
User Security Best Practices
To further enhance security, Sage Payroll promotes best practices for user accounts and data protection. Strong passwords, regular password changes, and multi-factor authentication are crucial in preventing unauthorized access. Users are encouraged to utilize these security protocols to maintain the confidentiality of their accounts and the associated data.
Table of Security Features
| Security Feature | Functionality |
|---|---|
| Data Encryption | Utilizes AES encryption for data at rest and in transit, rendering data unreadable to unauthorized individuals. |
| Access Controls | Limits access to payroll data based on user roles and responsibilities, restricting unauthorized modifications. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Adds an extra layer of security by requiring multiple verification methods (e.g., password and code from a mobile device) to access accounts. |
| Regular Security Audits | Periodically evaluates security protocols and systems to identify vulnerabilities and maintain compliance with evolving security standards. |
| Strong Password Policies | Enforces complex password requirements to enhance account security. |
Sage Payroll Compliance
Staying compliant with labor laws and regulations is crucial for any business. Sage Payroll, with its comprehensive features, assists businesses in navigating the complexities of payroll compliance, ensuring accuracy and avoiding potential penalties. Proper compliance protects your business and your employees.
Sage Payroll provides a robust framework for managing payroll accurately, considering various labor laws and regulations across different jurisdictions. This ensures that your payroll processes align with legal requirements, reducing the risk of costly errors and legal issues.
Payroll Compliance Requirements Overview
Payroll compliance involves adhering to federal, state, and local labor laws regarding wages, taxes, and benefits. These regulations often differ significantly based on location and industry. Understanding and implementing these requirements is essential to avoid penalties and maintain a positive employer-employee relationship.
How Sage Payroll Aids in Compliance
Sage Payroll’s features are designed to facilitate compliance with various labor laws and regulations. The software helps manage complex tax calculations and deductions, ensuring accurate withholdings for federal, state, and local taxes. Its comprehensive reporting features allow for easy tracking and verification of compliance with all relevant regulations. It also provides tools for managing employee data, such as hours worked and pay rates, which helps ensure compliance with wage and hour laws.
Staying Updated on Compliance Changes
Staying informed about changes in payroll regulations is crucial for maintaining compliance. Government agencies regularly update labor laws and regulations. Sage Payroll offers resources and updates to keep users informed about relevant changes. These updates are designed to ensure businesses can quickly adapt to any modifications in labor laws and regulations. Regularly reviewing official government websites for specific jurisdiction updates is also a vital step.
Sage Payroll and Tax Reporting
Sage Payroll streamlines the tax reporting process. The software handles the calculations and reporting of various taxes, including federal, state, and local taxes. It also assists in generating tax reports required by the IRS and relevant state and local authorities. These reports are typically required on a regular basis, such as quarterly or annually. This feature ensures accurate tax reporting and avoids potential delays or errors, safeguarding businesses from tax penalties.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Sage Payroll presents a robust and versatile platform for managing payroll. Its comprehensive features, flexible integrations, and strong support network make it a compelling option for businesses of all sizes. Understanding the implementation process, security protocols, and compliance considerations is key to successful payroll management. By carefully considering your specific needs and comparing Sage Payroll to alternative solutions, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your business objectives.