Dive into the fascinating world of business intelligence software! This isn’t just about numbers; it’s about unlocking hidden insights within your data to make smarter decisions. Imagine transforming raw information into actionable strategies that propel your business forward. We’ll explore the ins and outs, from fundamental concepts to cutting-edge trends, providing a comprehensive guide to harnessing the power of your data.
From reporting and visualization to advanced analytics and predictive modeling, business intelligence software empowers organizations to gain a deeper understanding of their operations and make data-driven choices. This guide will walk you through the essential aspects of selecting, implementing, and maintaining this vital tool.
Introduction to Business Intelligence Software
Business intelligence (BI) software empowers businesses to extract insights from data and make informed decisions. It’s a powerful tool for understanding market trends, customer behavior, and internal operational efficiency. By transforming raw data into actionable knowledge, BI software helps companies stay ahead of the competition.
BI software collects, processes, and analyzes data to provide businesses with a comprehensive understanding of their performance. This understanding allows for proactive strategies and better resource allocation, ultimately leading to improved profitability and strategic growth.
Definition of Business Intelligence (BI) Software
Business intelligence (BI) software is a set of applications and technologies designed to collect, analyze, and present data from various sources. These tools transform raw data into meaningful insights that support informed decision-making across all levels of an organization.
Key Functionalities and Features
BI software typically includes functionalities such as data warehousing, data mining, reporting, and data visualization. These features allow companies to gain a comprehensive view of their business performance, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions. Data warehousing stores and manages large volumes of data, while data mining techniques uncover hidden patterns and relationships within the data. Reporting tools present the data in a structured format, often in the form of dashboards and reports. Data visualization tools provide an intuitive way to understand complex data through charts, graphs, and other visual representations.
Types of BI Software
Different types of BI software cater to various organizational needs and technical environments. Cloud-based BI solutions offer scalability and flexibility, often accessed through web browsers. On-premise solutions provide greater control and customization, typically installed on a company’s own servers.
Examples of Successful Implementations
Numerous companies across diverse industries have successfully implemented BI software. Retailers use BI to analyze customer purchasing patterns, optimizing inventory management and targeted marketing campaigns. Manufacturing companies leverage BI to identify production bottlenecks and improve efficiency, resulting in cost reductions. Financial institutions utilize BI to detect fraudulent activities and manage risk more effectively.
Comparison of BI Software Categories
| Category | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Reporting | Generates structured reports and dashboards to track key performance indicators (KPIs). | Sales reports, customer acquisition reports, profitability reports. |
| Data Visualization | Presents data in graphical formats (charts, graphs, maps) for easier understanding and pattern identification. | Interactive dashboards, trend analysis charts, geographic visualizations of sales data. |
| Predictive Analytics | Uses statistical algorithms to forecast future trends and outcomes based on historical data. | Demand forecasting, risk assessment, customer churn prediction. |
Benefits of Using Business Intelligence Software
Business intelligence (BI) software empowers organizations to transform raw data into actionable insights. This transformative power translates directly into enhanced decision-making, improved operational efficiency, and a strengthened strategic footing. By analyzing historical trends and current performance, businesses can anticipate future challenges and opportunities.
BI software provides a comprehensive view of business operations, enabling informed choices across all levels of the organization. This holistic understanding is crucial for navigating the complexities of the modern business environment and achieving sustainable growth.
Enhanced Decision-Making Processes
BI software significantly improves decision-making by providing access to a wealth of data. Users can quickly analyze key performance indicators (KPIs) and identify trends, patterns, and anomalies that might otherwise go unnoticed. This data-driven approach allows for more informed choices, minimizing reliance on guesswork and intuition. Consequently, businesses can make faster, more accurate decisions, leading to better outcomes.
Improved Operational Efficiency
BI software streamlines operations by automating tasks and identifying areas for improvement. By analyzing operational data, BI tools can pinpoint bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas where resources can be allocated more effectively. This often results in reduced costs and increased productivity. For example, a retail store using BI software might discover that a particular checkout lane is consistently slower than others, leading to longer customer wait times. Addressing this bottleneck through staff reassignment or equipment upgrades can improve overall operational efficiency.
Facilitated Strategic Planning
BI software facilitates strategic planning by providing historical data and predictive models. This allows businesses to anticipate future trends, assess potential risks, and develop more effective strategies. The ability to model different scenarios based on varying market conditions or internal adjustments is a key benefit. BI software can provide insights into customer preferences, market trends, and competitor activities, enabling companies to make proactive and informed strategic decisions.
Role in Risk Management
BI software plays a crucial role in risk management by identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities. By analyzing historical data and market trends, BI tools can highlight potential issues such as declining sales, emerging regulatory changes, or shifts in customer behavior. Proactive identification of these risks allows businesses to implement mitigating strategies and minimize potential negative impacts. For example, a manufacturing company using BI software might detect a sudden increase in defective products, prompting a thorough investigation into potential production issues and preventative measures.
Return on Investment (ROI) of BI Software
The following table illustrates a hypothetical ROI for a company implementing BI software. The data represents a simplified example and may vary depending on specific business needs and implementation strategies.
| Year | Revenue Increase (USD) | Cost Savings (USD) | Total Benefit (USD) | ROI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 50,000 | 10,000 | 60,000 | 15% |
| 2 | 75,000 | 15,000 | 90,000 | 22.5% |
| 3 | 100,000 | 20,000 | 120,000 | 30% |
Note: ROI is calculated as (Total Benefit / Initial Investment) * 100.
This hypothetical ROI highlights the potential for BI software to generate significant financial gains. The actual ROI will vary depending on the specific business, its implementation strategy, and the features of the software utilized.
Key Features and Capabilities
Business intelligence software empowers businesses to transform raw data into actionable insights. It does this by utilizing a combination of powerful features, allowing companies to make informed decisions and achieve significant improvements in performance. These features are designed to provide a clear and comprehensive understanding of business operations, from sales trends to customer behavior.
Data warehousing, data mining, data visualization, and reporting tools work together to provide a holistic view of business performance. Each plays a crucial role in supporting the decision-making process, ultimately helping businesses achieve their goals.
Data Warehousing in BI Software
Data warehousing is the core of business intelligence. It’s a centralized repository that collects and organizes data from various sources, transforming it into a consistent format. This structured data is then used for analysis and reporting, providing a historical perspective on business performance. By consolidating data from different systems, data warehousing helps to create a unified view of the organization’s operations, facilitating better understanding of trends and patterns.
Data Mining and Data Visualization in BI Software
Data mining techniques uncover hidden patterns and relationships within the stored data. This process allows businesses to identify valuable insights that might otherwise go unnoticed. Sophisticated algorithms are used to sift through large datasets, revealing trends, correlations, and anomalies. Data visualization tools present these complex findings in a clear and easily understandable format. These tools convert raw data into compelling charts, graphs, and maps, making it simple to spot crucial trends, predict future outcomes, and make informed decisions.
Reporting and Analytics Tools in BI Software
Reporting and analytics tools are essential for extracting insights from the data warehouse. These tools generate reports that summarize key performance indicators (KPIs), allowing businesses to track progress and identify areas needing attention. The analytics tools delve deeper into the data, performing sophisticated calculations and modeling to predict future trends and outcomes. These tools help businesses understand “why” certain patterns occur and how to optimize processes for maximum efficiency.
Comparison of Reporting Methods
Different reporting methods provide various levels of detail and insight. Dashboards present an overview of key metrics, providing a snapshot of the current state of the business. Reports delve deeper, offering detailed information on specific aspects of the business. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are crucial metrics that track progress towards business goals, helping monitor performance over time. For instance, a dashboard might show overall sales figures, while a report could detail sales performance by region.
Common Data Visualization Techniques
Data visualization techniques play a vital role in transforming complex data into easily understandable formats. Effective visualizations enhance understanding, identify trends, and improve decision-making.
- Bar Charts: Represent categorical data and compare values across different categories. For example, they could display sales figures for different product lines.
- Line Charts: Illustrate trends over time. For example, a line chart can display sales figures for the last quarter.
- Pie Charts: Show the proportion of different parts of a whole. For example, they can display the percentage of sales coming from different customer segments.
- Scatter Plots: Display the relationship between two variables. For example, a scatter plot could show the relationship between advertising spend and sales.
- Maps: Represent geographical data. For example, a map could display sales figures by region.
- Heatmaps: Highlight the importance of specific data points. For example, a heatmap could display the performance of different products in different regions.
Selecting the Right Business Intelligence Software
Choosing the right Business Intelligence (BI) software is crucial for unlocking the full potential of your data. A poorly selected system can lead to wasted resources and missed opportunities, while a well-chosen solution can transform your business insights. Careful evaluation and consideration of key factors are essential for success.
Evaluating BI software options requires a systematic approach, going beyond just features and price. Consider the long-term implications of your choice, ensuring the software aligns with your current needs and can adapt to future growth. This includes user-friendliness, integration capabilities, and scalability to support your evolving business.
Factors to Consider When Evaluating BI Software
Selecting the right BI software is a significant investment, and thorough consideration of various factors is paramount. These factors range from the immediate needs of your organization to the future growth potential of your data. This involves a careful analysis of your present situation and future expectations.
- Data Volume and Complexity: The amount and type of data you handle significantly impact your software needs. A system designed for small datasets may struggle with the complexities of large, high-velocity data streams. A crucial aspect to consider is the system’s ability to handle various data types (structured, semi-structured, and unstructured) and formats.
- Scalability and Future Needs: Your business is likely to grow and evolve. Choose software that can scale to accommodate increasing data volumes and user demands. Consider the potential for future data sources and the system’s ability to integrate them seamlessly.
- User-Friendliness and Training: A user-friendly interface minimizes training time and maximizes employee productivity. Look for intuitive dashboards, clear reporting tools, and comprehensive documentation. This simplifies the learning curve and accelerates the adoption of the new system.
- Integration Capabilities: The software must integrate smoothly with existing systems and applications. Ensure seamless data flow between your BI platform and other tools used in your organization.
- Vendor Support and Reliability: A reputable vendor with robust support resources is crucial. Assess their track record, available support channels, and the overall reliability of the system.
Assessing Potential Software Vendors
Evaluating potential vendors requires a methodical approach. Consider their experience, reputation, and commitment to customer support. A checklist helps streamline this process, ensuring key aspects are not overlooked.
- Experience and Reputation: Inquire about the vendor’s experience in similar industries and the overall reputation they have built in the market. Look for case studies and testimonials to gauge the quality of their work.
- Customer Support and Resources: Assess the support resources provided by the vendor, including documentation, training materials, and the availability of support staff. A vendor with dedicated support is crucial for addressing any issues that may arise.
- Security Measures: Verify the security protocols and measures implemented by the vendor to safeguard your sensitive data. This is critical for maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of your information.
- Pricing Models and Contracts: Compare various pricing models offered by different vendors to understand the total cost of ownership. Carefully review the terms and conditions of any contracts to avoid future surprises.
Comparing Pricing Models
Different BI software vendors employ various pricing models. Understanding these models is vital to making an informed decision. Factors like the number of users, data volume, and required features influence the pricing.
| Pricing Model | Description | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Per User/Seat | A fixed price per licensed user. | Suitable for organizations with a predictable number of users. |
| Per Data Point | Charges based on the volume of data processed. | Best for organizations with large and rapidly growing datasets. |
| Tiered Pricing | Offers various pricing plans based on features and usage levels. | Allows flexibility for scaling up or down based on needs. |
| Subscription Model | Monthly or annual fees for access and use. | Provides predictable ongoing costs and regular updates. |
Implementation and Maintenance
Bringing business intelligence software into your organization is a journey, not a destination. Careful planning and consistent maintenance are crucial for realizing the full potential of BI. It’s about more than just installing the software; it’s about integrating it seamlessly into your workflows and empowering your team to use it effectively.
Effective implementation and ongoing maintenance ensure your BI system becomes a valuable asset, not a cumbersome addition. This involves understanding the steps required, the importance of meticulous data preparation, and the necessity of user training and support. A robust troubleshooting process is also critical to maintaining smooth operation.
Implementation Steps
Implementing BI software involves a structured approach. The initial phase includes defining clear objectives and aligning them with the software’s capabilities. This ensures the chosen system truly addresses your organization’s needs. Careful consideration of data sources, integration methods, and desired reports is also essential. This phase culminates in a detailed implementation plan.
Data Preparation and Cleansing
High-quality data is the cornerstone of reliable insights. Data preparation and cleansing are critical steps before implementing BI software. Incomplete, inconsistent, or inaccurate data will lead to misleading reports and flawed analyses. This involves identifying missing values, correcting errors, and standardizing data formats. The process is often iterative and requires collaboration between data analysts and stakeholders.
User Training
Effective user training is vital for maximizing the value of BI software. Training should cover the software’s functionalities, report generation, and data visualization tools. Hands-on exercises and real-world examples are beneficial to reinforce understanding. Training materials should be tailored to the specific roles and responsibilities of different users.
Ongoing Maintenance and Support
Maintaining a BI system is an ongoing process. Regular updates and maintenance ensure the software remains compatible with evolving technologies and addresses potential security vulnerabilities. Proactive monitoring of system performance and data quality are also key aspects. Support teams should be readily available to address user questions and resolve issues.
Troubleshooting Guide
A well-defined troubleshooting process is crucial for resolving issues quickly and effectively. Common issues include connectivity problems, report generation errors, and data access restrictions. A step-by-step guide should be available for resolving these issues. This guide should include detailed descriptions of common problems, potential causes, and solutions.
- Connectivity Issues: Check network connections, verify server access, and confirm user credentials. If issues persist, consult network administrators or IT support.
- Report Generation Errors: Review report parameters, data source configurations, and user permissions. Ensure that the data required for the report is available and accessible.
- Data Access Restrictions: Verify user permissions, roles, and data security protocols. If access issues persist, consult IT administrators or security personnel.
Emerging Trends in Business Intelligence Software
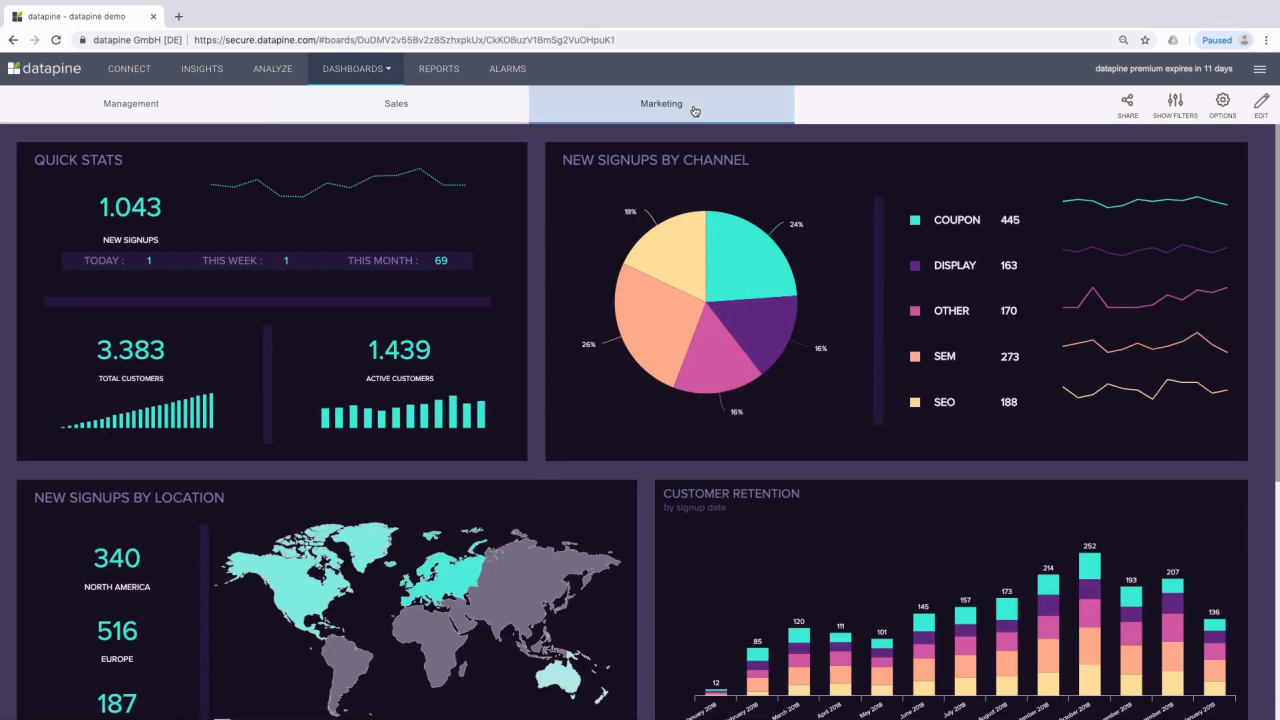
Business intelligence (BI) software is constantly evolving to meet the growing needs of modern businesses. The latest trends focus on making BI more accessible, powerful, and integrated with other business functions. This evolution is driven by the increasing volume and complexity of data, the rise of artificial intelligence, and the need for faster, more accurate insights.
Artificial Intelligence in BI Software
AI is transforming BI software by automating tasks, improving data analysis, and providing more insightful predictions. AI-powered tools can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies, generating actionable recommendations. For instance, AI can predict future sales trends based on historical data, customer behavior, and market conditions. This allows businesses to proactively adjust their strategies and optimize their operations.
Machine Learning Enhancing BI Capabilities
Machine learning (ML) is significantly enhancing BI capabilities by enabling sophisticated data analysis and pattern recognition. ML algorithms can identify complex relationships in data that would be missed by traditional methods. This leads to more accurate predictions and a deeper understanding of business performance. For example, ML models can analyze customer data to predict which customers are most likely to churn, enabling businesses to proactively address their concerns and retain them.
Big Data Analytics in BI Software
Big data analytics is playing a crucial role in BI software, enabling organizations to extract valuable insights from massive datasets. Tools for big data analysis allow businesses to gain a comprehensive understanding of their operations, customers, and market trends. For example, a retailer using big data analytics can track customer purchasing patterns across various channels to personalize recommendations and tailor marketing campaigns.
Integration with Other Business Applications
Integration of BI with other business applications is a key trend. This integration allows for seamless data flow and real-time insights. By connecting BI tools with CRM, ERP, and other systems, businesses can gain a holistic view of their operations and make more informed decisions. For example, a manufacturing company can use BI to analyze data from its ERP system to identify bottlenecks in the production process and implement corrective measures, all in real-time.
Case Studies of Business Intelligence Software

Business intelligence (BI) software has proven transformative for organizations across diverse industries. Real-world implementations demonstrate the significant impact of effective BI solutions, illustrating both successes and challenges. These case studies provide valuable insights for businesses considering implementing BI software.
Successful BI implementations often lead to improved decision-making, increased efficiency, and a deeper understanding of market trends. These examples highlight the potential for BI to drive positive change within an organization.
Retail Industry Example
A large retail chain used BI software to analyze customer purchase patterns. By identifying trends in product preferences and seasonal buying behaviors, the company optimized inventory management. This resulted in reduced stockouts, minimized waste, and increased profitability. The software also helped pinpoint areas needing targeted marketing campaigns, boosting sales in those regions. Challenges included integrating disparate data sources and training employees on new analytical tools. However, the company overcame these hurdles with clear communication and dedicated training programs. Long-term benefits included improved customer satisfaction and a more responsive business model.
Manufacturing Industry Example
A manufacturing company leveraged BI to monitor production efficiency and identify bottlenecks in their assembly lines. The BI software tracked real-time data on machine performance, resource utilization, and defect rates. The insights gained allowed the company to proactively address issues and optimize production schedules. This led to a significant reduction in production downtime and improved output. Challenges included data migration from legacy systems and ensuring data accuracy. They overcame these obstacles by investing in robust data quality processes. Long-term benefits include enhanced operational efficiency, reduced production costs, and a greater ability to adapt to market fluctuations.
Financial Services Industry Example
A financial services firm implemented BI to enhance risk management and improve customer service. The BI system provided a comprehensive view of customer interactions, transaction patterns, and potential risks. This helped the company identify fraudulent activities early and proactively mitigate financial losses. The software enabled faster and more accurate risk assessments, allowing the company to adjust its investment strategies in real-time. Challenges included ensuring data security and maintaining compliance with regulations. These were overcome through robust security measures and compliance training. Long-term benefits include improved regulatory compliance, reduced risk exposure, and enhanced customer trust.
Key Lessons Learned
| Lesson | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Quality is Crucial | Accurate and reliable data is the foundation of effective BI. Data cleansing and validation processes are essential to ensure meaningful insights. |
| Proper Implementation Planning | A well-defined implementation plan, encompassing data integration, training, and ongoing support, is vital for successful BI deployment. |
| Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation | Regular monitoring and evaluation of BI system performance and its impact on business objectives are critical for adapting to changing needs. |
| Employee Training and Adoption | Effective training and ongoing support are essential for employees to effectively utilize BI tools and derive maximum value from the system. |
Data Security and Privacy in BI Software
Protecting sensitive business information is paramount in today’s data-driven world. Business intelligence (BI) software handles vast amounts of confidential data, making robust security measures essential. Failure to prioritize data security can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions.
Data breaches can have a devastating impact on organizations. They expose sensitive information like customer details, financial records, and intellectual property, potentially resulting in substantial financial penalties and irreparable harm to the company’s reputation. Implementing robust security protocols within BI software is therefore crucial for safeguarding these assets.
Importance of Data Security in BI Software
Data security in BI software is critical for maintaining trust, protecting sensitive information, and upholding compliance with regulations. A secure BI environment ensures that only authorized personnel can access and analyze data, minimizing the risk of unauthorized disclosure or modification. It also protects against data breaches, cyberattacks, and other security threats.
Role of Data Encryption and Access Controls
Data encryption plays a vital role in safeguarding sensitive data. By converting data into an unreadable format, encryption makes it virtually impossible for unauthorized individuals to access or understand its contents. Access controls, which define who can access specific data and what actions they can perform on it, further enhance security. These controls can be based on user roles, departments, or specific data elements. For instance, a sales team might only have access to sales data, while senior management has access to all company data.
Strategies for Maintaining Data Privacy
Maintaining data privacy is a crucial aspect of BI security. Organizations must implement policies and procedures to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and misuse. These strategies may include anonymization techniques to de-identify data, data masking to obscure sensitive information, and data minimization to store only the necessary data. Data retention policies should also be in place to ensure that data is not retained longer than necessary. Regular audits and assessments are also necessary to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
Compliance Requirements for Data Handling
Compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA is essential for BI software. These regulations mandate specific data handling practices, including obtaining consent for data collection, ensuring data accuracy and completeness, and implementing measures to protect data from unauthorized access. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant penalties and legal repercussions.
Best Practices for Data Security in BI
| Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Encryption | Encrypting data at rest and in transit protects it from unauthorized access. This includes using strong encryption algorithms and ensuring proper key management. |
| Access Control | Implement strict access controls based on user roles and responsibilities. Restrict access to sensitive data to authorized personnel only. |
| Regular Security Audits | Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities in the BI system. This helps proactively identify and mitigate potential risks. |
| Data Loss Prevention (DLP) | Implement DLP tools to monitor and prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control. This includes monitoring emails, files, and other data transfer mechanisms. |
| Employee Training | Provide regular training to employees on data security best practices. This includes awareness training on phishing scams, social engineering attacks, and other security threats. |
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, business intelligence software is a game-changer for businesses of all sizes. By understanding its features, benefits, and trends, you can leverage data to drive better decision-making, optimize processes, and gain a competitive edge. From selecting the right software to implementing it effectively, we’ve covered the essential aspects. Remember, data-driven insights are the key to success in today’s dynamic market.