Task management is crucial in today’s fast-paced world. Effective task management isn’t just about getting things done; it’s about optimizing your workflow, boosting productivity, and achieving your goals. This comprehensive guide explores various methods, tools, and strategies to transform your approach to task handling.
From understanding core principles and different methodologies to leveraging powerful tools and fostering effective collaboration, this guide equips you with practical insights and actionable steps to elevate your task management skills. Learn how to prioritize tasks effectively, manage your time efficiently, and measure your progress to optimize your output and achieve a fulfilling work-life balance.
Introduction to Task Management
Task management is a crucial process for individuals and teams to organize, prioritize, and complete tasks efficiently. It’s about proactively structuring work to achieve goals and avoid wasted effort. Effective task management fosters productivity and reduces stress associated with overwhelming workloads. By implementing a structured approach, individuals and teams can maintain control over their projects and ensure timely completion.
Effective task management relies on a clear understanding of the tasks at hand and a well-defined process for handling them. This encompasses not only completing individual tasks but also coordinating them within a larger project or workflow. It’s about understanding dependencies, deadlines, and resource allocation to optimize the entire process.
Definition of Task Management
Task management is the systematic process of planning, assigning, tracking, and completing tasks to achieve specific objectives. This involves identifying the tasks needed, determining the resources required, setting deadlines, and monitoring progress to ensure successful completion. It encompasses both individual and team-based projects, encompassing all steps from initial planning to final execution.
Core Principles of Effective Task Management
Effective task management rests on several key principles. Firstly, clarity is paramount. Clearly defined tasks, with well-defined deliverables and deadlines, are essential for avoiding ambiguity and ensuring everyone understands their roles. Secondly, prioritization is critical. Prioritizing tasks based on urgency and importance ensures that the most critical items are addressed first, optimizing workflow. Thirdly, effective communication and collaboration are vital for successful task management, especially in team settings. Regular updates and transparent communication channels are key to staying on track. Finally, adaptability is crucial in task management. Unexpected obstacles and changes in priorities are inevitable. Effective task management involves adapting plans and strategies to accommodate these changes.
Benefits of Implementing a Robust Task Management System
Implementing a robust task management system offers numerous benefits. Increased productivity is a key advantage, as systems streamline workflows and reduce wasted time. Improved communication and collaboration are other significant benefits, fostering teamwork and reducing misunderstandings. Enhanced accountability and transparency result from clear assignments and progress tracking. Reduced stress and improved time management are further benefits, as the system provides a clear framework for managing tasks and deadlines.
Framework for Organizing Tasks
A simple framework for organizing tasks involves the following steps:
- Define Tasks: Clearly identify all the tasks required to achieve the desired outcome. This includes breaking down complex tasks into smaller, manageable sub-tasks. For instance, a large project might involve multiple stages, such as research, design, development, testing, and deployment. Each of these stages could be further subdivided into smaller, specific tasks.
- Prioritize Tasks: Use a method like the Eisenhower Matrix (Urgent/Important) or a similar technique to prioritize tasks based on their urgency and importance. This helps allocate time and resources effectively.
- Assign Tasks: Assign tasks to specific individuals or teams, ensuring clarity of responsibilities and accountability.
- Set Deadlines: Establish realistic deadlines for each task, ensuring that they are achievable and aligned with the overall project timeline.
- Track Progress: Regularly monitor task progress and identify potential delays or bottlenecks. This allows for proactive adjustments to keep the project on track.
This structured approach allows for greater control over tasks, enabling better organization and efficiency. By adhering to these principles, individuals and teams can maximize their output and achieve their goals more effectively.
Different Task Management Methods
Choosing the right task management method can significantly impact project success. Different approaches cater to various project needs and team dynamics, making it crucial to understand the strengths and weaknesses of each. This section explores common methodologies like Kanban, Scrum, and to-do lists, highlighting their applicability to diverse project types.
Effective task management hinges on selecting a system that aligns with project requirements. This involves considering factors such as team size, project complexity, and desired level of structure. Understanding the nuances of each method empowers project managers to make informed decisions, optimizing productivity and minimizing potential pitfalls.
Kanban
Kanban, originating from lean manufacturing, emphasizes visualizing workflow and limiting work in progress (WIP). This system focuses on continuous improvement and adapting to changing demands. Visualizing tasks on a board, often with columns representing different stages (e.g., To Do, In Progress, Done), provides a clear overview of project progress.
- Strengths: Kanban promotes flexibility and responsiveness to change. Its visual nature fosters transparency and communication within the team. It allows for easy adaptation to evolving project requirements. The system is adaptable to various team sizes and project types, making it a versatile option.
- Weaknesses: Kanban might lack the structured framework of other methods like Scrum. It can be challenging to maintain consistent workflow if the team isn’t disciplined. Tracking progress might not be as granular as with other systems.
- Suitability: Kanban is ideal for projects with fluctuating demands and a need for continuous adaptation. It is well-suited for teams who value flexibility and visual representation of progress.
- Real-World Applications: Many software development teams use Kanban for agile development, where tasks and features are constantly being added and modified. Customer service departments also utilize Kanban for managing incoming requests and support tickets. Any project where work is iterative and needs flexibility will benefit.
Scrum
Scrum is a framework for managing complex projects. It’s characterized by short iterations (sprints) where teams work on specific deliverables. Daily stand-up meetings facilitate communication and collaboration. Scrum emphasizes iterative development and continuous improvement.
- Strengths: Scrum provides a structured framework for managing complex projects, allowing for better control and predictability. Its iterative approach allows for early feedback and adjustments, minimizing risks. The focus on daily stand-ups promotes open communication and collaboration within the team.
- Weaknesses: Scrum can be more demanding in terms of team discipline and commitment to the framework. It requires a dedicated Scrum Master to guide the team. The fixed sprint duration might not be ideal for projects with highly variable requirements.
- Suitability: Scrum is particularly well-suited for complex projects with evolving requirements, such as software development, product design, or large-scale marketing campaigns. It is effective in environments where teams need a defined structure for project delivery.
- Real-World Applications: Numerous software development teams utilize Scrum for project management. In product design, Scrum helps teams deliver incremental improvements to a product or service. Scrum is highly adaptable and can be used in various sectors, but it is most effective with a structured project plan.
To-Do Lists
To-do lists are the most basic task management method. They involve creating a list of tasks and marking them off as completed. While simple, they can be highly effective for individual tasks or small projects.
- Strengths: To-do lists are simple to understand and use. They are easily adaptable to various contexts. They provide a clear overview of individual tasks, enabling individuals to focus on completing them.
- Weaknesses: To-do lists lack the structure and collaboration features of more complex methods. They can become unwieldy for large projects with many interconnected tasks. There is limited visibility for progress outside of the individual user.
- Suitability: To-do lists are ideal for personal tasks, small projects, or managing individual tasks within larger projects. They are a good starting point for those new to task management.
- Real-World Applications: Individuals use to-do lists for personal errands and chores. They can also be used for simple project tasks like writing a report or preparing a presentation. To-do lists are useful for daily or weekly planning, where a simple and straightforward approach is sufficient.
Tools and Technologies for Task Management
Task management is significantly enhanced by the use of appropriate software and tools. These tools streamline workflows, improve collaboration, and provide valuable insights into project progress. Choosing the right tool is crucial for optimizing efficiency and achieving desired outcomes.
Effective task management relies on the right technological support. By leveraging the power of task management software, teams can improve organization, reduce errors, and boost productivity. The correct selection of tools can be a game-changer for any project.
Popular Task Management Software Applications
Various task management software applications cater to diverse needs and project complexities. Choosing the right software depends on the specific requirements of the task at hand.
- Asana: A versatile platform for project management, Asana allows teams to organize tasks, set deadlines, and track progress visually. It facilitates collaboration through shared workspaces and real-time updates. Asana is particularly effective for complex projects requiring detailed task breakdowns and cross-functional collaboration.
- Trello: This visual task management tool uses a Kanban-style approach, arranging tasks in columns to represent different stages of a project. Trello’s simplicity and flexibility make it a great choice for teams seeking a user-friendly platform to visualize workflow and track progress.
- Jira: Primarily designed for agile software development, Jira provides a robust platform for tracking bugs, managing sprints, and facilitating collaboration within development teams. Its extensive features and customization options are suited for complex development projects.
- Monday.com: A highly customizable platform, Monday.com offers a flexible workspace for various project types. Users can create custom views, automate workflows, and integrate with other applications. Its wide range of templates and integrations makes it a strong contender for general project management needs.
- ClickUp: This platform is known for its powerful features, including task management, project management, and automation capabilities. ClickUp’s adaptability makes it suitable for diverse teams and complex projects, offering a centralized hub for all project-related activities.
Key Features of Each Application
Understanding the key features of each application is essential for choosing the best fit for a specific task. This involves evaluating the functionalities that align with team needs and project requirements.
- Asana: Key features include task creation, assignment, and deadlines. It provides reminders, collaborative workspaces, and the ability to attach files and track progress visually. Integration with other applications is also a key advantage.
- Trello: Key features include a visual Kanban board, task categorization, and customizable workflows. It allows for real-time collaboration and provides an easy way to visualize project progress. Its simplicity and visual nature make it intuitive for many users.
- Jira: Key features are focused on agile development, including issue tracking, sprint management, and reporting. Jira also provides advanced customization options, allowing for intricate workflow configuration.
- Monday.com: Key features include customizable dashboards, automated workflows, and extensive integration options. It allows users to create custom views, track progress in various ways, and customize workflows based on their project’s needs.
- ClickUp: Key features include task management, project management, and automation. It supports diverse project types and workflows with its flexibility and wide range of integrations. Its powerful features cater to a wide range of needs.
Comparison Table of Task Management Applications
This table provides a concise overview of the strengths and weaknesses of the various applications.
| Application | Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asana | Task creation, deadlines, reminders, collaboration, integrations | User-friendly, flexible, affordable | Limited customization options for complex projects |
| Trello | Visual Kanban boards, task categorization, workflows | Simple, intuitive, visual representation | Limited reporting capabilities, may not be ideal for complex projects |
| Jira | Issue tracking, sprint management, agile workflows | Robust for agile development, advanced features | Steeper learning curve, complex interface |
| Monday.com | Customizable dashboards, automated workflows, integrations | Highly customizable, flexible, strong integrations | Can be complex to set up, potential cost for advanced features |
| ClickUp | Task management, project management, automation, integrations | Versatile, comprehensive features, strong integrations | Steeper learning curve compared to simpler tools |
Integrating Tools with Work Processes
Effective integration of task management tools with existing work processes is key to maximizing efficiency. This often involves customizing workflows to match the specific tools’ capabilities.
- Workflow Automation: Tools like Asana, Monday.com, and ClickUp offer automation capabilities. This can automate repetitive tasks, such as sending reminders or updating project statuses. This integration can significantly reduce manual effort and improve consistency.
- Data Integration: Integrating task management tools with other applications like email clients or project databases allows for seamless data flow. This approach improves efficiency by reducing the need for manual data entry and ensures consistency across different platforms.
- Customizable Workflows: Most task management software allows customization. Tailoring workflows to the specific needs of a team can significantly improve productivity. Adapting to the unique aspects of a project or team dynamic can enhance the tool’s effectiveness.
Task Prioritization and Organization

Effective task management hinges on not just completing tasks, but also prioritizing and organizing them strategically. This crucial step ensures projects are completed efficiently and effectively, minimizing wasted time and maximizing output. Prioritization and organization are not merely nice-to-haves; they are essential for success in any endeavor, from personal projects to complex business initiatives.
Prioritization and organization go hand-in-hand. Effective prioritization guides the organization of tasks, ensuring that the most critical and impactful items receive the necessary attention and resources. This approach not only leads to higher quality output but also enhances overall project success. A well-organized system is a critical component for successful task management.
Importance of Task Prioritization
Prioritization is vital because it directs effort toward the most impactful tasks first. This focus prevents wasted time on less critical items, ensuring the completion of the most important tasks first. Without prioritization, projects can easily become bogged down in less impactful work, leading to delays and potentially missed deadlines.
Methods for Effective Task Prioritization
Various methods exist for prioritizing tasks effectively. One widely used technique is the urgency/importance matrix, which categorizes tasks based on their urgency and importance. This matrix helps identify which tasks demand immediate attention and which can be scheduled for later.
- Urgency/Importance Matrix: This matrix categorizes tasks into four quadrants: urgent and important, important but not urgent, urgent but not important, and neither urgent nor important. This framework allows for a clear understanding of which tasks require immediate action, which can be scheduled, and which can be eliminated or delegated. For example, a critical project deadline (urgent and important) takes precedence over a routine report (important but not urgent).
Techniques for Organizing Tasks
Effective task organization is crucial for maintaining clarity and flow within projects. Project management software provides a structured approach to task organization, breaking down complex projects into manageable components. These tools often include features for task dependencies, deadlines, and collaboration, facilitating a seamless workflow.
- Project Management Software: Tools like Asana, Trello, Jira, and Monday.com offer features for organizing tasks within projects. These tools allow users to create task lists, set deadlines, assign tasks to team members, and track progress. This structure helps in maintaining a clear overview of the project’s components and progress. These tools often incorporate features for collaboration, which are crucial in team-based projects.
Task Breakdown Structures for Different Projects
Different project types require varying levels of task breakdown complexity.
| Project Type | Task Breakdown Structure Example |
|---|---|
| Simple Project (e.g., writing a blog post) |
|
| Complex Project (e.g., software development) |
|
Collaboration and Communication in Task Management
Effective task management hinges on seamless collaboration and communication within teams. Clear communication channels and strategies are crucial for ensuring tasks are completed efficiently, on time, and to the desired quality. This section dives into the vital role of communication and Artikels key strategies for smooth teamwork.
The Role of Communication in Successful Task Management
Effective communication is the cornerstone of successful task management. It fosters understanding, reduces ambiguity, and enables teams to work together cohesively. Without proper communication, tasks can become misconstrued, deadlines missed, and conflicts unresolved. Clear communication establishes shared understanding, leading to better execution and more satisfying outcomes.
Strategies for Effective Communication within Teams
Strong communication strategies are vital for productive teamwork. Active listening, respectful dialogue, and consistent feedback are key components. Regular check-ins, using project management software for updates, and designated communication channels for specific issues streamline the process. Establishing clear expectations and roles from the start, followed by consistent communication, creates a positive and productive work environment. This promotes accountability and minimizes misunderstandings.
Communication Channels for Different Task Management Situations
Maintaining open lines of communication is crucial for various task management situations. Different channels are best suited for different types of communication. The table below Artikels suitable communication channels for specific situations.
| Task Status | Communication Channel | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| New Task Assignment | Email/Internal Chat | Initial task details, deadlines, responsibilities, and expected deliverables. |
| Progress Updates | Project Management Software | Regular updates on task completion, potential roadblocks, and any necessary adjustments. |
| Issue Reporting | Dedicated Channel/Forum (e.g., Slack channel, project management software’s issue tracker) | Quick escalation of problems, enabling rapid response and preventing delays. This allows for targeted support and prevents the issue from spreading. |
| Team Meetings | Video Conference/In-person Meeting | Addressing complex issues, brainstorming solutions, resolving conflicts, and fostering a sense of shared purpose. Face-to-face interaction can be crucial for building rapport and addressing nuanced concerns. |
Best Practices for Managing Conflicts and Disagreements
Disagreements are inevitable in any collaborative environment. The key is to manage them constructively. Establishing clear conflict resolution procedures, encouraging open dialogue, and fostering a culture of respect are essential. Active listening, acknowledging differing viewpoints, and focusing on finding mutually beneficial solutions are crucial steps in managing disagreements. Mediation or a designated third party can help facilitate productive conversations and resolve conflicts efficiently. Remember, conflicts, when addressed effectively, can lead to stronger teams and improved problem-solving.
Time Management and Task Management
Effective task management is inextricably linked to effective time management. Understanding how to allocate time strategically is crucial for completing tasks efficiently and achieving goals. Poor time management often leads to missed deadlines, increased stress, and ultimately, less satisfying results.
Time management isn’t about cramming more into a day; it’s about optimizing your time to maximize productivity and reduce wasted effort. This involves understanding your own work patterns, identifying time-wasting activities, and creating systems that allow you to focus on the most important tasks.
The Interplay of Time and Task Management
Time management and task management are two sides of the same coin. Effective task management requires a clear understanding of how much time each task needs, while effective time management involves scheduling and prioritizing tasks based on their importance and urgency. This interconnectedness ensures a structured approach to work, reducing stress and enhancing productivity.
Time Management Techniques for Task Completion
Various time management techniques can significantly improve task completion. These methods often involve structuring your day, setting realistic goals, and managing distractions effectively.
- Time Blocking: This technique involves scheduling specific time slots for particular tasks. This approach creates a structured framework, minimizing distractions and improving focus on each task. For example, allocating 2 hours for writing a report ensures dedicated time for the task, preventing interruptions and promoting focused work.
- The Pomodoro Technique: Working in focused intervals (e.g., 25 minutes) followed by short breaks (e.g., 5 minutes) can significantly boost concentration. This method combats burnout and allows for consistent productivity. Using a timer is essential for this technique, which helps maintain the scheduled work intervals.
- The Eisenhower Matrix: This matrix categorizes tasks based on urgency and importance. This helps prioritize tasks, focusing on high-priority items first. For example, an urgent and important task might be a client deadline, while an important but not urgent task might be a strategic planning session.
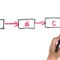
Task Planning and Execution Flowchart

(A flowchart depicting the process of task planning and execution. This flowchart visually Artikels the steps from task identification to completion, including assignment of time blocks, task prioritization, execution, and feedback loops for improvement. This illustrative flowchart helps visualize the workflow, highlighting the stages involved in each task.)
Preventing Procrastination and Maintaining Focus
Procrastination is a common issue that can significantly impact productivity. Understanding the reasons behind procrastination and developing effective strategies to overcome it is crucial.
- Break Down Large Tasks: Breaking large tasks into smaller, more manageable sub-tasks can make the overall task less daunting and more approachable. This gradual approach can significantly reduce feelings of overwhelm and increase motivation to complete the tasks.
- Create a Dedicated Workspace: A dedicated workspace free from distractions can significantly improve focus. This creates an environment conducive to uninterrupted work, allowing for better concentration and task completion.
- Establish Realistic Deadlines: Unrealistic deadlines can lead to stress and procrastination. Setting realistic deadlines allows for more manageable time allocation and reduces feelings of pressure, promoting a more relaxed approach to task completion.
Final Conclusion

In conclusion, mastering task management is a continuous journey of learning and refinement. By understanding the core principles, utilizing diverse methods, selecting appropriate tools, and prioritizing effective communication and collaboration, you can dramatically enhance your productivity and achieve remarkable results. Remember, the key to successful task management lies in consistent practice and a proactive approach to adapting your strategies based on your unique needs and project requirements.