Tableau Desktop is more than just a tool; it’s your gateway to unlocking hidden stories within data. Imagine transforming raw numbers into captivating visuals, effortlessly connecting with your data sources, and crafting interactive dashboards that tell a compelling narrative. Get ready to dive deep into the world of data analysis with Tableau Desktop.
This comprehensive guide explores the functionalities of Tableau Desktop, from connecting to various data sources to building interactive dashboards and performing insightful analyses. We’ll cover everything from basic data preparation to advanced techniques, empowering you to harness the full potential of your data.
Introduction to Tableau Desktop

Tableau Desktop is a powerful data visualization tool designed for creating interactive dashboards and reports. It empowers users to connect to diverse data sources, transform raw data into insightful visualizations, and share their findings with stakeholders effectively. Its intuitive interface and robust features make it accessible to both novice and experienced data analysts.
Tableau Desktop’s primary function is to facilitate the exploration and communication of data insights. It’s more than just a charting tool; it’s a platform for data storytelling, enabling users to uncover hidden patterns, trends, and correlations within their data sets. This ultimately leads to informed decision-making across various industries.
Typical User Scenarios
Tableau Desktop finds applications in a wide range of scenarios. Businesses across sectors leverage it to gain a comprehensive understanding of their operations, identify areas for improvement, and ultimately enhance profitability. Marketing teams use Tableau to track campaign performance and customer behavior, while sales teams analyze sales data to optimize strategies. Financial analysts utilize it to monitor financial performance, identify potential risks, and forecast future trends. Essentially, any department needing to understand data and present it visually can benefit from Tableau Desktop.
Available Versions and Editions
Tableau offers various versions and editions tailored to different needs and budgets. The specific version and edition chosen depend on factors like the size of the data set, the required functionalities, and the number of users. Generally, Tableau Desktop comes in a personal version for individual use and professional versions designed for teams. Enterprise versions are also available for large-scale deployments with more advanced features. Specific details regarding pricing, features, and support vary with each version.
History of Tableau Desktop
Tableau Desktop has evolved significantly since its inception. Initially, it focused on simple data visualization, but the subsequent versions introduced more advanced functionalities, including more complex calculations, custom visualizations, and improved data blending capabilities. The evolution has been driven by user feedback and the need for more sophisticated data analysis tools in an increasingly data-driven world. This evolution highlights Tableau’s commitment to providing the best possible data visualization tools to its users.
Features, Benefits, and Use Cases
| Features | Benefits | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Interactive dashboards and reports | Enable users to explore data dynamically, identify trends, and gain insights | Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), monitoring sales performance, analyzing customer behavior |
| Connection to various data sources | Support for a wide range of data formats and databases, allowing for seamless integration with existing systems | Analyzing data from relational databases, spreadsheets, cloud-based services, and other sources |
| Data blending and calculations | Allows users to combine data from multiple sources and perform complex calculations to derive meaningful insights | Merging sales data with customer data to understand customer purchasing patterns, creating custom metrics for performance analysis |
| Drag-and-drop interface | Streamlines the visualization process, making it user-friendly for individuals with various skill levels | Quickly creating visualizations, designing dashboards, and generating reports with minimal technical expertise |
| Extensive visualization options | Provides a variety of chart types, enabling users to choose the most appropriate visualization for their needs | Creating bar charts, line graphs, scatter plots, maps, and other visualizations to effectively communicate data insights |
Data Connection and Preparation
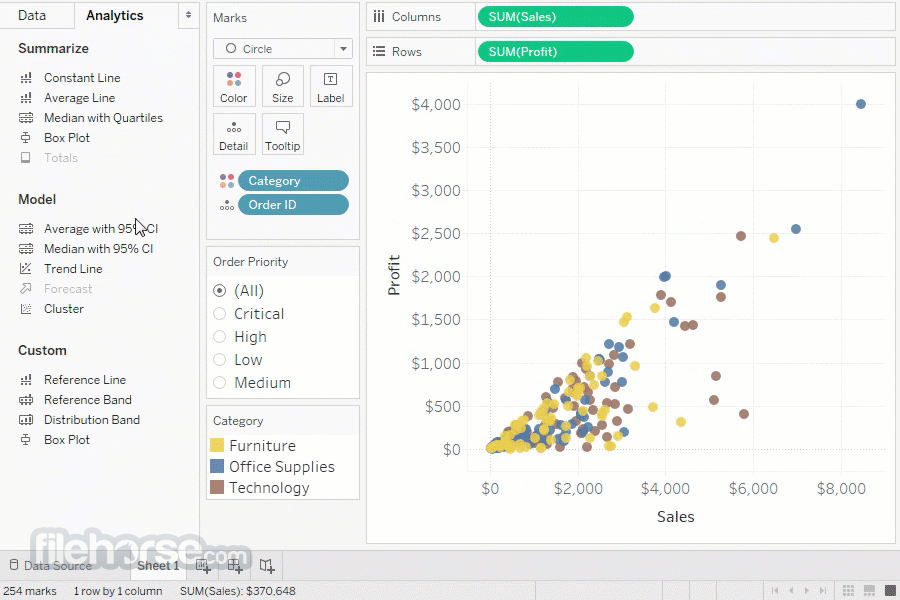
Connecting to and preparing data is a crucial first step in any Tableau analysis. Effective data preparation ensures the quality and accuracy of insights derived from the data. This process involves not only importing data from various sources but also meticulously cleaning and transforming it to meet the requirements of Tableau’s analytical engine. Properly structured data leads to more reliable and actionable results.
Tableau Desktop supports a wide array of data sources, enabling users to leverage data from diverse platforms and applications. The seamless integration with these sources allows for quick and efficient data acquisition, enabling analysts to focus on deriving valuable insights rather than wrestling with complex data import procedures. Furthermore, the built-in data preparation tools streamline the process of cleaning, transforming, and structuring data, facilitating the creation of robust analytical models.
Data Source Connections
Tableau Desktop boasts a vast network of supported data sources. This versatility enables analysts to connect to a wide range of data repositories, ensuring compatibility with diverse business needs.
- Databases (SQL, MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and more): Direct connections to relational databases allow for querying and retrieving specific data subsets tailored to the analysis requirements.
- Spreadsheets (Excel, CSV, and others): Common spreadsheet formats are easily imported, enabling quick access to data stored in widely used formats.
- Cloud Services (Google Sheets, Dropbox, and more): Cloud-based data sources are directly accessible, streamlining the process of incorporating data from various cloud platforms.
- Big Data Sources (Hadoop, Spark): Advanced connectivity options allow access to large-scale datasets residing in big data environments, enabling the analysis of extensive volumes of data.
Data Import and Preparation
Importing data into Tableau Desktop is straightforward. Once a connection is established, the appropriate data source components can be selected, and data is ready to be imported.
- Import Options: Users can choose specific tables or sheets within a spreadsheet or database. This granularity ensures that only the relevant data is brought into the Tableau environment, minimizing storage requirements and improving analysis efficiency.
- Data Preview: A preview of the data enables users to examine its structure, identifying potential issues or inconsistencies before proceeding with the analysis.
- Data Cleansing: This crucial step involves identifying and correcting errors, inconsistencies, or missing values in the imported data. Addressing these issues early on ensures the reliability of the analysis.
Data Cleaning and Transformation
Tableau Desktop offers robust tools for cleaning and transforming data. These tools simplify the process of preparing data for analysis.
- Data Filtering: Users can select specific data subsets based on criteria, such as date ranges or specific values. This process helps refine the dataset and focus on relevant information.
- Data Aggregation: Data can be aggregated to create summary statistics or to summarize data into meaningful groups. This consolidation simplifies the analysis and reveals overall trends.
- Data Transformation: Tableau provides various tools for transforming data. This includes converting data types, creating calculated fields, and aggregating data into meaningful summaries. These operations are crucial for shaping the data into a format suitable for the desired analysis.
Examples of Common Data Preparation Tasks
Several common data preparation tasks are crucial for effective analysis. These include handling missing values, standardizing data formats, and creating calculated fields.
- Handling Missing Values: Missing values can be imputed using techniques like replacing missing values with the mean or median. This ensures the integrity and completeness of the dataset, avoiding bias in the analysis.
- Standardizing Data Formats: Data formats need to be consistent to ensure accurate analysis. Converting data types or applying formatting rules are important steps to achieve consistency.
- Creating Calculated Fields: New fields can be created from existing data, such as calculating ratios, averages, or percentages. These calculated fields can provide deeper insights and enhance the analysis.
Data Connection Method Comparison
Different data connection methods offer varying performance characteristics. The choice of method often depends on the size and complexity of the data source.
| Connection Method | Performance Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Direct Database Connection | Generally faster for large datasets, especially when using optimized database queries. |
| Spreadsheet Import | Faster for smaller datasets, but can be slower for large spreadsheets due to the file processing nature. |
| Cloud Service Connection | Performance depends on the cloud service’s infrastructure and network latency. Can be efficient for real-time data updates. |
| Big Data Source Connection | Requires specialized configurations for optimal performance. Performance is often influenced by data size and processing methods. |
Data Visualization Techniques
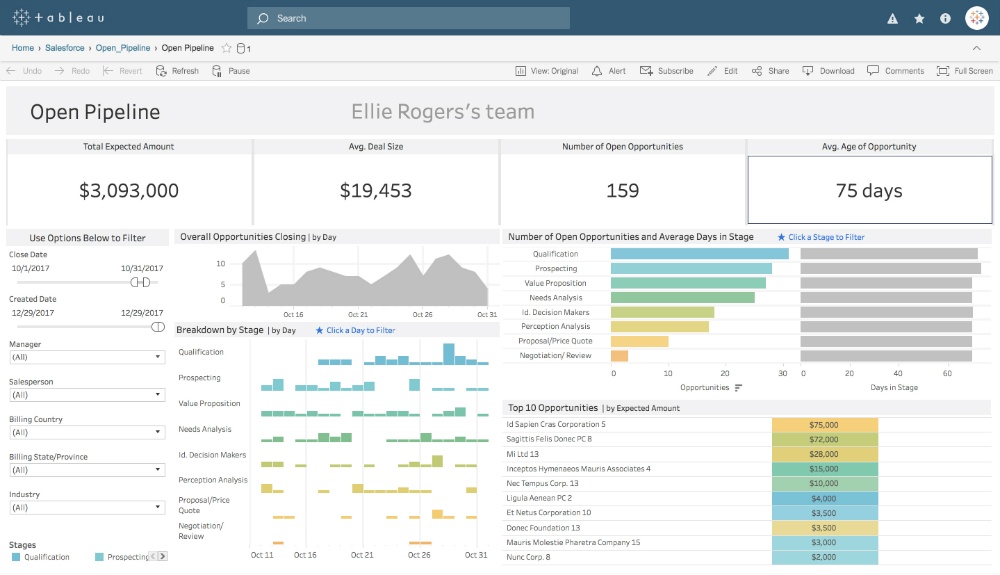
Tableau Desktop empowers users to transform raw data into compelling narratives. Effective visualization techniques are crucial for extracting insights and communicating them effectively to stakeholders. This section delves into the diverse chart types available, emphasizing the design principles for impactful visualizations and dashboards, ultimately highlighting the vital role of data visualization in business decision-making.
Chart Types Supported by Tableau Desktop
Tableau Desktop offers a rich array of chart types, each designed for specific data exploration and presentation needs. These include bar charts, line charts, scatter plots, area charts, pie charts, maps, and more. Choosing the appropriate chart type directly influences the clarity and impact of the visualization. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each chart is paramount for effective data communication.
Designing Effective Visualizations
Effective visualizations require careful consideration of design elements. Visual clarity is paramount; use clear labels, appropriate scales, and intuitive color palettes. The selection of the right chart type, in alignment with the story being told, is key to enhancing the message. Consider the audience and the intended message when designing visualizations. For example, a scatter plot might be ideal to showcase the relationship between two variables, while a bar chart might effectively compare categorical data. By prioritizing clarity, accuracy, and context, visualizations become powerful tools for communicating insights.
Best Practices for Dashboards and Stories
Dashboards should be meticulously organized, with clear navigation and intuitive filtering options. The use of consistent branding and color palettes enhances the user experience. Data stories should provide a clear narrative, with visualizations seamlessly linking together to reveal insights. They should also include concise, impactful captions and descriptions. Storytelling in dashboards is crucial to presenting a compelling narrative that transcends simple data points. Interactive dashboards, for example, allow users to explore data dynamically, uncovering hidden patterns and correlations.
Importance of Data Visualization in Business Decision-Making
Data visualization plays a pivotal role in business decision-making. By quickly and easily comprehending complex data sets, businesses can identify trends, patterns, and outliers. Visualizations allow for a more profound understanding of business performance, facilitating informed strategic decisions. The ability to quickly see patterns and relationships in data empowers faster and more effective problem-solving.
Chart Type Strengths and Weaknesses
| Chart Type | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Bar Chart | Excellent for comparing categorical data; easily understandable. | Less effective for showing trends over time; can be cluttered with many categories. |
| Line Chart | Ideal for showcasing trends over time; highlights changes in data values. | Can be difficult to interpret if data points are numerous; may not be suitable for comparing categories. |
| Scatter Plot | Effective for identifying relationships between two variables; reveals correlations or trends. | Can become difficult to interpret with a large number of data points; may require additional visual cues for clarity. |
| Area Chart | Effective for highlighting changes in data over time; emphasizes magnitude of values. | Can be visually overwhelming if too many areas are stacked; may not be suitable for comparing categories directly. |
| Pie Chart | Suitable for displaying proportions of a whole; easy to understand at a glance. | Less effective for comparing multiple categories; can be misleading if data proportions are not significant. |
| Map | Ideal for geographical data analysis; visually showcases spatial patterns and distributions. | May require specialized data formats; can be challenging to use for non-geographical data analysis. |
Building Interactive Dashboards
Transforming static reports into dynamic, insightful dashboards is a key aspect of leveraging Tableau’s power. Interactive dashboards allow users to explore data, drill down into specific details, and uncover hidden patterns with ease. This capability empowers stakeholders to make data-driven decisions and gain a deeper understanding of their business.
Interactive Dashboard Components
Interactive dashboards are more than just visual representations; they are dynamic tools that respond to user actions. Core components enable this interactivity. Filters, parameters, and actions are fundamental elements that drive user exploration. Calculated fields and table calculations further enrich the analysis by adding custom logic and insights. Sharing dashboards effectively communicates these findings and facilitates collaboration.
Using Filters
Filters are the cornerstone of interactive exploration. They allow users to selectively view data based on specific criteria. A filter can be applied to any dimension or measure, enabling users to focus on particular subsets of data. For instance, a filter on a sales region allows users to isolate and analyze sales performance within that region. This targeted analysis helps in identifying trends and potential issues. Filters can be applied directly to visualizations, enabling on-the-fly adjustments to focus on specific areas of interest.
Implementing Parameters
Parameters are predefined values that users can select to influence visualizations. They are especially useful when dealing with dynamic data ranges or specific values. For example, a parameter allowing users to select a specific year can be used to compare sales performance across multiple years. This flexibility empowers users to explore data at various granularities. Parameters also facilitate consistency in analysis across different views and reports.
Employing Actions
Actions establish links between visualizations, enabling users to navigate between different views based on selections. For instance, selecting a specific product in a bar chart can automatically filter the related sales data in a line graph. This interconnectedness allows users to follow the flow of data and understand the context of different variables. This “drill-down” functionality is crucial for understanding intricate relationships.
Calculated Fields and Table Calculations
Calculated fields allow users to create new measures or dimensions by combining existing data. This is essential for creating custom insights. For example, calculating a profit margin or identifying sales growth rates are achievable through calculated fields. Table calculations perform calculations on the data within a specific table or visualization. This feature allows users to see trends and patterns within specific groups. These calculations offer a way to analyze the data at different levels of granularity, enhancing the overall analytical capability.
Sharing Dashboards
Dashboards can be shared with colleagues and stakeholders in several ways. Tableau provides features for exporting dashboards as images or embedding them into web pages or presentations. This accessibility ensures that key findings are readily available and easily communicated. Sharing is critical for collaborative data exploration and knowledge sharing within an organization.
Interactive Dashboard Components: Example Table
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Filters | Allow users to select specific subsets of data. |
| Parameters | Enable users to select predefined values to influence visualizations. |
| Actions | Establish links between visualizations to enable drill-down and exploration. |
| Calculated Fields | Create custom measures or dimensions based on existing data. |
| Table Calculations | Perform calculations on data within a specific table or visualization to identify trends and patterns. |
Advanced Features and Techniques
Unleashing the full potential of Tableau Desktop involves delving into its advanced features. These go beyond basic data visualization, enabling deeper exploration and more insightful analysis. Data blending, data mining, and geographic analysis are powerful tools for uncovering hidden patterns and trends within complex datasets. This section will demonstrate how to utilize these features to gain deeper insights, providing examples of complex data analysis scenarios and their solutions. Data storytelling is also highlighted, emphasizing its crucial role in effectively communicating insights derived from the analysis.
Data Blending
Data blending in Tableau combines data from multiple sources into a single view. This is crucial when working with disparate datasets that contain related information, such as sales data from different regions or customer information from various databases. Blending allows for the creation of composite visualizations that show the relationships between the different data sources, enabling a more comprehensive understanding of the overall picture. For instance, blending sales data with customer demographics allows for a more nuanced analysis of sales performance by specific customer segments. This reveals patterns that might be missed by examining the data in isolation.
Data Mining
Data mining techniques within Tableau facilitate the discovery of hidden patterns and relationships within datasets. These methods use algorithms to identify trends, clusters, and anomalies. For example, a retail company can use data mining to identify customer segments with similar purchasing behaviors. This allows for the development of targeted marketing campaigns and personalized product recommendations. This targeted approach is significantly more effective than a generalized approach. Tableau’s built-in data mining capabilities help in automating the identification of these hidden insights.
Geographic Analysis
Geographic analysis in Tableau leverages the power of maps to visualize and analyze data based on location. This feature allows users to explore spatial relationships and identify patterns across different geographic regions. A telecommunications company, for example, could use geographic analysis to pinpoint areas with high call volume and low network coverage. This information allows for targeted investment in infrastructure improvements, optimizing network performance.
Data Storytelling
Data storytelling is an essential component of effective communication of analytical findings. It involves crafting narratives that effectively communicate insights derived from data analysis. A compelling data story uses visualizations, clear language, and a logical structure to engage the audience and make the data meaningful. By weaving a narrative around data, one can transform complex insights into understandable and actionable information. For instance, a story about declining sales in a particular region can be illustrated with maps, charts, and narrative descriptions, which will be far more persuasive and impactful than just presenting raw data.
Advanced Features Overview
| Feature | Use Cases |
|---|---|
| Data Blending | Combining data from multiple sources to create a holistic view. |
| Data Mining | Identifying hidden patterns and relationships within data to extract actionable insights. |
| Geographic Analysis | Visualizing and analyzing data based on location to identify spatial relationships and trends. |
Tableau Desktop and Related Tools
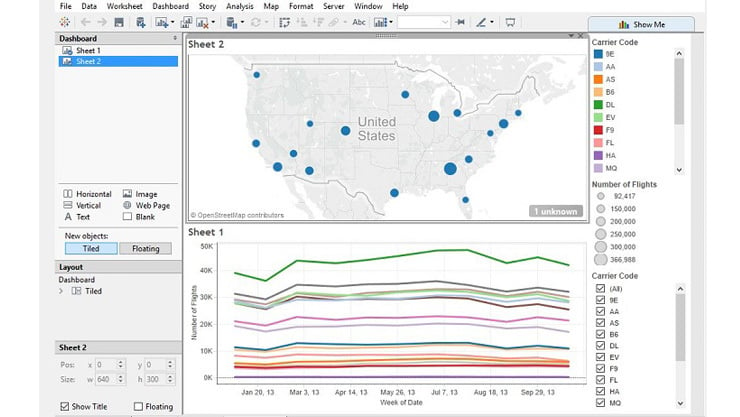
Tableau Desktop, a powerful data visualization tool, empowers users to transform raw data into insightful narratives. Its intuitive interface and comprehensive features make it a go-to solution for data exploration and analysis across diverse industries. Understanding its capabilities and how it interacts with other tools is crucial for maximizing its potential.
Comparison with Other Data Visualization Tools
Tableau Desktop stands out among its competitors due to its drag-and-drop interface, which simplifies the creation of complex visualizations. Its interactive dashboards and robust data blending capabilities provide an edge over other tools. While tools like Power BI offer a similar functionality, Tableau excels in specific areas, particularly when handling large datasets and complex calculations. Other visualization tools might lack the sophisticated analytics engine or the breadth of connectivity options Tableau offers.
Use Cases Favoring Tableau Desktop
Tableau Desktop is the preferred choice for numerous use cases. Its superior performance in handling large datasets makes it ideal for business intelligence (BI) reporting, particularly within organizations dealing with significant data volumes. The ability to create highly interactive dashboards allows for real-time monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs) and quick identification of trends. Further, Tableau excels in situations requiring advanced data blending and calculation capabilities, such as in financial modeling or scientific analysis.
Tableau Prep Builder’s Role in Data Preparation
Tableau Prep Builder is a critical component of the Tableau ecosystem. It facilitates the preparation of data before it’s imported into Tableau Desktop. Prep Builder provides a visual interface for cleaning, transforming, and shaping data, automating and streamlining the data preparation process. This significantly reduces the time and effort required to get data ready for analysis in Tableau Desktop. Its capabilities extend beyond basic data cleaning, encompassing tasks like data blending and joining from disparate sources.
Integration with Other Business Intelligence Tools
Tableau Desktop integrates seamlessly with other business intelligence (BI) tools, enhancing its value proposition. This integration allows for a unified view of data across different platforms. Connecting Tableau with enterprise data warehouses or data lakes provides access to a wider range of information. Tableau’s APIs enable connections with various business systems, facilitating the creation of comprehensive dashboards that combine data from multiple sources.
Comparison Table: Tableau Desktop vs. Alternative Tools
| Feature | Tableau Desktop | Power BI | Qlik Sense | Google Data Studio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | High, drag-and-drop interface | High, intuitive interface | Medium, requires some learning curve | High, straightforward interface |
| Data Handling (Large Datasets) | Excellent, optimized for large datasets | Good, capable of handling large datasets | Good, but might require optimization for extremely large datasets | Good, suitable for mid-sized datasets |
| Data Blending | Excellent, powerful data blending capabilities | Good, data blending features available | Excellent, strong data blending | Limited data blending capabilities |
| Customization | High, extensive customization options | High, robust customization features | High, offers advanced customization | Moderate, good customization options |
Ending Remarks

In conclusion, Tableau Desktop provides a powerful and versatile platform for data visualization and analysis. From connecting to diverse data sources to creating interactive dashboards, Tableau empowers users to extract valuable insights and make data-driven decisions. Mastering Tableau Desktop opens up a world of possibilities for anyone seeking to unlock the power of their data.