Navigating the world of project management software can be daunting, especially when choosing the right tool. This comprehensive guide demystifies the Microsoft Project download process, covering everything from version comparisons and download methods to installation, troubleshooting, and even exploring alternative solutions. Whether you’re a seasoned project manager or a newcomer to the field, this resource will equip you with the knowledge to successfully download and utilize Microsoft Project.
From understanding the nuances of different editions to mastering the installation process, this guide provides a detailed roadmap. We’ll dissect the system requirements, troubleshoot potential issues, and even offer alternative options for project management. This resource will empower you to make informed decisions and seamlessly integrate Microsoft Project into your workflow.
Different Versions and Editions
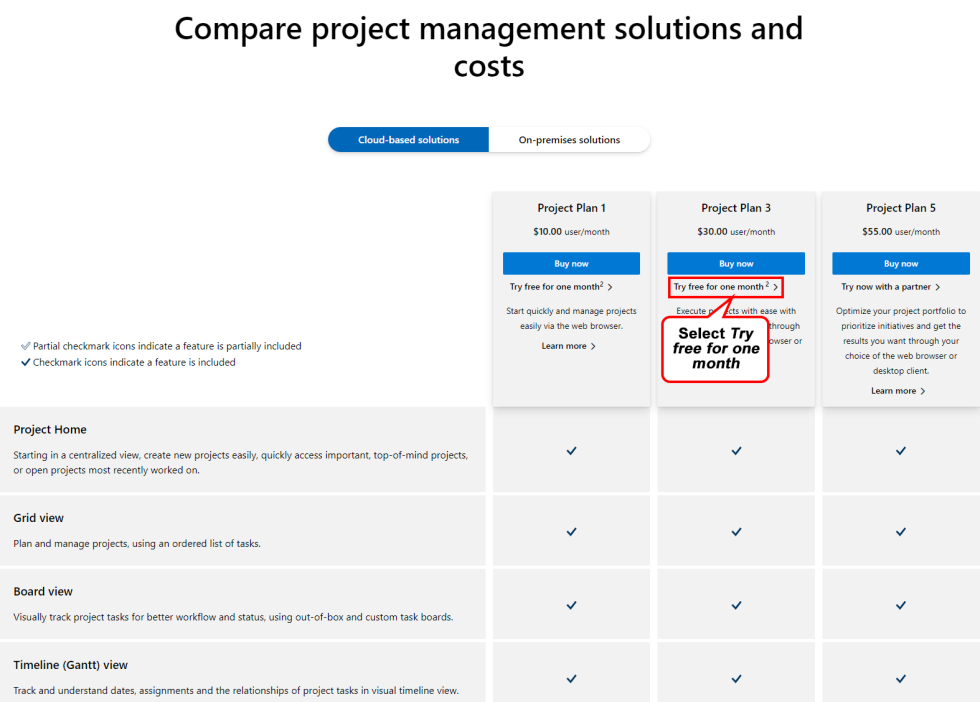
Microsoft Project offers various editions tailored to different project management needs and user groups. Understanding the distinctions between these editions is crucial for selecting the right software for your specific requirements. This section provides a comprehensive comparison of the available versions and editions.
Choosing the appropriate Microsoft Project edition hinges on factors like project complexity, team size, and the level of features required. Different editions cater to distinct user profiles, from individual project managers to large enterprise teams.
Available Editions Comparison
Various editions of Microsoft Project cater to diverse project management needs. This table summarizes the key features, pricing, and target user groups for each edition.
| Edition | Key Features | Pricing | Target User Group |
|---|---|---|---|
| Project Standard | Provides essential project management tools including task scheduling, resource allocation, and basic reporting. It’s suitable for smaller projects or individual users. | Affordable, typically a one-time purchase. | Individual project managers, small teams, and those with limited project management needs. |
| Project Professional | Offers advanced features like collaborative workspaces, detailed reporting, and more robust scheduling capabilities. It is geared towards teams and larger projects. | Higher price point than Project Standard, often requiring a subscription. | Teams and project managers involved in complex projects, requiring detailed collaboration and reporting. |
| Project Online | A cloud-based solution for large-scale projects. This edition facilitates seamless collaboration across teams, provides centralized project data, and leverages cloud-based storage. | Subscription-based, cost varies based on the number of users and features utilized. | Large organizations and teams requiring a centralized project management system with enhanced collaboration features. |
| Project for the Web | A web-based version of Project, accessible through a web browser. It’s designed for users who primarily work remotely or need a more accessible option. | Subscription-based, often bundled with other Microsoft 365 services. | Remote workers, occasional project managers, and those needing a flexible access method. |
Features and Functionalities
Project Standard provides core project management tools, like task scheduling and basic reporting. Project Professional builds on this foundation with enhanced features for collaboration and complex project management. Project Online, the cloud-based option, is suited for large-scale, distributed teams. Project for the Web offers a streamlined web-based experience.
Pricing and Licensing Models
Pricing models for each edition vary significantly. Project Standard often comes as a one-time purchase, whereas Project Professional and Project Online usually involve a subscription model, dependent on the number of users. Project for the Web is typically included in a Microsoft 365 subscription. Licensing considerations should be carefully evaluated when selecting an edition to ensure alignment with project needs and budgetary constraints.
Target User Groups
The target user groups for each edition differ considerably. Project Standard is appropriate for individual project managers or small teams. Project Professional caters to larger teams and more intricate projects. Project Online is ideal for large enterprises with dispersed teams, while Project for the Web suits those who work remotely or need web-based access. Understanding the target user group helps determine the best-suited edition for a specific project and organization.
Download Methods and Platforms
Microsoft Project offers various download methods catering to different user needs and operating systems. Understanding these options ensures a smooth installation process and optimal software performance. This section details the different avenues for acquiring Microsoft Project, including the steps involved and the compatibility across various platforms.
Available Download Methods
Different methods for downloading Microsoft Project exist, each with its own set of advantages and considerations. Direct downloads from the Microsoft website are a common approach. Alternatively, users can download through authorized resellers or distributors. The choice of method depends on the user’s preference and access to resources.
- Direct Download from Microsoft: This method typically involves navigating to the Microsoft website, identifying the desired Project version, and clicking a download button. The process usually involves selecting the appropriate file format and confirming the download location. Microsoft frequently updates download protocols, so users should consult the official website for the latest guidelines.
- Download through Resellers/Distributors: Some resellers or distributors may offer Microsoft Project for download. These methods often involve registering with the reseller, obtaining a download link, and following the specific instructions provided by the vendor. This method can be convenient for users who prefer a specific distribution channel or for bulk purchases.
Download Platforms
Microsoft Project is available for download across various platforms. The platform compatibility directly affects the user experience and functionality of the software. Choosing the correct platform is crucial to ensure seamless operation.
- Windows: Microsoft Project is primarily designed for Windows operating systems. Different versions of Windows support various editions of Project, and users should confirm compatibility before downloading. Windows 11, for example, offers enhanced compatibility with newer Project versions, while older Windows versions may require specific configurations to run the software.
- MacOS: Microsoft Project is also available for macOS. However, the macOS version might have limited features compared to the Windows counterpart. The download process for macOS mirrors that of Windows, involving navigating to the Microsoft website and selecting the appropriate macOS installer.
Operating System Comparison
The download processes for Microsoft Project vary slightly across operating systems. Understanding these differences can streamline the installation procedure.
- Windows Download: The download process on Windows typically involves clicking a download button, saving the file, and running the installer. Post-download, users may need to configure certain settings or grant administrator privileges for installation.
- macOS Download: The download process for macOS involves downloading a package file. Users then need to double-click the package to initiate the installation process, following the on-screen prompts.
System Requirements
System requirements for running Microsoft Project vary based on the specific edition and operating system. These requirements ensure the software operates efficiently and smoothly.
- Windows: Windows-based Project installations typically require a certain amount of RAM, hard disk space, and processor speed to operate optimally. Newer versions often have higher system requirements. Users should check the official Microsoft specifications for the specific Project version they are downloading.
- macOS: macOS requirements for Project are similar to Windows in that they depend on the specific version. Users should refer to the Microsoft support documentation to confirm compatibility and recommended system specifications.
Download Options Table
This table Artikels the download options, platform compatibility, and steps for installation.
| Download Option | Platform Compatibility | Installation Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Download from Microsoft | Windows, macOS | 1. Navigate to Microsoft website. 2. Select desired version. 3. Click download. 4. Run installer. |
| Reseller/Distributor Download | Windows, macOS (varies) | 1. Register with reseller/distributor. 2. Obtain download link. 3. Follow vendor instructions. 4. Run installer. |
Installation and Setup
Installing Microsoft Project involves a series of steps tailored to the chosen operating system and edition. A proper installation ensures the software functions optimally, with all features accessible. This section details the typical installation process, prerequisites, and setup procedures for various platforms.
Installation Process Overview
The installation process for Microsoft Project is generally straightforward, mirroring the procedures for other Microsoft applications. The process involves downloading the installation package, accepting license terms, and configuring the software. Successful completion depends on meeting the specified prerequisites and following the guided steps.
Prerequisites for Installation
Before initiating the installation process, ensure your system meets the minimum requirements. These prerequisites vary depending on the specific Project version and edition. Common prerequisites include sufficient hard disk space, adequate RAM, and a compatible processor. Specific operating system requirements should also be confirmed to guarantee a smooth installation.
Operating System-Specific Setup
Installation procedures slightly differ based on the operating system. This section provides a general guideline for common operating systems.
- Windows Installation: The installation process for Windows typically involves running the downloaded installer. This typically involves accepting the license agreement, choosing the installation location, and configuring specific options. The installer will guide you through the steps. Post-installation, configuration may be required to personalize the software’s interface.
- macOS Installation: Installation on macOS usually involves opening the downloaded package. Similar to Windows, the installer will guide you through the steps, including accepting the license agreement, selecting the installation location, and potentially configuring specific options. Post-installation, configuration may be necessary to match the user’s preferences.
- Linux Installation: Microsoft Project isn’t natively supported on Linux. The installation process for other software applications often involves using a package manager, which will vary based on the specific Linux distribution.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide (Windows Example)
This guide provides a step-by-step overview of the installation process for Windows.
- Download: Download the Microsoft Project installer from the official Microsoft website.
- Run Installer: Execute the downloaded installer file.
- License Agreement: Review and accept the software license agreement.
- Installation Location: Specify the installation location on your hard drive.
- Custom Options (Optional): Choose additional components to install, if desired.
- Installation Progress: Allow the installer to complete the installation process.
- Configuration: After installation, configure settings such as default data storage locations and display preferences. These are often accessible through the application’s settings menu.
- Verification: Launch the application to confirm successful installation and proper functionality.
Configuration Settings
Specific configuration settings will depend on the chosen edition and the user’s preferences. Common configuration settings include:
- User Interface Customization: Users can adjust the look and feel of the application by modifying the interface colors, fonts, and layout.
- Data Storage Locations: The location where project files are saved can be configured.
- Add-ins and Extensions: Users can install add-ins to extend the software’s capabilities, which are often managed through the application settings.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Encountering problems during the download, installation, or use of Microsoft Project can be frustrating. This section details common issues and provides solutions to help you resolve them quickly and efficiently. Understanding these issues and their resolutions will significantly enhance your experience with the software.
Often, problems stem from incompatibility issues, incorrect installation procedures, or insufficient system resources. Careful attention to detail and the steps Artikeld below can prevent and address many common problems.
Identifying Download Problems
Download failures can stem from various network or server-side issues. Slow internet connections, network congestion, or temporary server outages can all impede the download process. Verifying your internet connection and checking the download server’s status can often resolve these issues.
Resolving Installation Errors
Installation failures are frequently due to insufficient disk space, corrupted installation files, or conflicting applications. Ensure adequate disk space on the target drive and check the integrity of the downloaded installation file. Also, temporarily disable or uninstall any applications that might conflict with Microsoft Project’s installation process.
Common Error Messages and Resolutions
| Error Message | Solution |
|---|---|
| “Error 0x80070002” during installation | This error often indicates a problem with file access permissions. Ensure you have administrator privileges and try reinstalling the software. If the issue persists, run the installation as an administrator. |
| “Insufficient disk space” error | Insufficient space on the target drive is a frequent cause. Free up disk space on the drive where you’re installing Microsoft Project. |
| “The application could not start because the application’s configuration file is missing or corrupt” | Ensure the download was complete. If the download was successful, re-run the installer and verify if the issue persists. If the problem continues, repair or reinstall the software. |
| “Microsoft Project cannot be installed on this system” | This error frequently indicates incompatibility issues. Check the minimum system requirements for your desired version of Microsoft Project. Ensure that your system configuration meets these requirements. |
Troubleshooting Steps
- Verify your internet connection and download speed. A stable, high-speed connection is crucial for successful downloads.
- Check the integrity of the downloaded installation file using the file verification tools provided by your operating system. Corrupted files can lead to installation failures.
- Close all other applications and programs running on your computer. Running multiple applications simultaneously can sometimes cause conflicts during installation.
- Ensure you have enough free disk space on the target drive. Insufficient space is a common cause of installation errors.
- Run the installer as an administrator. This often grants the necessary permissions for a smooth installation process.
- Restart your computer after installation to ensure all changes take effect.
Resolving Incompatibility Issues
System incompatibility can prevent the installation or proper functioning of Microsoft Project. The minimum system requirements should be met for the intended version of the software to run properly. Ensure that your processor, RAM, and operating system meet the necessary specifications.
System Requirements and Compatibility
Proper system requirements are crucial for a smooth and efficient Microsoft Project experience. Meeting these specifications ensures optimal performance, avoiding compatibility issues, and preventing unexpected errors during project management tasks. Understanding the varying needs of different versions is key to selecting the right version for your specific hardware and software configuration.
Microsoft Project’s performance directly correlates with the system’s ability to handle the application’s resources. Different versions may demand varying amounts of processing power, memory, and storage space. Consequently, understanding these requirements is essential to avoid performance bottlenecks and ensure a seamless user experience. Compatibility issues can arise if the system’s configuration falls below the minimum standards.
Minimum and Recommended System Requirements
Meeting the minimum system requirements is the baseline for Project to function. However, for optimal performance and a responsive user experience, exceeding the minimum is strongly recommended. This is especially important for complex projects and large datasets.
| System Component | Minimum Requirement | Recommended Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Operating System | Windows 10 or later (64-bit) | Windows 11 (64-bit) |
| Processor | Intel Core i3 or AMD equivalent | Intel Core i5 or AMD equivalent |
| RAM | 8 GB | 16 GB or more |
| Storage Space | 4 GB | 10 GB or more |
| Display | 1024 x 768 resolution | 1920 x 1080 resolution |
Compatibility Across Versions
Different versions of Microsoft Project may have varying compatibility with specific hardware and software configurations. Older versions might not function optimally on newer hardware, or might not be compatible with specific software applications or extensions. Users should carefully review the system requirements for the specific version they intend to use.
Compatibility with Hardware and Software
Microsoft Project is designed to be compatible with a wide range of hardware and software configurations. However, the optimal performance depends on meeting the minimum and recommended requirements. For instance, a high-resolution display will provide a better visual experience for charts and diagrams. Furthermore, the use of specialized hardware like a graphics card with advanced capabilities might lead to improved visualization for complex project data.
Importance of Meeting System Requirements
Failure to meet the minimum system requirements can lead to a variety of issues, including:
- Application crashes or freezes.
- Slow performance or unresponsive application.
- Inability to open or load large projects.
- Display issues, including blurry text or graphics.
Meeting the system requirements ensures that the application operates reliably and efficiently. This is especially important for project managers who rely on the software to track deadlines, resources, and progress.
Compatibility Issues
Potential compatibility issues may arise due to:
- Outdated Operating Systems: Using older operating systems might lead to compatibility problems with newer versions of Microsoft Project.
- Incompatible Hardware: Certain hardware configurations may not meet the required processing power or memory capacity.
- Third-party Software Conflicts: Conflicts with other software applications or extensions can affect the operation of Microsoft Project.
Addressing these issues is essential to ensure a smooth user experience and avoid frustration during project management tasks.
Alternatives to Microsoft Project
Microsoft Project, while a powerful project management tool, isn’t the only option available. Numerous alternative software solutions cater to diverse project management needs and budgets. Understanding these alternatives can help project managers choose the best fit for their specific requirements.
Many alternatives offer similar features to Microsoft Project, but with differing strengths and weaknesses. Some focus on specific project types or offer unique functionalities. This section explores popular alternatives, comparing their capabilities and highlighting their advantages and disadvantages.
Alternative Project Management Software Options
Several project management software solutions provide comparable functionality to Microsoft Project. These include applications designed for specific industries, project sizes, or project types. Choosing the right alternative often depends on factors such as team size, project complexity, and budget.
- Asana: Asana is a popular project management tool known for its user-friendly interface and collaborative features. It excels in task management and communication, making it a strong choice for teams working on projects with multiple tasks and dependencies. Asana’s strength lies in its simplicity and ability to manage workflows effectively. However, its advanced features may be limited compared to dedicated project management software.
- Trello: Trello leverages a visual approach using boards, lists, and cards to represent project tasks and progress. This visual representation is particularly helpful for teams who prefer a more flexible and agile approach to project management. While Trello is excellent for visualizing tasks and workflows, its reporting and advanced scheduling capabilities may be less robust than those found in other alternatives.
- Jira: Jira, originally designed for software development, has evolved to become a versatile project management tool. It excels in managing complex projects with numerous tasks and dependencies, particularly in agile environments. Jira’s strengths include its robust issue tracking and agile methodologies support. However, its steeper learning curve might be a disadvantage for users unfamiliar with agile principles.
- Monday.com: Monday.com is a highly customizable platform that can be adapted to fit various project management needs. Its flexibility and wide range of features allow for intricate project setups. Monday.com excels in its adaptability and customization, but the extensive customization can lead to a more complex learning curve.
- ClickUp: ClickUp offers a centralized hub for managing tasks, projects, and communication. It’s highly configurable and supports various project management methodologies. ClickUp stands out for its flexibility and features. However, its complex interface may require more time to master compared to other alternatives.
Comparison of Features and Functionalities
A comparison of features and functionalities helps in evaluating alternative project management software options against Microsoft Project. This allows users to select the best-suited alternative.
| Software | Key Features | Pricing | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Project | Detailed scheduling, resource management, budgeting | Variable, depends on edition | Industry standard, robust features | Can be complex to learn, high cost |
| Asana | Task management, collaboration, workflow visualization | Variable, tiered plans | User-friendly, flexible | Limited advanced features |
| Trello | Visual project organization, Kanban boards | Variable, tiered plans | Intuitive, adaptable | Limited reporting, less sophisticated scheduling |
| Jira | Issue tracking, agile methodologies, task management | Variable, tiered plans | Powerful for complex projects | Steep learning curve, not ideal for simple projects |
| Monday.com | Customizable workflows, task management, reporting | Variable, tiered plans | Highly adaptable, flexible | Can be complex to configure, higher learning curve |
| ClickUp | Centralized hub for tasks, projects, communication | Variable, tiered plans | Highly configurable, various features | Complex interface, potentially steep learning curve |
Licensing and Activation

Microsoft Project licensing is crucial for legitimate use and ensures access to the software’s full functionality. Proper licensing not only adheres to the terms of service but also protects users from potential legal issues. Understanding the licensing model and activation process is essential for seamless operation.
Licensing Model Overview
Microsoft Project utilizes a subscription-based licensing model, primarily offering perpetual licenses for certain specific instances or cases. This model allows users to access the latest software features and updates through regular subscriptions. Different license types cater to varying project management needs and company sizes.
Activation Steps
The activation process typically involves using a valid product key, often included with the purchased license. This key is unique to each license and is used to authenticate the software. Following the activation steps ensures that the software is authorized and functional.
- Obtain the product key from the purchase confirmation or the product packaging.
- Open Microsoft Project.
- Locate the activation section within the software interface.
- Enter the product key and follow the on-screen prompts to complete the activation process.
Different License Types and Benefits
Various license types are available to meet the diverse needs of users and organizations.
| License Type | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Perpetual License | A one-time purchase allowing permanent access to the software. | Offers ownership and no ongoing subscription costs. |
| Subscription License | Regular payments for access to the software, typically with access to updates and support. | Provides continuous access to the latest features, updates, and technical support. |
| Volume Licensing | Bulk purchasing for organizations that use the software extensively. | Significant cost savings and tailored support. |
Importance of Legitimate Licensing
Utilizing legitimate licenses is crucial for legal compliance. It helps maintain the integrity of the software and its associated services. Employing illegitimate copies poses potential risks, including software malfunctions, loss of support, and legal ramifications. Violation of licensing agreements may result in penalties.
Common Licensing Questions
The following are common questions related to Microsoft Project licensing.
- How do I obtain a valid product key? A valid product key is typically provided at the time of purchase. Consult the purchase confirmation or documentation.
- What happens if my license expires? Renewal of the subscription or purchase of a new license is typically required to continue use.
- How can I contact support for licensing issues? Microsoft Project’s official support channels can provide assistance with licensing-related inquiries.
Final Thoughts

In conclusion, this guide provides a thorough overview of the Microsoft Project download experience. By comparing editions, detailing download methods, and outlining the installation process, we aim to empower users with the knowledge they need. Furthermore, we’ve addressed troubleshooting and system requirements, ensuring a smooth transition. Ultimately, this resource serves as a one-stop shop for all things Microsoft Project download, fostering successful project management endeavors.