HRIS systems are transforming how organizations manage their human resources, streamlining processes and enhancing efficiency. From automating payroll to enabling employee self-service, these systems offer a wealth of capabilities to optimize HR operations. This guide explores the core functionalities, benefits, implementation strategies, and security considerations of HRIS systems, providing a comprehensive overview for businesses seeking to leverage this technology.
This exploration delves into the intricacies of various HRIS deployment models, comparing cloud-based and on-premise solutions. We’ll also examine key features like employee self-service and performance management, highlighting their impact on productivity and overall organizational effectiveness.
Introduction to HRIS Systems
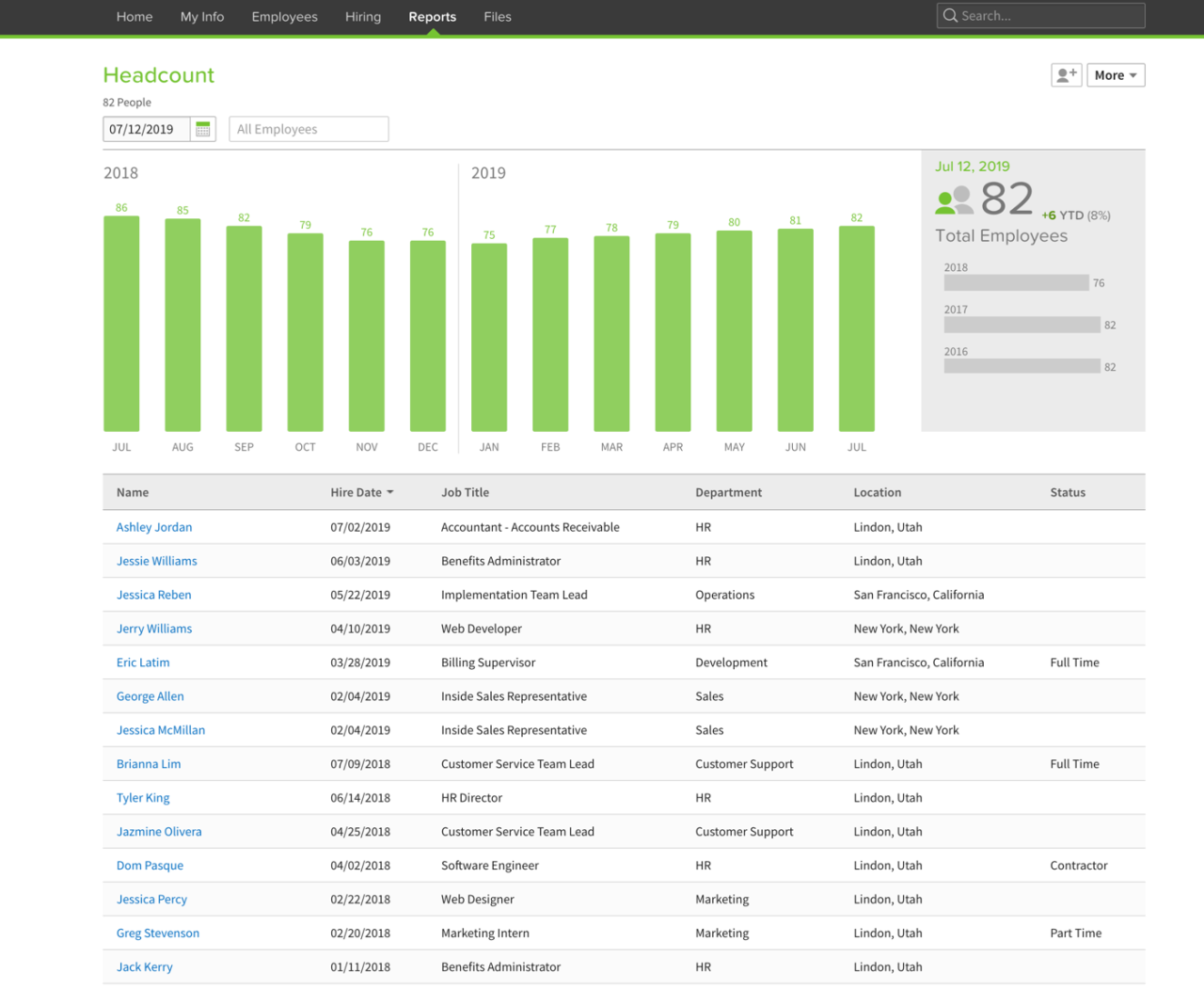
HRIS systems, or Human Resource Information Systems, are sophisticated software solutions designed to streamline and manage various aspects of human resources (HR) functions within an organization. They provide a centralized platform for storing, processing, and analyzing employee data, ultimately improving efficiency and decision-making in the HR department. These systems integrate various HR processes, offering a holistic view of the workforce and enabling better strategic HR planning.
These systems go beyond basic record-keeping, offering a comprehensive suite of tools to automate tasks, track performance, and manage compensation. They facilitate data-driven insights, enabling HR professionals to make informed decisions based on concrete evidence. Effective implementation of HRIS systems leads to a more organized and productive workforce, enabling organizations to achieve their strategic objectives more effectively.
Core Functionalities of a Typical HRIS System
HRIS systems encompass a range of functionalities that cater to various HR processes. These functionalities are critical for streamlining administrative tasks and improving overall efficiency. Key areas typically addressed include employee data management, payroll processing, benefits administration, performance management, and training and development.
- Employee Data Management: This includes maintaining accurate and comprehensive records of employee information, such as personal details, contact information, employment history, and compensation data. This feature enables easy retrieval and analysis of employee data, supporting various HR functions.
- Payroll Processing: Automated payroll processing reduces errors and ensures timely payments to employees. HRIS systems can handle complex calculations, deductions, and tax regulations, minimizing manual intervention and the risk of errors.
- Benefits Administration: HRIS systems provide a platform for managing employee benefits, including health insurance, retirement plans, and other perks. This feature allows for easy tracking of enrollment, contributions, and claims, providing transparency and efficiency in benefit administration.
- Performance Management: These systems facilitate performance evaluations, goal setting, and performance feedback. Data analysis from performance reviews helps identify areas for improvement and track employee progress.
- Training and Development: HRIS systems can be used to track employee training and development activities, including courses completed, certifications obtained, and skill enhancement programs. This feature enables organizations to manage their talent pool effectively and meet future needs.
Types of HRIS Systems
HRIS systems come in various forms, catering to different organizational needs and resources. The most common types include cloud-based and on-premises systems.
Deployment Models Comparison
Different deployment models offer varying levels of control, cost, and scalability. The choice depends on factors such as organizational size, budget, and technical expertise.
| Feature | Cloud-Based | On-Premise |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Software hosted on a remote server accessible via the internet. | Software installed and maintained on the organization’s own servers. |
| Maintenance | Vendor responsible for updates and maintenance. | Organization responsible for updates, maintenance, and security. |
| Scalability | Scalable to accommodate growth by increasing or decreasing resources as needed. | Scalability can be limited by the capacity of the organization’s infrastructure. |
Key Features and Benefits
Modern HRIS systems are transforming human resource management by streamlining processes, improving data accuracy, and fostering better employee engagement. These systems offer a comprehensive suite of features designed to optimize various HR functions, from recruitment to payroll. Understanding the key features and benefits of these systems is crucial for organizations seeking to enhance their HR operations and gain a competitive edge.
Key Features of Modern HRIS Systems
Modern HRIS systems are packed with robust features that cater to the diverse needs of organizations. These features automate and streamline tasks, leading to significant improvements in efficiency and productivity. Employee self-service portals, performance management tools, and integrated payroll processing are common components, all designed to improve the overall HR experience.
Benefits of Using HRIS Systems
HRIS systems offer a multitude of advantages for organizations. By automating repetitive tasks, HR professionals can focus on strategic initiatives, such as talent development and employee engagement. The improved accuracy of data management minimizes errors and allows for better informed decision-making. Increased efficiency leads to cost savings and frees up valuable resources for other essential activities.
How HRIS Systems Improve Efficiency and Productivity
HRIS systems significantly improve efficiency and productivity by automating numerous tasks. Automating processes like onboarding, payroll, and performance reviews frees up HR staff from time-consuming administrative duties, allowing them to concentrate on more strategic initiatives. Improved data accuracy reduces errors and ensures that HR decisions are based on reliable information. The ability to track employee data and performance metrics effectively facilitates data-driven decisions.
Benefits of Automating HR Tasks with HRIS Systems
Automating HR tasks with HRIS systems offers numerous benefits, including improved accuracy, reduced costs, and enhanced employee experience. Automating repetitive tasks like data entry, reduces the risk of errors and saves valuable time. The streamlined processes contribute to reduced administrative costs and increased efficiency. Employees benefit from self-service portals that allow them to access and manage their information, enhancing engagement.
Table of Key Features and Benefits
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Employee Self-Service | Provides employees with convenient access to their personal information, allowing them to update details, request leave, and view pay stubs. This improves employee satisfaction and reduces the workload on HR staff. |
| Performance Management | Facilitates the tracking and evaluation of employee performance. This enables organizations to identify high-performing employees, provide constructive feedback, and develop effective improvement plans. It also facilitates transparent performance reviews and objective assessments. |
| Payroll Processing | Automates the payroll process, ensuring accuracy and reducing the risk of errors. This feature also allows for timely payment of salaries and benefits, reducing administrative burden and improving employee morale. It also complies with legal requirements, minimizing the risk of penalties. |
HRIS System Implementation
Implementing an HRIS system is a significant undertaking requiring careful planning and execution. A well-implemented system can streamline HR processes, improve data accuracy, and enhance employee experience. Conversely, a poorly planned implementation can lead to significant disruption and wasted resources. This section details the critical steps involved in a successful HRIS implementation.
A comprehensive approach to HRIS implementation ensures that the system aligns with the organization’s strategic goals and operational needs. This involves a thorough understanding of the organization’s current HR processes, anticipated future needs, and the capabilities of the chosen HRIS system.
Steps Involved in HRIS Implementation
A structured approach to implementation minimizes disruptions and maximizes the system’s effectiveness. This involves a series of clearly defined steps, from initial planning to ongoing maintenance.
- Needs Assessment: Thoroughly evaluating current HR processes and identifying areas for improvement is crucial. This includes analyzing existing data management systems, identifying pain points in current processes, and defining future HR needs. This stage involves stakeholders from various departments to gain a holistic understanding of their requirements and the potential impact of the new system.
- Selection of HRIS System: A detailed evaluation of available HRIS systems is critical. This involves assessing features, functionality, scalability, vendor support, pricing, and integration capabilities. Careful consideration of future needs is essential. This step should involve a comparative analysis of different systems to identify the best fit for the organization’s specific requirements.
- System Configuration and Customization: Once the HRIS system is selected, configuring it to meet specific organizational needs is crucial. This includes defining data fields, setting up workflows, and configuring reporting mechanisms. Customizations should be tailored to the organization’s unique structure and workflows.
- Data Migration: Transferring existing HR data into the new system is a crucial and often complex phase. This requires careful planning to ensure data accuracy and integrity. This step should include a thorough data validation process to prevent errors and ensure data quality.
- Training and Change Management: Adequate training for HR and employee personnel on the new system is essential for successful adoption. A well-designed training program helps users understand the system’s functionality and how to utilize it effectively. This step also involves change management strategies to address potential resistance to change.
- Testing and Validation: Comprehensive testing of the system across various scenarios is crucial to identify and rectify potential issues before full implementation. Thorough testing should involve both functional and user acceptance testing. This ensures the system operates as expected and meets the defined requirements.
- Go-Live and Post-Implementation Support: A smooth transition to the new system is crucial. Post-implementation support, including ongoing maintenance, updates, and user assistance, is vital to ensure continued system functionality and user satisfaction.
Procedure for Choosing the Right HRIS System
A methodical approach to selection ensures the system aligns with organizational needs.
- Define Requirements: Clearly Artikel the specific needs of the organization, considering current HR processes and future growth plans. This includes identifying necessary features, functionalities, and integration points.
- Research and Evaluate Options: Conduct thorough research on available HRIS systems, considering factors such as pricing, vendor reputation, system features, and scalability. Seek reviews and testimonials from other organizations using similar systems.
- Develop a Shortlist: Narrow down the options to a manageable list of systems based on the defined requirements and evaluation criteria. This stage should involve a comprehensive comparison matrix to evaluate potential candidates.
- Pilot Testing: Implement a pilot program using the shortlisted systems to assess their suitability and functionality within the organizational context. This step provides a realistic evaluation of the system’s performance.
- Decision Making: Based on the pilot program results, make a well-informed decision regarding the most suitable HRIS system. This should involve considering both short-term and long-term needs.
HRIS System Implementation Checklist
A comprehensive checklist ensures all essential steps are addressed during implementation.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Needs Assessment | Identify current HR processes, future needs, and data sources. |
| System Selection | Evaluate and select the appropriate HRIS system. |
| Configuration | Configure the system to meet organizational requirements. |
| Data Migration | Migrate existing data to the new system. |
| Training | Provide training to HR and employees. |
| Testing | Conduct thorough testing and validation. |
| Go-Live | Execute a smooth transition to the new system. |
| Post-Implementation Support | Ensure ongoing system maintenance and support. |
Potential Challenges During HRIS System Implementation
Implementing an HRIS system can present various challenges.
- Data Migration Issues: Errors during data migration can lead to inaccuracies and inconsistencies, potentially impacting HR processes and reporting.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist adopting a new system, requiring effective change management strategies.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating the HRIS system with existing systems can be complex and time-consuming.
- Budgetary Constraints: Implementation costs may exceed the allocated budget, requiring adjustments to the plan.
- Project Timeline Overruns: Implementation timelines can be affected by unforeseen circumstances, leading to delays.
Step-by-Step Guide on Successful HRIS Implementation
A structured approach ensures a successful HRIS implementation.
- Planning and Assessment: Thoroughly analyze current HR processes, define system requirements, and establish a clear implementation timeline.
- Selection and Configuration: Research, evaluate, and select the most suitable HRIS system, configuring it to meet organizational needs.
- Data Migration and Validation: Migrate data, validate data integrity, and create a robust data quality plan.
- Training and Communication: Develop and implement comprehensive training programs, communicating the new system to all stakeholders.
- Testing and Validation: Thoroughly test the system, addressing identified issues before full implementation.
- Go-Live and Support: Execute a smooth go-live, providing ongoing support and maintenance to users.
HRIS System Integration
HR systems are no longer islands unto themselves. Modern businesses demand seamless integration between HR information systems and other crucial business applications. This interconnectedness streamlines workflows, enhances data accuracy, and empowers data-driven decision-making across the organization. Effective integration is critical for optimizing HR processes and maximizing the value of HRIS investments.
HRIS integration is not just a technical exercise; it’s a strategic imperative for businesses aiming to achieve greater operational efficiency and improve employee experience. A well-integrated system allows for a holistic view of employee data, reducing redundancies and errors inherent in isolated systems. This integrated approach unlocks the potential of HR data to drive strategic initiatives and support business objectives.
Importance of Integration
Integrating HRIS systems with other business applications is crucial for several reasons. It eliminates data silos, leading to a unified view of employee information. This holistic view empowers better decision-making and strategic planning. Automated workflows reduce manual data entry and errors, ensuring accuracy and timeliness in HR processes. Real-time access to data enhances responsiveness to business needs and facilitates faster decision-making. Furthermore, integration often unlocks advanced analytics capabilities, enabling businesses to derive valuable insights from employee data.
Examples of Successful Integrations
Several successful HRIS integrations exist. A common integration is with payroll systems, automating the transfer of employee data for salary calculations and deductions. This eliminates the need for manual data entry, significantly reducing errors and saving time. Another successful integration is with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. By integrating HRIS with ERP, businesses can track employee information alongside financial data, leading to more informed budgeting and resource allocation decisions. Integrating HRIS with talent management systems facilitates a streamlined recruitment process and supports employee performance management.
Potential Issues and Challenges During Integration
Integration projects often encounter challenges. Compatibility issues between different systems can be a significant hurdle. Data migration can be complex and time-consuming, requiring careful planning and execution to avoid data loss or inconsistencies. Lack of proper training for users on the integrated system can lead to low adoption rates and decreased efficiency. Security concerns and data privacy regulations are critical considerations that must be addressed.
Addressing Integration Issues Effectively
Addressing these challenges requires a well-defined integration strategy. Thorough planning, including system requirements analysis and data mapping, is critical. Using established best practices and employing expert consultants during the integration process can help mitigate potential issues. Comprehensive training programs for end-users are essential to ensure successful system adoption. Robust security measures and adherence to data privacy regulations are paramount throughout the integration process. Regular monitoring and maintenance are crucial for ensuring system stability and addressing any emerging issues.
Potential Integrations and Their Benefits
| System | Integration | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Payroll | HRIS | Automated data transfer, reduced errors, streamlined payroll processes, real-time data visibility, improved compliance. |
| ERP | HRIS | Unified view of employee and financial data, enhanced budgeting and resource allocation, improved reporting and analytics, streamlined workflows, optimized decision-making. |
| Talent Management System | HRIS | Streamlined recruitment processes, improved performance management, enhanced employee engagement, reduced administrative burden. |
| Applicant Tracking System (ATS) | HRIS | Automated candidate tracking, improved hiring efficiency, reduced administrative tasks, enhanced candidate experience. |
HRIS System Security and Privacy
HRIS systems hold sensitive employee data, making robust security and privacy measures paramount. Protecting this data is crucial not only for legal compliance but also for maintaining employee trust and organizational reputation. Data breaches can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. A secure HRIS system safeguards sensitive information, ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of HRIS data is essential for a multitude of reasons. A well-protected system fosters trust among employees, who are more likely to engage with HRIS functions and provide accurate information when they feel secure. This, in turn, leads to improved HR processes and decision-making.
Significance of Security and Data Privacy
HRIS systems store a wealth of sensitive personal data, including employee salaries, benefits information, medical records (in some cases), and performance evaluations. Compromising this data can have severe consequences, ranging from financial penalties to legal action. Protecting this data is vital to maintaining a positive and productive work environment.
Best Practices for Maintaining Data Security and Privacy
Implementing robust security protocols and adhering to privacy regulations are crucial for protecting sensitive employee data. This includes establishing strict access controls, encrypting data both in transit and at rest, and conducting regular security audits. Regular employee training on data security best practices also plays a vital role in preventing accidental breaches.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Various legal and regulatory frameworks govern the handling of employee data. These include GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), and other national and regional regulations. HRIS systems must comply with these regulations to avoid potential legal challenges and penalties. This often involves implementing mechanisms to ensure data subject rights, such as the right to access, rectification, and erasure.
Best Practices to Maintain HRIS System Security
Maintaining the security of an HRIS system is an ongoing process. Proactive measures are necessary to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. This includes regularly updating security software, employing strong passwords and multi-factor authentication, and implementing robust access controls. Monitoring system logs for suspicious activity is also critical.
Security Measures for HRIS Systems
Protecting sensitive data requires a multi-layered approach. A comprehensive set of security measures should be implemented to minimize vulnerabilities.
- Strong Access Controls: Implementing strict access controls is crucial to limit access to sensitive data. This involves using role-based access control (RBAC), which grants users only the permissions necessary for their job functions. Strong password policies and multi-factor authentication should also be enforced.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular security audits helps identify potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the system. These audits should assess the effectiveness of existing security measures and recommend improvements where necessary. Regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing are critical components of this process.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data both in transit and at rest is essential for protecting sensitive information. This ensures that even if unauthorized access is gained, the data remains unreadable without the appropriate decryption key. Encryption protocols should be implemented across all data storage and transfer mechanisms.
Future Trends in HRIS Systems
The landscape of HRIS systems is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the ever-changing needs of organizations. This evolution necessitates a forward-thinking approach to HRIS design, implementation, and maintenance to ensure continued effectiveness and relevance in the future. Predicting the precise trajectory of future HRIS trends is challenging, but identifying key emerging technologies and their potential impacts allows organizations to prepare for the future of HR.
Emerging trends in HRIS systems reflect a shift toward more integrated, user-friendly, and data-driven solutions. This evolution is driven by the increasing need for streamlined workflows, enhanced employee experiences, and actionable insights from data analysis. The future of HRIS systems will be shaped by the integration of emerging technologies, particularly artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and mobile technologies.
Emerging Technologies Shaping HRIS
The future of HRIS is intricately linked with emerging technologies, transforming the way HR functions operate and interact with employees. These technologies offer the potential to automate tasks, improve data analysis, and provide more personalized employee experiences.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are poised to revolutionize HRIS by automating repetitive tasks, enhancing data analysis, and personalizing employee experiences. AI-powered chatbots can handle employee inquiries, streamline onboarding processes, and provide 24/7 support. Machine learning algorithms can analyze employee data to identify patterns, predict employee turnover, and recommend targeted training programs. An example of this is the use of AI in recruitment to identify candidates with the most relevant skills and experience.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud-based HRIS solutions offer scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, enabling organizations to adapt to changing needs easily. The accessibility of cloud-based systems also facilitates remote work and collaboration, a trend that will continue to gain importance.
- Big Data Analytics: HRIS systems will increasingly leverage big data analytics to provide deeper insights into employee behavior, performance, and engagement. Organizations can use this data to optimize HR processes, personalize employee experiences, and improve decision-making.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain can enhance HRIS security by improving data integrity and transparency. It can also be used for managing employee records, verifying credentials, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
Innovative Features and Functionalities in Future HRIS
Future HRIS systems will incorporate innovative features to address evolving employee needs and streamline HR processes. These features will empower employees, enhance data-driven decision-making, and increase efficiency.
- Personalized Employee Experiences: Future HRIS systems will provide personalized experiences for employees by tailoring content and resources to individual needs and preferences. This personalization extends to onboarding, training, performance management, and benefits administration.
- Automated Processes: HRIS systems will increasingly automate tasks such as payroll processing, benefits administration, and performance reviews, freeing up HR professionals to focus on strategic initiatives.
- Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics will become more sophisticated, enabling HR to anticipate trends, identify potential issues, and proactively address them. Examples include predicting employee turnover, identifying high-potential employees, and optimizing recruitment strategies.
Impact of Mobile Technology on HRIS
Mobile technology is fundamentally altering the way employees interact with HRIS systems. Increased accessibility and user-friendliness empower employees to manage their own information, participate in HR processes, and receive updates in real-time.
- Improved Accessibility: Mobile access to HRIS systems allows employees to access their information and manage their HR needs anytime, anywhere. This is particularly beneficial for remote workers.
- Enhanced Employee Engagement: Mobile HRIS apps can provide employees with personalized updates, notifications, and resources, fostering a more engaged workforce.
- Streamlined HR Processes: Mobile applications can streamline various HR processes, such as expense reporting, time tracking, and performance feedback.
Summary
In conclusion, HRIS systems represent a powerful tool for modern organizations. By streamlining HR processes, improving data management, and fostering greater employee engagement, these systems contribute significantly to organizational success. This guide has provided a roadmap for understanding, implementing, and maximizing the benefits of HRIS, equipping businesses with the knowledge to navigate the complexities and leverage the potential of these systems.