IBM SPSS is a powerful statistical software package that’s widely used for analyzing data. It handles everything from basic descriptive statistics to complex modeling. This guide dives deep into the ins and outs of IBM SPSS, covering everything from data input to advanced techniques. Learn how to unlock the power of your data using IBM SPSS.
From importing diverse data formats to creating insightful visualizations, this guide will show you how to get the most out of IBM SPSS. You’ll gain hands-on experience with various statistical procedures, and discover how to generate professional reports. Prepare to transform your data analysis game!
Introduction to IBM SPSS
Hey there, data detectives! Ever wished you could unlock the secrets hidden within your data, like a treasure hunter unearthing buried gold? IBM SPSS is your trusty sidekick, a powerful statistical software package designed to help you do just that. It’s a toolbox packed with tools for analyzing everything from customer satisfaction surveys to scientific experiments, turning raw data into actionable insights.
SPSS isn’t just a program; it’s a gateway to understanding. It simplifies complex statistical procedures, letting you focus on the “why” behind the numbers, not just the “what.” Forget endless calculations – SPSS handles the heavy lifting, allowing you to concentrate on drawing meaningful conclusions from your research.
Core Functionalities of IBM SPSS
SPSS offers a wide range of statistical techniques, from basic descriptive statistics to advanced modeling. Imagine creating stunning visualizations of your data, revealing patterns and trends that might otherwise be invisible. You can perform hypothesis testing, correlations, regressions, and much more. It’s like having a super-powered microscope for your data!
Different Versions and Editions
IBM SPSS comes in various versions and editions, tailored to different needs and budgets. Think of it like choosing the right tool for the job. There’s the standard base version, ideal for beginners and those with straightforward analysis requirements. Then, there are specialized editions, like the advanced modeling edition, providing powerful tools for complex research. It’s a flexible solution for everyone, from students to seasoned researchers.
Key Features Differentiating SPSS
What makes SPSS stand out from the crowd? Its user-friendly interface is one key advantage. It’s designed to be intuitive, even for those new to statistical analysis. SPSS also boasts a comprehensive library of statistical procedures, ensuring you have the tools you need for virtually any analysis task. Furthermore, SPSS offers excellent data management capabilities, simplifying the process of organizing, cleaning, and transforming your data.
Comparison with Other Statistical Software
Want to see how SPSS stacks up against the competition? Here’s a quick comparison table:
| Feature | IBM SPSS | R | SAS | STATA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | Generally considered user-friendly | Steeper learning curve | Can be complex | Relatively intuitive |
| Price | Variable, depending on features and edition | Generally free and open-source | Expensive | Variable, depending on features |
| User Reviews | Positive reviews regarding ease of use and functionality | Positive reviews regarding flexibility and power | Positive reviews regarding advanced features and capabilities | Positive reviews regarding robustness and flexibility |
This table provides a basic overview. Keep in mind that specific features and pricing models can change over time. Choosing the right software often depends on your individual needs and budget. So, do your research and find the perfect tool for your data adventures!
Data Input and Management in SPSS
Hey there, data enthusiasts! SPSS is like a super-powered spreadsheet, but with way more analytical finesse. Getting your data into SPSS and making it presentable for analysis is key to unlocking its power. Let’s dive into the nitty-gritty of data input and management.
So, you’ve got your data – spreadsheets, databases, even text files. SPSS can handle them all. We’ll show you how to import various formats, clean up any messy data, and transform it into something SPSS can happily crunch. Think of it as data transformation – turning raw ingredients into a delicious statistical dish.
Importing Data Formats
Different data sources require different importing techniques. SPSS is surprisingly versatile, accepting data from various formats. You can import spreadsheets (like .xls, .xlsx), databases (like .csv, .txt), or even specific statistical packages’ outputs. This ensures your data, regardless of origin, is ready for SPSS’s analysis magic.
- Spreadsheets (.xls, .xlsx): SPSS handles Microsoft Excel files with ease. You simply select the file, specify the sheet you want to import, and voilà! Your spreadsheet data is now in SPSS.
- Databases (.csv, .txt): Comma-separated values (.csv) and text files (.txt) are common for database exports. SPSS can import these formats straightforwardly, making data from various database systems easily accessible.
- Other Formats: SPSS also supports importing data from other formats, including specific statistical packages’ output files. Check the SPSS manual for details on importing these files.
Data Cleaning and Preparation
Raw data is often messy. Missing values, inconsistent formats, or errors can skew your results. Data cleaning is a crucial step to ensure your analysis is accurate. Think of it as scrubbing your data before you cook with it.
- Handling Missing Values: Missing data points are a common issue. SPSS offers various methods to deal with them. You can delete cases with missing values, replace them with the mean, or use more sophisticated imputation techniques.
- Data Transformation: Sometimes, your data needs a little makeover. For example, you might need to convert a numerical variable to a categorical one or vice-versa. SPSS provides tools to perform these transformations effortlessly.
- Error Correction: Errors creep into datasets. SPSS can help you identify and correct these errors, ensuring accurate analysis.
Data Types Supported by SPSS
SPSS understands several data types, each playing a specific role in analysis. Knowing these types is essential for choosing the right statistical methods.
- Numeric: Represents numbers, such as ages, incomes, or scores.
- String: Represents text, like names, addresses, or descriptions. SPSS handles these strings for textual analysis.
- Date/Time: Represents dates and times, useful for tracking events or trends.
Common Data Issues and Solutions
Here’s a table outlining common data issues and how to address them in SPSS:
| Data Issue | Description | SPSS Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Missing Values | Data points are absent. | Delete cases, replace with mean/median, or use imputation techniques. |
| Inconsistent Formats | Different formats for the same variable. | Transform variables to a uniform format. |
| Errors | Typos or data entry mistakes. | Identify and correct errors using SPSS’s data editing tools. |
| Outliers | Extreme values that deviate significantly from other data points. | Identify and investigate outliers; decide on how to handle them based on the analysis’s purpose. |
Statistical Analysis Techniques in SPSS
Hey there, data detectives! SPSS is like a super-powered calculator for statisticians, allowing you to crunch numbers and uncover hidden patterns in your data. This section will explore the incredible statistical procedures SPSS offers, from basic to complex. Get ready to unlock the secrets your data holds!
Available Statistical Procedures in SPSS
SPSS boasts a vast array of statistical procedures, each designed for a specific type of analysis. From simple descriptive statistics to complex multivariate analyses, SPSS provides tools to answer virtually any research question. Let’s take a look at some key procedures.
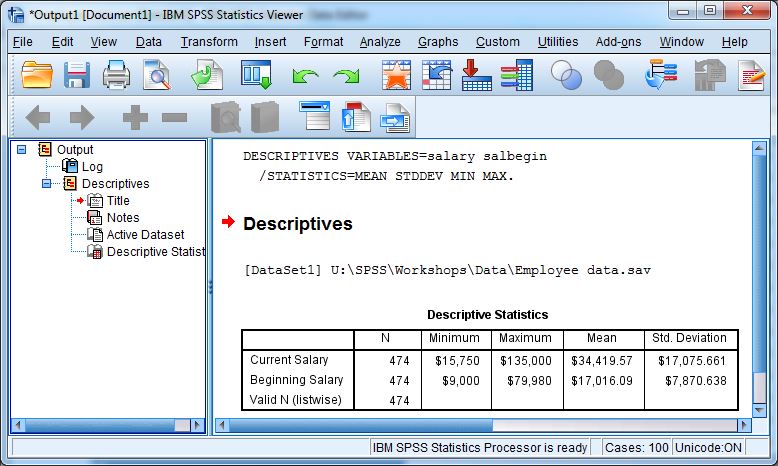
- Descriptive Statistics: These procedures provide summaries of your data, like calculating means, standard deviations, and frequencies. Imagine you’re trying to understand customer demographics. Descriptive statistics tell you the average age, the most common gender, and the distribution of income. This helps you understand the general characteristics of your customer base.
- Frequencies: Ideal for counting how many times each value appears in a variable. Perfect for market research where you want to see which product features are most popular. For example, if you’re launching a new phone, you can use frequencies to see which color is the most desired by potential customers.
- Crosstabs: This procedure examines the relationship between two or more categorical variables. Imagine you’re studying the association between a customer’s education level and their spending habits. Crosstabs will reveal if there’s a connection.
- T-tests: Used to compare the means of two groups. A classic example is comparing the average test scores of students in two different teaching methods.
- ANOVA (Analysis of Variance): This technique compares the means of three or more groups. Imagine comparing the effectiveness of three different advertising campaigns on sales.
- Regression: Used to model the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables. A common example is predicting house prices based on factors like size, location, and age.
- Correlation: This procedure assesses the strength and direction of the relationship between two variables. Perfect for understanding if there’s a link between exercise and weight loss.
Conducting a T-test in SPSS
T-tests are fundamental for comparing group means. Here’s a simplified example, focusing on the steps involved.
- Data Input: Ensure your data is properly entered into SPSS. This is crucial for accurate results. You should have a variable representing the group membership (e.g., treatment group vs. control group) and a variable representing the measured outcome (e.g., test scores).
- Choose Analyze > Compare Means > Independent-Samples T Test. Select the variables for testing.
- Define Groups: Specify which values in your grouping variable correspond to each group. For instance, if you have a variable called “Group” with values 1 for the treatment group and 2 for the control group, you need to define this.
- Analyze: Click “OK” to run the analysis. SPSS will provide you with the output, including the t-statistic, degrees of freedom, and p-value. The output will help you determine if there’s a statistically significant difference between the group means.
Statistical Tests and Their Uses
This table summarizes various statistical tests and their appropriate uses.
| Test | Use Case |
|---|---|
| T-test | Comparing means of two groups |
| ANOVA | Comparing means of three or more groups |
| Regression | Modeling the relationship between a dependent and one or more independent variables |
| Correlation | Assessing the relationship between two variables |
| Chi-Square | Testing for association between categorical variables |
Data Visualization in SPSS
Hey there, data detectives! Ever felt lost in a sea of numbers? SPSS is your trusty lifeboat, and data visualization is your compass. We’re about to unlock the secrets of transforming raw data into compelling visuals that’ll make your boss (and your colleagues) say “Wow!” Let’s dive in!
SPSS provides a treasure trove of charting options, transforming your data from cryptic tables into crystal-clear graphs. Visualizations are key for spotting trends, patterns, and outliers – things that might be hidden in a spreadsheet. They also help tell a story with your data, making it easier to communicate insights to anyone, from colleagues to clients. Imagine your analysis going viral – because your graphs are just that compelling!
Creating Charts and Graphs in SPSS
SPSS offers a dazzling array of charts, from simple bar graphs to complex 3D scatter plots. The process is straightforward; just choose the type of graph that best represents your data and SPSS will handle the rest. Think of it as having a friendly graphic designer right within your software! You simply select the variables, and SPSS does the heavy lifting.
Creating a Scatter Plot in SPSS
Let’s map out a scatter plot. This is a powerful tool for visualizing the relationship between two variables. Imagine plotting sales figures against advertising spend. A scatter plot will reveal whether increased spending correlates with higher sales. The steps are usually as follows:
- Select “Graphs” from the menu bar.
- Choose “Scatter/Dot” and then “Simple Scatter.” This will bring up a dialog box.
- Select the variable you want to use for the x-axis (e.g., advertising spend) and put it in the “X-axis” box. Select the variable you want to use for the y-axis (e.g., sales) and put it in the “Y-axis” box.
- Click “OK” and SPSS will generate the scatter plot.
Importance of Effective Data Visualization in SPSS
Clear, concise visuals are crucial in any data analysis. They communicate complex findings quickly and effectively. Imagine presenting a report to a client – you want to make your point in a way that is not only accurate but also engaging. Data visualization allows you to do precisely that. Well-designed graphs can reveal patterns, highlight outliers, and showcase trends that might otherwise go unnoticed in tables of numbers. Your data, your story, your visualization!
Different Types of Graphs and Their Uses
Understanding which graph to use is essential for effective communication. The right graph can turn a dry dataset into a captivating narrative.
| Graph Type | Description | Appropriate Variables | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bar Graph | Compares categorical data | Categorical variable and a numerical variable | Show the difference in sales between different regions. |
| Scatter Plot | Shows the relationship between two numerical variables | Two numerical variables | Determine if there’s a correlation between advertising and sales. |
| Histogram | Displays the distribution of a single numerical variable | One numerical variable | Visualize the frequency distribution of customer ages. |
| Pie Chart | Shows proportions of a whole | Categorical variable and a numerical variable (for the proportion) | Display the market share of different product categories. |
Reporting and Output in SPSS
Alright, folks, we’ve crunched the numbers, now let’s present them in a way that’s not just impressive, but *understandable*. Reporting in SPSS is about turning your statistical insights into compelling narratives. Think polished presentations, insightful reports, and data visualizations that wow your audience. Let’s dive in!
SPSS gives you the power to customize reports and outputs beyond basic tables and charts. You can tailor the look and feel, adding headers, footers, and even changing the font styles to make your reports stand out. The goal is to create reports that are both informative and visually appealing. Think professional, not just academic.
Customizing Reports and Outputs
You can adjust the appearance of tables and graphs to suit your needs. From changing colors and fonts to adding titles and legends, you’re in charge of making your output visually engaging. Formatting is key to making your reports look professional. Remember, a well-designed report can significantly improve the impact of your analysis. Think about your target audience and adjust the presentation accordingly. Too much fluff and it’s just a mess.
Creating Professional Reports
To make reports stand out, you can use different layouts and combine various charts, tables, and descriptive text. This provides a holistic view of the data and lets you showcase your insights in a compelling way. Think of it as telling a story, with data as your characters and visualizations as your plot devices. This isn’t just about numbers; it’s about communication. Combine your SPSS findings with insightful commentary to create a professional report.
Exporting Data and Outputs
SPSS lets you export your data and outputs in various formats, such as .CSV, .PDF, and .XLSX. This is crucial for sharing your work with others, incorporating it into presentations, or using it in other analysis tools. Exporting lets you save the results for later use or for distribution to stakeholders. It’s like having a digital toolkit for your data.
Different Report Formats and Their Uses
- Summary Reports: These reports condense large datasets into key findings. Perfect for high-level overviews and executive summaries. They highlight the most important aspects of the analysis, making them ideal for stakeholders who don’t need the full detail. Essentially, you’re giving them the ‘big picture’ in a concise format.
- Detailed Reports: These provide a comprehensive breakdown of the data, including all calculations and tables. Ideal for in-depth analysis and internal reports. You’re diving deep into the data, letting the details speak for themselves.
- Interactive Reports: These reports allow users to explore data interactively, for instance, through embedded dashboards. These reports are designed for user exploration, and are perfect for presentations or allowing users to make their own conclusions. Think of them as dynamic, data-driven presentations.
| Report Format | Suitable Use |
|---|---|
| Summary Reports | High-level overviews, executive summaries |
| Detailed Reports | In-depth analysis, internal reports |
| Interactive Reports | Data exploration, presentations |
Advanced Features and Applications
Alright, buckle up buttercups! We’re diving into the deep end of SPSS – the advanced features that’ll turn you from a data dabbler to a data detective. Forget basic bar charts; we’re talking sophisticated statistical modeling and real-world problem-solving. Get ready to unleash the power within SPSS!
SPSS isn’t just for counting jellybeans; it’s a powerhouse for analyzing complex data. From predicting market trends to understanding customer behavior, SPSS can help you uncover hidden patterns and make data-driven decisions. Let’s explore the fascinating world of advanced statistical modeling and see how SPSS can help us in various fields.
Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is a fundamental tool for understanding the relationship between variables. It helps us predict the value of one variable based on the values of others. Imagine trying to predict house prices – you’d use regression analysis to see how factors like size, location, and amenities influence the price. SPSS makes this complex process straightforward and efficient.
- Multiple Regression: This technique allows you to consider multiple independent variables simultaneously. For instance, you could analyze how advertising spend (TV, radio, print), product features, and competitor actions affect sales. This is crucial in business analytics for developing accurate forecasting models.
- Logistic Regression: Ideal for analyzing categorical dependent variables, logistic regression is essential in market research. For example, predicting customer churn or determining the likelihood of a customer purchasing a product based on their demographics and purchasing history.
- Polynomial Regression: When the relationship between variables isn’t linear, polynomial regression models can capture the curve. Imagine predicting the growth of a company’s revenue over time – a polynomial model might be more accurate than a simple linear model.
Advanced Statistical Modeling
Beyond regression, SPSS offers powerful tools for more intricate analyses. Time series analysis, for example, allows us to examine trends and patterns in data over time, enabling us to predict future values. This is extremely helpful in finance for forecasting stock prices or predicting sales patterns.
- Time Series Analysis: Imagine tracking sales figures for a product over the past year. SPSS can help you identify seasonal patterns, trends, and cycles to forecast future sales. This is essential for businesses to anticipate demand and manage inventory effectively.
- Factor Analysis: This method helps uncover underlying factors that explain observed correlations among variables. For instance, in marketing research, it can identify key consumer segments based on their attitudes and behaviors. This is vital for tailoring marketing campaigns and optimizing product development.
- Survival Analysis: This technique is perfect for studying time-to-event data. In medical research, it can model the time it takes for patients to experience a particular event, like disease recurrence or death. This helps in determining treatment efficacy and predicting outcomes.
SPSS in Business Analytics
SPSS is a valuable asset in business analytics, empowering businesses to make data-driven decisions. Analyzing customer data to identify profitable segments, predicting future sales trends, or optimizing pricing strategies are just a few examples of its applications.
- Customer Segmentation: SPSS helps businesses understand their customers better. By analyzing data on demographics, purchase history, and website behavior, companies can identify distinct customer segments and tailor marketing campaigns to each group. This improves customer retention and increases revenue.
- Sales Forecasting: Using time series analysis, SPSS can help businesses predict future sales based on historical data. This allows them to optimize inventory levels, manage production capacity, and make strategic business decisions. This forecasting ability can be a game-changer for business operations.
Conducting Multiple Regression Analysis in SPSS
Let’s illustrate how to perform a multiple regression analysis in SPSS using a real-world example.
- Problem: Predict house prices based on size, location, and number of bedrooms.
- Data: Gather data on house prices, size, location, and number of bedrooms for a sample of houses.
- Steps:
- Import data into SPSS.
- Define the dependent variable (house price) and independent variables (size, location, bedrooms).
- Select “Regression” from the menu.
- Choose “Linear” from the regression options.
- Move the dependent variable to the “Dependent” box and the independent variables to the “Independent(s)” box.
- Click “OK” to run the analysis.
Learning Resources and Support
Feeling lost in the SPSS jungle? Fear not, intrepid data explorers! We’ve got you covered with a wealth of resources to help you master this powerful statistical software. From online courses to supportive communities, we’ll equip you with the tools to conquer any data analysis challenge.
Knowing where to start can be daunting, but with the right guidance, SPSS becomes a friend, not a foe. We’ll highlight excellent learning platforms and insightful communities to help you on your data analysis journey.
Recommended Learning Resources
Learning SPSS effectively involves more than just reading; it requires hands-on practice and a supportive network. Here are some top-notch resources to fuel your SPSS adventure:
- IBM SPSS Statistics Documentation: This comprehensive guide provides in-depth explanations of every feature, function, and command within SPSS. It’s like having a personal SPSS encyclopedia at your fingertips. The official documentation is your ultimate reference for understanding the nuances of the software.
- Online Tutorials and Courses: Numerous websites offer free or paid tutorials specifically designed to teach SPSS. These range from introductory courses to advanced techniques. Sites like YouTube and dedicated learning platforms are great places to find these tutorials. You can find step-by-step instructions and practical examples to reinforce your learning.
- Books: Books dedicated to SPSS offer a structured approach to learning the software. They provide theoretical background, practical examples, and exercises. They are a fantastic resource for in-depth knowledge, particularly for those who prefer a more structured learning experience.
Online Communities and Forums
Connecting with other SPSS users is crucial for seeking help, sharing experiences, and getting feedback. Online communities provide a space to ask questions, receive assistance, and learn from others’ successes and challenges.
- Online Forums: Numerous online forums dedicated to statistical software, including SPSS, exist. These platforms allow you to connect with experienced users, pose questions, and receive tailored support. You can gain valuable insights from fellow users’ experiences, especially in addressing specific problems or exploring advanced techniques.
- Social Media Groups: Social media platforms like LinkedIn and Facebook have dedicated groups for SPSS users. These groups provide a space for sharing tips, asking questions, and staying up-to-date on the latest advancements in SPSS. You can connect with professionals and gain insights into real-world applications.
SPSS Tutorials and Documentation
Having access to well-structured tutorials and easily digestible documentation is key to mastering SPSS. These resources offer practical guidance and illustrate how to apply various SPSS functions.
- Tutorials: Tutorials serve as your guide in SPSS. They walk you through different techniques and help you apply the tools. These can be interactive, offering hands-on practice. Tutorials are your allies in understanding the software’s practical applications.
- Documentation: The documentation from IBM provides a thorough understanding of SPSS. It covers everything from the basic functions to the advanced techniques. It’s an invaluable reference for every step of your journey.
Table of Online Learning Resources
This table provides a concise overview of various online courses, tutorials, and communities related to IBM SPSS.
| Resource Type | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Online Courses | Coursera, edX | Offer structured learning paths, often with certificates. |
| Tutorials | YouTube Channels (e.g., SPSS Tutorials) | Provide step-by-step instructions and practical examples. |
| Communities | SPSS discussion forums on Reddit, Stack Overflow | Allow interaction with other users, asking questions, and sharing experiences. |
Troubleshooting and Common Errors
Ah, SPSS, the statistical wizard. But even wizards can stumble! Sometimes, you encounter little hiccups, errors that can make your analysis go haywire. Fear not, brave data analyst! This section will equip you to identify and conquer those pesky errors, turning them from frustrating roadblocks into stepping stones.
Data analysis is like a delicate dance; one misstep can throw everything off. Understanding common pitfalls and how to fix them is key to achieving reliable results. We’ll explore the most frequent SPSS errors, showing you the precise steps to correct them. Get ready to master the art of SPSS troubleshooting!
Identifying Common SPSS Errors
Troubleshooting begins with recognition. Knowing the symptoms of a problem is half the battle. SPSS errors often manifest as cryptic error messages, unhelpful warnings, or unexpected output. Understanding the specific error message is crucial to finding the correct solution. A good rule of thumb is to copy and paste the entire error message into a search engine—you might find an existing solution or similar issue already discussed online.
Troubleshooting Data Import Issues
Data import is a common source of errors. Mismatched file formats, incorrect delimiters, missing headers, or inconsistencies in data types can all lead to problems. SPSS needs data in a specific format, and any deviation can cause it to choke. Let’s dissect how to address these import issues.
- Incorrect File Format: If SPSS can’t recognize the file type (e.g., .txt instead of .csv), you need to ensure the correct file type is selected during the import process. SPSS is like a picky eater; it needs the right kind of data.
- Incorrect Delimiters: Commas, tabs, or semicolons separate data in text files. If SPSS misinterprets these separators, the data will be jumbled. Make sure you choose the correct delimiter in the import wizard.
- Missing Headers: If the data file lacks a header row with column names, SPSS might assign default names. This could cause problems when analyzing the data later. Ensure that the file has a clear header row to let SPSS know what each column represents.
- Inconsistent Data Types: Mixing data types (e.g., numbers in text columns) can lead to import errors. SPSS needs to know whether a column contains numbers, dates, or text. Double-check that the data type of each column in the file matches the expected data type in SPSS.
Common SPSS Errors and Solutions
This table Artikels some frequent SPSS errors and their solutions. Don’t be afraid to seek help online; there are numerous forums and communities dedicated to SPSS.
| Error Message/Symptom | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| “File not found” | Incorrect file path or file deleted | Verify the file path is correct, check if the file exists, and try again. |
| “Invalid data type” | Mixed data types in a column | Check each column’s data type; convert or fix the problematic entries. |
| “Insufficient memory” | Large dataset exceeds available memory | Reduce the dataset size, use appropriate data management techniques, or increase memory allocation. |
| “Syntax error” | Incorrect syntax in command | Carefully review the command syntax for errors. Use the SPSS syntax editor for complex commands. |
| “Missing values” | Missing data points in the dataset | Identify the missing data, decide how to handle them (e.g., imputation). |
Conclusion
This comprehensive overview of IBM SPSS provides a solid foundation for anyone looking to leverage its capabilities. We’ve covered everything from basic data manipulation to advanced techniques like regression analysis, offering a complete picture of this powerful tool. Hopefully, you now have a clearer understanding of how IBM SPSS can help you extract valuable insights from your data.





