Navigating the modern world of transactions has become increasingly seamless, with pay by phone apps leading the charge. These applications have revolutionized how we handle everyday payments, offering a convenient and often secure alternative to traditional methods. From quick in-store purchases to online transactions, pay by phone apps are reshaping the landscape of financial services.
This comprehensive exploration delves into the intricacies of pay by phone apps, examining their functionality, security protocols, user experience, market trends, and integration with other services. We’ll also analyze their business models and the revenue streams they utilize.
Overview of Pay by Phone Apps
Pay-by-phone applications are revolutionizing the way we make payments, offering a convenient and secure alternative to traditional methods. These apps simplify transactions, eliminating the need for physical cash or cards in many situations. They leverage mobile technology to provide users with a streamlined and accessible payment platform.
These apps are rapidly gaining popularity due to their ease of use and the diverse range of transactions they support. Their integration into daily life streamlines financial interactions, making them an integral part of the modern financial landscape.
Types of Transactions Supported
Pay-by-phone apps facilitate a wide array of transactions. Beyond simple retail purchases, they often support utility bill payments, transportation fares, and even peer-to-peer transfers. This expanded functionality caters to a broader spectrum of financial needs, making these applications more versatile and useful. This adaptability distinguishes them from traditional payment methods.
User Journey for a Pay by Phone Transaction
The typical user journey involves initiating the payment through the app. The user selects the desired merchant or recipient, enters the payment amount, and confirms the transaction using their chosen authentication method. This process, from start to finish, is generally quick and straightforward. Modern user interfaces enhance the overall experience.
Payment Methods Integrated
Most pay-by-phone apps support various payment methods, including linked bank accounts, credit/debit cards, and sometimes even stored digital wallets. The flexibility of these options caters to diverse user preferences and financial situations. This variety is a significant advantage, offering users more control over their transactions.
Comparison of Pay by Phone Apps
| App Name | Features | Cost | User Reviews |
|---|---|---|---|
| App A | Supports peer-to-peer transfers, utility bill payments, and in-app purchases; offers a rewards program; integrated with popular e-commerce platforms; basic international transaction support. | Free core service; small transaction fees for international transfers and some utility bill payments. | Generally positive, highlighting ease of use and speed of transactions; some users report occasional technical glitches. |
| App B | Wide range of supported merchants, including local businesses; offers loyalty programs tied to partner stores; advanced security features, including biometric authentication; robust international payment options. | Free basic service; tiered pricing for enhanced features like priority customer support. | Strong user base; positive reviews regarding customer support and transaction security; some users find the tiered pricing structure slightly confusing. |
| App C | Focuses on local commerce; integrated with various transportation networks; provides detailed transaction history and budgeting tools; offers real-time transaction tracking and notifications. | Free; some additional fees for premium features like personalized financial advice. | High user ratings; praised for its user-friendly interface and helpful budgeting tools; some users suggest a wider range of supported merchants. |
Security and Privacy Considerations

Pay-by-phone apps have become increasingly popular, offering convenience and speed for various transactions. However, the security and privacy of user data are paramount concerns. These apps handle sensitive financial information, and robust security measures are crucial to build user trust and maintain financial stability.
Modern payment systems are designed with multiple layers of security to mitigate risks. These measures aim to protect user data from unauthorized access and misuse. Furthermore, transparency in data handling practices is essential for user confidence.
Security Measures Employed by Pay-by-Phone Apps
Various security measures are implemented in pay-by-phone apps to safeguard user data and transactions. These include encryption, two-factor authentication, and regular security audits. The specific security protocols vary across different apps.
Potential Privacy Concerns
Privacy concerns regarding pay-by-phone apps center on data collection and usage. Users need to understand how their data is collected, stored, and shared with third parties. Transparency in data usage policies is vital to maintaining user trust.
Data Protection and Utilization
Pay-by-phone apps employ various methods to protect user data. These include encryption of sensitive information during transmission and storage in secure databases. Data is often anonymized to the extent possible, and access is limited to authorized personnel. Furthermore, these apps must comply with relevant data protection regulations.
Comparison of Security Protocols Across Different Apps
Security protocols differ significantly across various pay-by-phone apps. Some apps might prioritize multi-factor authentication, while others might emphasize encryption protocols. The level of security varies depending on the app’s design, technological infrastructure, and adherence to industry best practices. Comparing these security measures allows users to choose apps with robust security protocols.
Security Measures for Different Transaction Types
| Transaction Type | Security Measures | Data Protection |
|---|---|---|
| In-store payment | Typically utilizes secure payment gateways, encryption during data transmission, and point-of-sale (POS) terminal security. The POS terminal itself might employ tokenization or other security measures to further protect the sensitive data. | Payment information is often tokenized, meaning the actual credit card number isn’t directly processed. The token is used for the transaction, safeguarding the original sensitive data. |
| Online payment | Employs robust encryption protocols, such as TLS/SSL, to protect data transmitted over the internet. Secure servers and strong authentication methods (like passwords and multi-factor authentication) are essential. | Data is encrypted during transmission and stored securely on the app’s servers. Access controls and regular security audits are implemented to prevent unauthorized access. |
| Peer-to-peer (P2P) payment | Security measures in P2P transactions often include end-to-end encryption, limiting the ability of the app itself to access sensitive information. Secure communication channels and user authentication are crucial. | User data is protected through end-to-end encryption, ensuring only the sender and receiver have access to the transaction details. Data stored on the app’s servers might be limited to metadata, such as transaction timestamps. |
User Experience and Interface Design
Pay-by-phone applications are increasingly important for seamless and convenient transactions. A user-friendly interface is crucial for adoption and satisfaction. This section delves into the design principles, usability considerations, and user feedback associated with these apps.
Typical User Interface
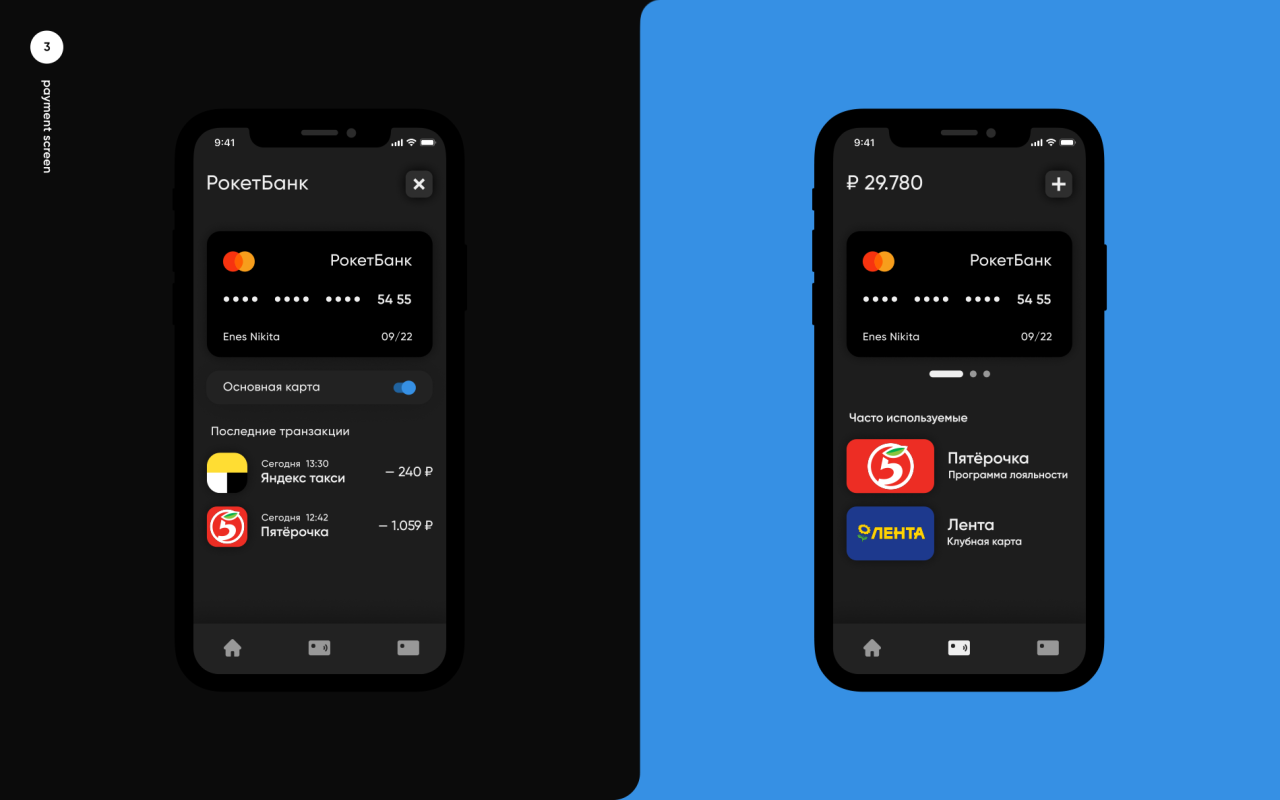
The typical pay-by-phone app interface usually features a clean and intuitive design. Key elements often include a prominent payment button, a clear display of transaction details (amount, merchant, date), and options for managing payment methods and account information. Users are presented with a straightforward process for selecting payment methods, inputting amounts, and confirming transactions.
Design Principles
Several design principles are employed to create user-friendly pay-by-phone interfaces. These include simplicity, consistency, and clear visual hierarchy. Simplicity aims to reduce cognitive load by avoiding unnecessary complexity. Consistency ensures that elements and actions function predictably across the app. A clear visual hierarchy guides users through the interface, drawing attention to important information and actions.
Usability and Accessibility
Usability and accessibility are paramount in pay-by-phone app design. Usability focuses on making the app easy to learn and use, even for infrequent users. Accessibility ensures that the app is usable by people with disabilities, adhering to accessibility guidelines. Clear and concise instructions, intuitive navigation, and support for various input methods (e.g., voice input for visually impaired users) are vital.
User Feedback
User feedback on pay-by-phone apps varies, with some apps receiving positive feedback for their intuitive interfaces and smooth transaction processes. Other apps may receive criticism for confusing navigation or slow loading times. Positive feedback often highlights ease of use, quick transactions, and a secure experience. Negative feedback often focuses on usability issues, such as unclear instructions or difficult navigation. Specific user feedback is often collected through app reviews and user forums.
Navigation and Interaction
Navigation within a pay-by-phone app typically involves a simple structure. Users often navigate between screens using buttons, taps, or swipes. The interface typically displays relevant information based on the user’s current actions. A key interaction is the confirmation step, where users review transaction details before completing the payment.
Comparison of User Interfaces
| App Name | Interface Design | User Experience |
|---|---|---|
| App A | Clean, modern design with clear visual hierarchy. Uses a consistent color scheme and typography. | Generally positive user experience. Fast transaction processing and easy navigation. |
| App B | Slightly cluttered interface with inconsistent design elements. Uses a variety of colors and fonts. | Mixed user experience. Some users found the interface confusing, while others found it acceptable. |
| App C | Simple and straightforward design with a focus on accessibility. Clear labels and concise instructions. | Highly positive user experience, especially among users with disabilities. |
Market Trends and Future Prospects
The pay-by-phone app market is experiencing rapid growth, fueled by increasing mobile payment adoption and the need for seamless, secure transactions. This surge in popularity is driven by user convenience, coupled with a shift towards digital-first lifestyles. The future of this market hinges on continued innovation and the ability to address evolving user needs and security concerns.
The market is characterized by dynamic competition, as established players and new entrants vie for market share. This competitive landscape necessitates a focus on user experience, security enhancements, and innovative features to stand out. Emerging technologies are playing a significant role in shaping the future of pay-by-phone apps.
Current Market Trends
The current pay-by-phone app market is dominated by a few major players, but smaller, niche apps are also gaining traction. This competition fosters innovation and encourages the development of specialized features catering to specific user needs and industry segments. Integration with existing loyalty programs and rewards systems is also a growing trend.
Growth and Adoption Rates
Data suggests significant growth in the adoption of pay-by-phone apps. The global mobile payment market is experiencing double-digit growth, driven by factors such as rising smartphone penetration, increasing consumer confidence in digital transactions, and government initiatives promoting digital payments. This trend is anticipated to continue in the foreseeable future.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are influencing the development of more sophisticated and user-friendly pay-by-phone apps. AI can personalize user experiences and improve fraud detection, while machine learning can predict user behavior and enhance transaction security. For example, AI-powered chatbots can assist users with resolving payment issues, streamlining the customer service process.
Innovative Features
Many pay-by-phone apps are incorporating innovative features to enhance user experience and engagement. These features include seamless integration with other mobile services like ride-sharing apps, real-time transaction notifications, and personalized rewards programs. One prominent example is the integration of QR code scanning for quick and convenient payments.
Potential for Future Development
The potential for future development in the pay-by-phone market is vast. Innovations in biometrics, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, could further enhance security and streamline the payment process. The integration of blockchain technology for enhanced transparency and security is another area of potential growth. The incorporation of augmented reality (AR) could also offer interactive and engaging experiences for users during transactions.
Projected Market Growth
| Year | Market Growth (%) | Key Trends |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 15% | Increased adoption of mobile wallets, integration with loyalty programs, and rise of contactless payments. |
| 2025 | 18% | Expansion into new markets, enhanced security features, and integration with emerging technologies like AI. |
| 2026 | 20% | Greater use of biometrics for security, more personalized user experiences, and broader acceptance of pay-by-phone across different industries. |
Integration with Other Services
Pay-by-phone apps are rapidly evolving beyond simple transaction processing, increasingly integrating with a wide array of financial and lifestyle services. This integration enhances user experience and broadens the app’s utility, making it a more comprehensive financial tool. The seamless connection to other services streamlines tasks and provides a more holistic financial management platform.
Integration with Financial Services
Pay-by-phone apps often integrate with existing bank accounts and payment platforms. This allows users to directly link their accounts for faster and more convenient transactions. The integration streamlines the payment process, eliminating the need for manual input of account details. Furthermore, many apps offer features like budgeting tools and expense tracking, providing users with insights into their spending habits.
Connection with Loyalty Programs
Many pay-by-phone apps are now partnering with loyalty programs. This integration enables users to earn rewards and discounts while making purchases. The app can automatically recognize a user’s membership in a loyalty program and apply associated benefits. This feature incentivizes users to utilize the app for their daily transactions, encouraging repeat use. For example, a user’s loyalty points for a specific store can be credited automatically upon completing a transaction.
Mobile Payments in Stores
Pay-by-phone apps are essential for enabling mobile payments in physical stores. This eliminates the need for physical cards or cash, making transactions faster and more efficient. The seamless integration with point-of-sale systems in stores allows for a frictionless checkout process, a key factor in driving adoption. Many apps utilize Near Field Communication (NFC) technology to facilitate these transactions, offering a convenient alternative to traditional methods.
Potential for Integration with Other Apps or Services
The potential for integration extends beyond financial services and loyalty programs. Imagine a scenario where a user can schedule a ride-sharing service directly from their pay-by-phone app or link their favorite grocery store app for in-store payments. Such integrations offer enhanced convenience and streamline everyday tasks.
Role of APIs in Facilitating Integrations
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) play a crucial role in enabling these integrations. APIs allow different applications to communicate and share data. By providing standardized interfaces, APIs facilitate the exchange of information between pay-by-phone apps and other services, enabling the seamless integration of various functionalities.
Integration Points for Different Apps
| App | Integration Points | Example Services |
|---|---|---|
| App A | Bank accounts, loyalty programs (e.g., Starbucks), ride-sharing services (e.g., Uber), and in-store mobile payments. | Chase Bank, Starbucks Rewards, Uber, local grocery stores |
| App B | Payment networks (e.g., Visa, Mastercard), loyalty programs (e.g., Sephora), and online shopping platforms (e.g., Amazon). | Visa, Mastercard, Sephora Beauty Insider, Amazon |
| App C | Credit and debit cards, grocery delivery services (e.g., Instacart), and entertainment ticketing. | American Express, Instacart, movie ticket vendors |
Business Models and Revenue Streams
Pay-by-phone apps are revolutionizing the way we make transactions, but their success hinges on robust business models that generate revenue. Understanding the diverse strategies employed by these platforms is crucial to grasping their potential and challenges. These models encompass various approaches to monetization, from direct user fees to partnerships and in-app purchases.
Business Models of Pay-by-Phone App Providers
Different pay-by-phone apps adopt various business models to generate revenue and sustain operations. These models vary significantly, reflecting the diverse nature of the services offered and the target user base. Some models focus on commissions from merchants, while others rely on subscriptions or a combination of approaches.
Revenue Streams for Pay-by-Phone Apps
Pay-by-phone apps employ a variety of revenue streams to generate income. These streams can be categorized into several key areas, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding the specific revenue streams of a given app provides valuable insight into its financial health and long-term sustainability.
- Commission-based models: Many pay-by-phone apps earn revenue by charging merchants a percentage of each transaction. This model is prevalent in apps designed for quick payments, such as those used for retail purchases or food delivery. The commission rate can vary significantly based on factors like transaction volume and merchant type.
- Subscription-based models: Some apps offer premium features or functionalities to users through a subscription service. This model is more common in apps providing advanced payment features or offering added benefits to their subscribers, such as exclusive discounts or financial tools. Subscription fees can be tiered, providing different levels of access and features.
- In-app purchases: Some pay-by-phone apps might allow users to purchase additional services or features within the app. This model is suitable for apps providing specialized financial tools, where users might need to pay for specific functionalities.
- Partnerships and collaborations: A substantial revenue stream can be derived through strategic partnerships with banks, financial institutions, or other service providers. This collaborative approach can allow apps to leverage the existing infrastructure and resources of their partners.
Pricing Strategies Employed by Pay-by-Phone Apps
Pricing strategies in the pay-by-phone app market vary significantly. Some apps might offer a freemium model, where basic functionalities are free, but advanced features are available for purchase. Others may opt for a flat-rate fee structure for all users, regardless of usage or transaction volume. The chosen pricing strategy is directly related to the overall business model and target market.
Examples of Successful Business Models
Successful pay-by-phone app business models often combine elements of the various approaches discussed. For example, a successful app might leverage a commission-based model for retail transactions while simultaneously offering a premium subscription service for enhanced security features or exclusive discounts. This integrated approach allows the app to cater to a broader range of users and generate revenue from different sources.
Comparison of Revenue Generation Methods
| App Name | Business Model | Revenue Streams |
|---|---|---|
| App A (Hypothetical) | Commission-based (merchants) | Transaction fees (variable rate) |
| App B (Hypothetical) | Subscription-based (users) | Monthly/annual subscriptions |
| App C (Hypothetical) | Hybrid (merchants & users) | Transaction fees + premium features (subscription) |
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, pay by phone apps have undeniably transformed the payment landscape. Their convenience, security features, and potential for future integration with other services make them a powerful force in the digital economy. As technology continues to advance, we can anticipate even more innovative features and applications of pay by phone technology in the years to come.