Applicant tracking systems (ATS) are revolutionizing modern recruitment, streamlining the hiring process from initial application to final selection. From simple job postings to sophisticated candidate management, ATS platforms have become essential tools for organizations of all sizes. This in-depth exploration dives into the evolution, features, and future of ATS, examining how they impact both recruiters and candidates.
This comprehensive guide covers everything from the fundamental purpose and history of applicant tracking systems to the advanced capabilities and challenges of using them. We’ll analyze the core features and benefits for both recruiters and candidates, exploring the integration aspects and the candidate experience. Finally, we will address the critical aspects of selection, implementation, and future trends.
Introduction to Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS)
Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) are crucial components of modern recruitment strategies. They streamline the entire hiring process, from initial job postings to candidate selection, significantly improving efficiency and reducing manual effort. This automation allows organizations to manage a large volume of applications, ensuring a fair and consistent evaluation of each candidate.
The increasing complexity of the job market and the escalating volume of applications necessitate the use of ATS. By automating tasks, ATS enable recruiters to focus on strategic aspects of the hiring process, such as talent acquisition and long-term workforce planning, rather than being bogged down by administrative duties. This optimized approach to recruitment translates to faster time-to-hire and ultimately, a better candidate experience.
Fundamental Purpose of an ATS
An ATS fundamentally serves to manage the entire recruitment lifecycle. From attracting potential candidates to evaluating and selecting the best fit, an ATS provides a centralized platform to handle the various stages of the hiring process. This centralized approach promotes consistency and transparency throughout the recruitment process, reducing bias and improving the overall candidate experience.
History of ATS Evolution
The evolution of ATS mirrors the advancements in technology itself. Early systems were rudimentary, primarily focused on automating basic tasks like application tracking and storing candidate data. Later advancements incorporated sophisticated algorithms for candidate matching and automated screening processes. A significant milestone was the introduction of cloud-based ATS, which enabled greater scalability and accessibility for organizations of all sizes. Today’s ATS are sophisticated tools, leveraging AI and machine learning to predict candidate performance and personalize the recruitment experience.
Typical Functionalities of a Modern ATS
Modern ATS encompass a wide range of functionalities, designed to streamline each stage of the recruitment process. These functionalities are essential for efficient candidate management and improved hiring outcomes.
- Job Posting: ATS facilitate the creation and dissemination of job postings across various job boards and platforms. This automated process ensures consistent and timely communication of job openings to potential candidates.
- Candidate Sourcing: Advanced ATS utilize sophisticated algorithms to identify and attract qualified candidates from various online sources. This capability allows recruiters to expand their talent pool and find candidates who may not be actively seeking employment.
- Candidate Screening and Evaluation: ATS offer tools for filtering candidates based on pre-defined criteria, such as skills, experience, and education. This automated screening process allows recruiters to prioritize qualified candidates and quickly eliminate unsuitable applicants.
Types of Applicant Tracking Systems
Different types of ATS cater to varying organizational needs and sizes. The choice depends on the specific requirements and resources of the company.
| Type of ATS | Features | Target Users |
|---|---|---|
| Basic ATS | Handles basic application tracking, storing candidate data, and simple reporting. | Small businesses and startups with limited hiring needs. |
| Intermediate ATS | Offers advanced functionalities such as candidate sourcing, automated screening, and basic reporting. | Medium-sized businesses seeking more sophisticated recruitment management. |
| Advanced ATS | Includes sophisticated AI-powered features for candidate matching, predictive analytics, and personalized candidate experiences. | Large enterprises and organizations with complex hiring requirements and large volumes of applicants. |
Core Features and Benefits of ATS
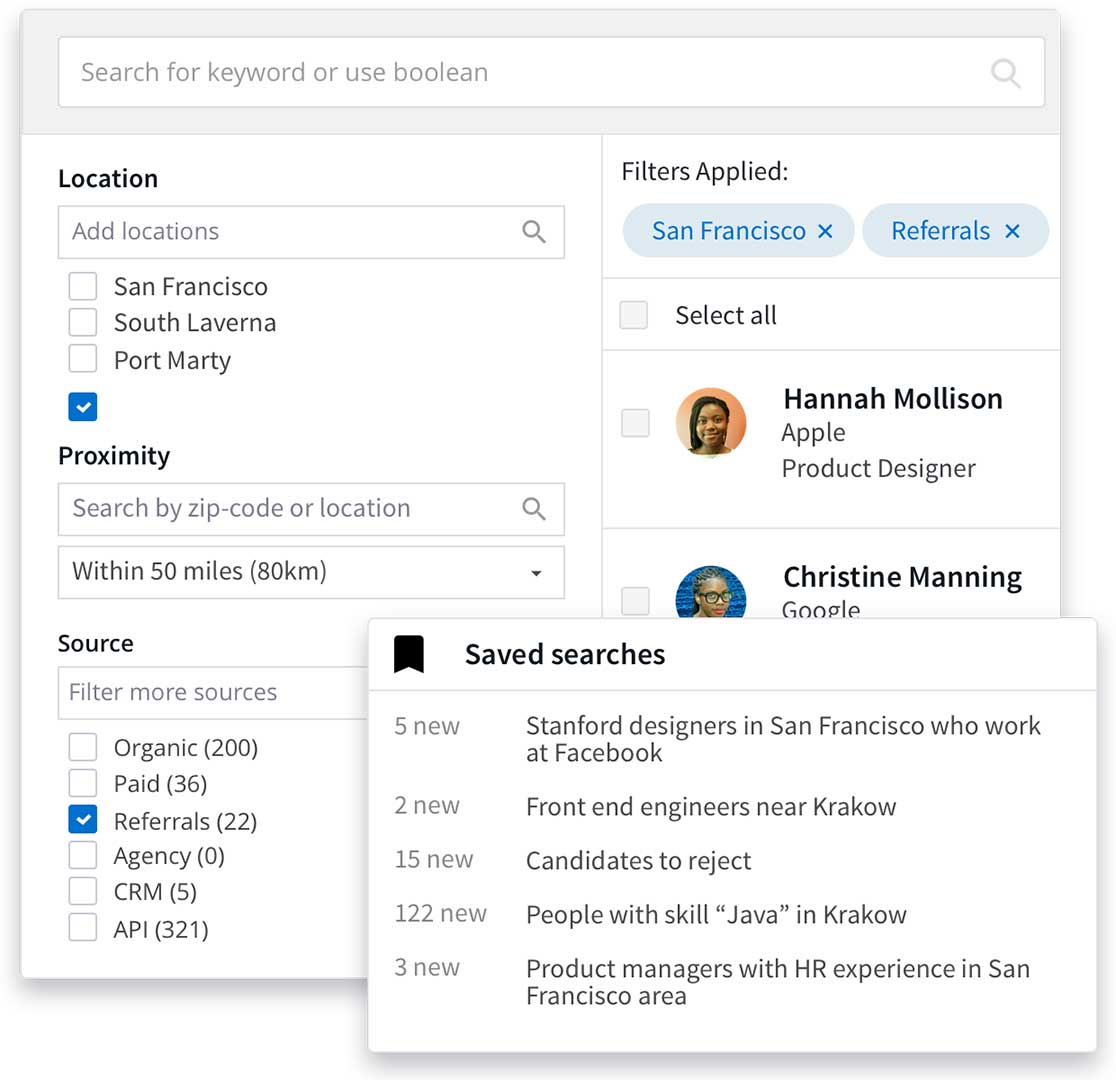
Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) are no longer a luxury but a necessity for modern recruitment. They streamline the hiring process, improve candidate experience, and significantly reduce the time and resources spent on manual tasks. A robust ATS empowers recruiters to make data-driven decisions, identify top talent, and ultimately, fill roles more effectively.
An effective ATS goes beyond basic applicant management; it provides a comprehensive platform for talent acquisition. This platform encompasses the entire recruitment lifecycle, from initial sourcing and screening to final hiring decisions. Crucially, it offers a structured and organized approach that enhances efficiency and optimizes resource allocation, ultimately benefiting both recruiters and candidates.
Key Features Differentiating High-Performing ATS
A high-performing ATS distinguishes itself from basic systems through several key features. These features are crucial for maximizing efficiency and achieving optimal results. Sophisticated search and filtering capabilities, advanced applicant tracking features, and robust reporting and analytics are hallmarks of a superior ATS. These advanced features allow recruiters to quickly identify qualified candidates, manage their application progress effectively, and track key metrics to improve future hiring strategies. For example, a powerful search function allows recruiters to filter applicants based on specific skills, experience, and education, ensuring they find the best fit for the role.
Benefits for Recruiters and Candidates
ATS benefits both recruiters and candidates in various ways. For recruiters, it streamlines the hiring process, reduces manual work, and improves overall efficiency. For candidates, it offers a more organized and transparent experience, providing greater control over their application process. This translates into a more streamlined and efficient experience for both parties involved in the recruitment process. For recruiters, an ATS reduces the time spent on manual tasks such as filtering resumes and contacting candidates, freeing them to focus on more strategic aspects of the hiring process. For candidates, it enhances their visibility and accessibility to potential employers.
Efficiency Improvements in Hiring Process
An ATS dramatically improves the efficiency of the hiring process by automating various stages. Automated tasks like screening applications, scheduling interviews, and tracking candidate progress free up recruiters’ time, allowing them to focus on more strategic tasks. This streamlined approach significantly reduces the time-to-fill, ultimately contributing to a faster and more efficient hiring process. Furthermore, a well-designed ATS facilitates communication between recruiters and candidates, keeping both parties informed about the status of their applications.
Cost Reduction through ATS Implementation
Implementing an ATS can lead to significant cost reductions in recruitment. Automating tasks reduces the need for extensive manual labor, leading to decreased operational costs. By reducing time-to-fill, ATS contributes to cost savings by minimizing the overall cost of recruitment. Improved candidate matching reduces the need for extensive advertising campaigns, further reducing recruitment costs. Reduced candidate turnover due to a streamlined process further contributes to long-term cost savings.
Return on Investment (ROI) of ATS Implementation
Implementing an ATS can yield a substantial return on investment (ROI). The ROI is often expressed as a percentage increase in efficiency, a reduction in time-to-fill, and a decrease in recruitment costs. The table below illustrates a potential ROI scenario, highlighting the significant financial benefits.
| Metric | Baseline (Without ATS) | With ATS (Projected) | ROI | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time to Fill (Days) | 30 | 15 | 50% Reduction | Faster hiring process, reduced time spent on each stage. |
| Recruitment Costs per Hire (USD) | 5,000 | 3,500 | 30% Reduction | Lower advertising costs, less time spent on manual tasks. |
| Number of Qualified Candidates per Application | 10% | 20% | 100% Increase | Improved candidate matching, better targeting of qualified candidates. |
| Overall Hiring Process Efficiency | 70% | 90% | 20% Increase | Streamlined process, improved communication, and data-driven decisions. |
Improved candidate experience and reduced time-to-fill contribute to a substantial return on investment.
Integration and Data Management
A robust Applicant Tracking System (ATS) is not just a repository for applicant information; it’s a vital component of a streamlined HR process. Effective integration with other HR systems and meticulous data management are crucial for accurate reporting, efficient candidate tracking, and informed decision-making. Maintaining data integrity ensures that all information is reliable and up-to-date, supporting a more transparent and efficient hiring process.
Data integrity is paramount in an ATS. Inaccurate or inconsistent data can lead to mismatched candidates, lost opportunities, and inefficient resource allocation. This necessitates a commitment to data validation and quality control procedures throughout the application lifecycle. Ensuring the accuracy and consistency of applicant information, from initial application to final hiring decision, is essential for a positive candidate experience and a successful hiring outcome. A system with poor data integrity can lead to inaccurate reports and hinder strategic decision-making.
Data Integrity in an ATS
Maintaining accurate and consistent applicant data is critical. This involves implementing validation rules to ensure data accuracy. Data cleansing procedures can identify and correct inconsistencies or errors in existing data. Regular audits are vital to detect and resolve data quality issues promptly. Robust data security measures are essential to protect sensitive information and maintain compliance with data privacy regulations. A meticulous data governance framework, encompassing data entry protocols and access controls, is necessary to ensure the integrity of the data within the ATS.
Integrating an ATS with Other HR Systems
Effective integration of the ATS with other HR systems is essential for seamless data flow and improved efficiency. This integration can include modules for payroll, performance management, and employee self-service. Integrating with other HR systems allows for the automated transfer of data, minimizing manual entry and reducing the potential for errors. This streamlined data flow enhances the speed and accuracy of the hiring process. For example, seamless integration with a company’s CRM system can allow for direct contact with potential candidates who are already engaged in the sales process.
Strategies for Ensuring Data Accuracy and Consistency
Maintaining data accuracy and consistency requires a multi-pronged approach. Implement robust data validation rules, which are programmed to flag potential errors during data entry. Establish clear data entry protocols and training programs for HR staff. Regular data quality checks are necessary to ensure that the ATS data remains accurate and consistent over time. By automating these procedures, the ATS can significantly improve data accuracy and efficiency. This also involves clear data mapping between systems to avoid redundancy and conflicts.
Managing and Analyzing Applicant Data
An ATS can be used as a powerful tool for managing and analyzing applicant data. Applicant tracking reports can reveal trends in sourcing channels, candidate demographics, and application completion rates. Advanced analytics can identify patterns in successful candidates, helping to refine sourcing strategies and improve the efficiency of the hiring process. These insights allow for informed decision-making, leading to more effective hiring practices. This data can also be used to optimize the overall recruitment process, potentially revealing areas for improvement.
Integration Options for ATS
| Integration Option | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| API Integration | Highly flexible, allows for custom data mapping, facilitates complex integrations. | Requires technical expertise, potential for integration errors if not handled carefully. |
| Third-Party Integrations | Pre-built integrations, often with specialized HR tools. | Limited customization options, potential for vendor lock-in. |
| Custom Development | Tailored solution to specific needs, maximum control. | High cost and time investment, requires dedicated resources and expertise. |
Applicant Experience within an ATS
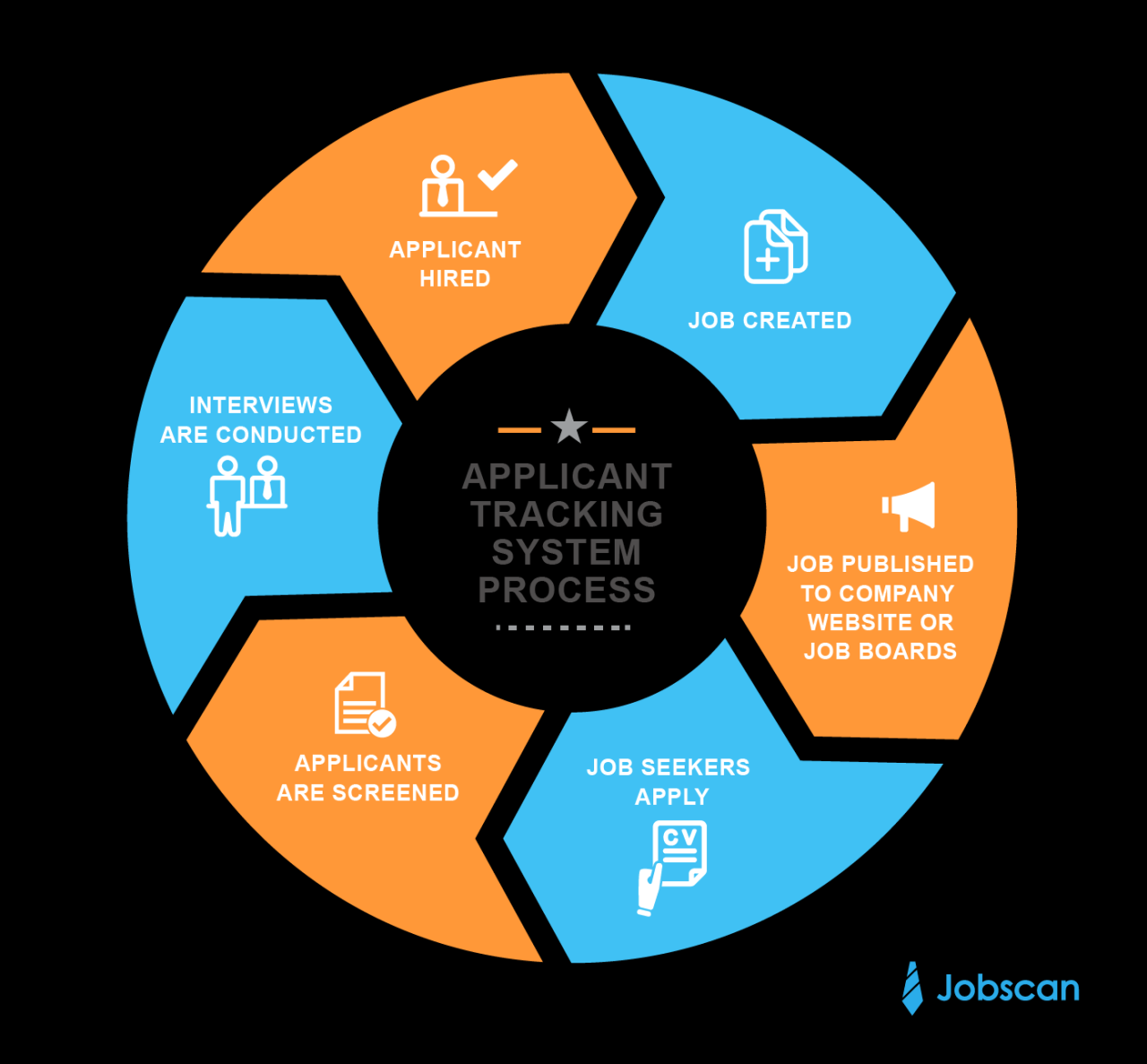
A user-friendly Applicant Tracking System (ATS) is paramount to attracting and retaining top talent. A positive candidate experience directly influences the success rate of hiring, shaping perceptions of the organization, and fostering a positive brand image. This section dives into the crucial role of candidate experience within an ATS, highlighting its impact on engagement and the importance of effective communication.
A well-designed ATS not only streamlines the hiring process for recruiters but also significantly impacts the candidate’s journey. A positive experience, characterized by clear communication, prompt feedback, and a seamless application process, fosters a sense of respect and value, ultimately influencing candidate satisfaction and loyalty. This positive experience can be a crucial differentiator in attracting and retaining top talent in today’s competitive job market.
Impact of a User-Friendly ATS on Candidate Engagement
A user-friendly ATS fosters a positive candidate experience. This positive experience leads to increased candidate engagement, which is reflected in higher application completion rates, quicker responses to communication, and a greater willingness to participate in the hiring process. A well-structured ATS with intuitive navigation, clear instructions, and accessible information encourages candidates to actively participate in the recruitment process.
Examples of a Well-Designed ATS Improving Candidate Experience
Several features contribute to a well-designed ATS that improves the candidate experience. These include automated email notifications for application status updates, personalized feedback, and a seamless resume upload and profile creation process. A responsive design that adapts to different devices, ensuring accessibility across various platforms, is also crucial. These features contribute to a more engaging and satisfying experience for the candidate, increasing the likelihood of successful candidate engagement.
Importance of Candidate Communication and Feedback within the ATS
Clear and timely communication throughout the application process is vital for a positive candidate experience. The ATS should facilitate consistent and transparent communication regarding application status, interview scheduling, and feedback. Candidates appreciate knowing where they stand in the process and receiving feedback on their application, even if it’s not a successful outcome. Providing feedback, whether positive or constructive, demonstrates respect for the candidate’s time and effort.
Methods for Enhancing the Applicant Experience Through Improved Communication Flows
Implementing features like automated email notifications for application status updates, personalized feedback, and the ability to track the status of their application significantly enhances communication flows. A dedicated communication center within the ATS allows recruiters to manage communication efficiently, ensuring prompt responses and transparency. Candidates should be able to easily access their application status and any relevant information at any time, fostering a sense of control and engagement.
Comparison of Candidate Experiences on Various ATS Platforms
| ATS Platform | Ease of Application | Communication Efficiency | Feedback Mechanism | Overall Candidate Experience |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Platform A | Good | Excellent | Effective | Very Positive |
| Platform B | Fair | Average | Limited | Neutral |
| Platform C | Excellent | Good | Excellent | Very Positive |
This table illustrates a comparative analysis of candidate experiences across different ATS platforms. Factors like application ease, communication efficiency, and feedback mechanisms significantly influence the overall candidate experience. A platform’s ability to streamline the process and provide clear communication directly impacts candidate satisfaction.
ATS Selection and Implementation
Selecting the right Applicant Tracking System (ATS) is crucial for optimizing the recruitment process and achieving desired outcomes. A poorly chosen or implemented ATS can hinder efficiency, increase costs, and negatively impact the candidate experience. A well-structured selection and implementation process, on the other hand, can streamline operations, enhance candidate engagement, and ultimately contribute to a more robust talent acquisition strategy.
A thorough understanding of organizational needs and a systematic evaluation process are paramount to selecting an ATS that aligns with those needs. The successful integration of an ATS hinges on a comprehensive implementation strategy and effective staff training.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an ATS
Careful consideration of various factors is vital when selecting an ATS. These factors include the organization’s specific requirements, budget constraints, and anticipated growth trajectory. A thorough assessment of existing processes and desired outcomes will guide the selection process.
- Scalability: The chosen ATS must be able to accommodate future growth and anticipated increases in applicant volume. Consider the system’s capacity to handle a surge in applications, particularly during peak hiring seasons. An ATS with limited scalability could become a bottleneck as the organization expands.
- Integration Capabilities: Evaluate the ATS’s compatibility with existing HR systems, CRM platforms, and other software applications. Smooth integration is essential for data consistency and efficient workflow. An ATS that does not integrate well can create redundant data entry and increase operational complexity.
- User-Friendliness: The ATS should be intuitive and easy to navigate for all users, from recruiters to hiring managers. A user-friendly interface reduces training time and ensures efficient adoption. A complex ATS can lead to resistance from users and decreased productivity.
- Customization Options: The system should allow for customization to meet specific organizational needs and workflows. This flexibility ensures the ATS adapts to the unique requirements of the hiring process.
- Vendor Support and Reliability: Evaluate the vendor’s reputation, support services, and response times. Reliable support is essential for addressing technical issues and ensuring smooth operation.
Evaluating ATS Vendors
A structured approach to evaluating ATS vendors is crucial. This involves a standardized process that considers various criteria and allows for a comparative analysis. A well-defined evaluation process helps ensure that the selected ATS meets the organization’s specific needs and aligns with its long-term goals.
| Criteria | Description | Scoring Options (1-5, 5 being highest) |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | Ability to handle increasing applicant volume | 1 (Poor) – 5 (Excellent) |
| Integration Capabilities | Compatibility with existing HR systems | 1 (Poor) – 5 (Excellent) |
| User-Friendliness | Ease of navigation and use | 1 (Poor) – 5 (Excellent) |
| Customization Options | Flexibility to meet specific needs | 1 (Limited) – 5 (Extensive) |
| Vendor Support | Quality and responsiveness of support | 1 (Poor) – 5 (Excellent) |
| Cost | Total cost of ownership (TCO) | 1 (High) – 5 (Low) |
Implementation Strategy
A well-defined implementation strategy is crucial for a successful ATS integration. This strategy should Artikel timelines, resource allocation, and communication protocols.
- Phased Rollout: Implementing the ATS in phases, starting with a pilot group, allows for a controlled testing and feedback process.
- Training Plan: A structured training program for all staff using the ATS ensures smooth transition and maximizes user adoption.
- Data Migration Strategy: A comprehensive plan for migrating existing data into the new system is essential to maintain continuity.
- Change Management Plan: Addressing potential resistance to change and ensuring buy-in from all stakeholders is vital for successful implementation.
Staff Training
Comprehensive training is essential for successful ATS adoption. A tailored training program that caters to the specific needs and roles of different staff members ensures effective utilization of the system. Training materials should cover all aspects of the system, including features, functionalities, and best practices.
- Role-Based Training: Different training modules should be tailored to the specific roles and responsibilities of each staff member.
- Hands-on Sessions: Practical exercises and simulations should be incorporated into the training to reinforce learning.
- Ongoing Support: Provide ongoing support and resources to address questions and provide assistance as needed.
- Documentation and Resources: Create clear documentation and readily available resources for staff to consult.
Advanced ATS Capabilities
Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) are evolving beyond basic recruitment functions. Modern ATS solutions incorporate advanced capabilities that streamline the entire hiring process, improve candidate experience, and provide valuable insights for strategic decision-making. These advancements often integrate artificial intelligence and machine learning, enhancing efficiency and accuracy in candidate selection.
Advanced ATS features go beyond the fundamental tasks of posting jobs, receiving applications, and scheduling interviews. They encompass a wider spectrum of functionalities that empower organizations to optimize their talent acquisition strategies and gain a competitive edge in the job market. These tools enable data-driven decisions, automating processes, and creating a more robust and informed approach to hiring.
AI-Powered Candidate Scoring and Filtering
Advanced ATS systems leverage artificial intelligence (AI) to automate candidate screening and scoring. This often involves algorithms that analyze resumes and applications to identify key skills and experience relevant to specific job descriptions. AI-powered tools can also predict candidate performance based on historical data and patterns, offering insights that may not be readily apparent to human recruiters. This can lead to more objective assessments and potentially faster hiring cycles.
Diversity and Inclusion Initiatives
ATS solutions are increasingly incorporating features to support diversity and inclusion initiatives. These features can include tools for tracking applicant demographics, analyzing the diversity of candidate pools, and identifying potential biases in the hiring process. Organizations can leverage these features to monitor their diversity efforts and ensure fair and equitable hiring practices. By understanding the composition of their applicant pool, companies can proactively work towards creating a more diverse and inclusive workforce.
Performance Management and Tracking
Beyond recruitment, advanced ATS systems can support performance management and tracking. They can integrate with performance review software and track employee performance metrics over time. This can help managers identify top performers, areas for improvement, and potential training needs. By linking recruitment data to performance metrics, organizations can gain a more comprehensive understanding of their workforce’s capabilities and tailor development strategies accordingly.
Comparison of Advanced ATS Features
| ATS Solution | AI-Powered Candidate Scoring | Diversity & Inclusion Tracking | Performance Management Integration |
|---|---|---|---|
| ATS1 | Yes, using analysis and experience matching | Yes, with applicant demographic tracking | Yes, through integration with performance management software |
| ATS2 | Yes, incorporating machine learning for predictive analysis | Yes, providing data visualizations for diversity analysis | Yes, with automated performance metrics reporting |
| ATS3 | Yes, using natural language processing for skill extraction | Yes, identifying potential bias in the hiring process | Yes, providing custom dashboards for performance tracking |
Note: This table provides a simplified comparison. Specific features and functionalities may vary between different ATS solutions. Organizations should carefully evaluate the specific needs of their hiring process when selecting an ATS.
Challenges and Considerations in Using an ATS
Implementing an Applicant Tracking System (ATS) can be a complex undertaking, often fraught with hurdles that require careful planning and execution. These challenges, while potentially significant, are surmountable with a proactive approach and a well-defined strategy. A robust ATS can significantly streamline the recruitment process, but overcoming implementation obstacles is critical for realizing its full potential.
Organizations frequently face difficulties in transitioning to a new ATS, ranging from user adoption issues to data migration complexities. Understanding these common problems and developing mitigation strategies is essential for a successful ATS deployment. Moreover, ongoing maintenance, security considerations, and proper data management are crucial aspects of a long-term ATS strategy.
Common Implementation Challenges
Successfully integrating an ATS into existing workflows requires careful consideration of potential roadblocks. Many organizations struggle with initial data migration, user training, and system configuration. Furthermore, cultural shifts and resistance to change can impact user adoption rates, ultimately hindering the ATS’s effectiveness.
- Data Migration Hurdles: Migrating existing applicant data into the new ATS can be time-consuming and complex. Inaccurate data mapping and incomplete data sets can lead to errors and inconsistencies, impacting reporting and decision-making. Careful planning, thorough data validation, and potentially engaging third-party experts for migration services can minimize these issues.
- User Adoption and Training: Lack of user training and clear communication regarding new processes can lead to resistance and low adoption rates. Effective training programs, comprehensive documentation, and ongoing support are crucial to ensure employees understand and utilize the system effectively. Demonstrating the system’s benefits to stakeholders and offering incentives can further boost adoption.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating the ATS with existing HR systems, CRM platforms, or other applications can be challenging. Compatibility issues and the need for custom integrations can lead to delays and unexpected costs. Thorough due diligence and careful planning are crucial in this phase.
Ongoing Maintenance and Updates
Regular maintenance and updates are essential for ensuring the ATS remains functional and effective. Failure to keep the system updated can lead to security vulnerabilities, compatibility issues with new software, and loss of functionality. Staying current with updates and patches is crucial for system performance and compliance with regulations.
- Software Updates: Regular software updates address security vulnerabilities and introduce new features or enhancements. Failing to implement these updates can leave the system exposed to risks and limit its functionality. Establish a schedule for applying updates and prioritize updates that address critical security issues.
- System Performance Monitoring: Monitoring system performance and identifying potential bottlenecks or issues proactively can prevent major disruptions. Regular performance checks and proactive problem resolution are crucial for maintaining optimal system efficiency. Using monitoring tools and dashboards can assist in this process.
Security Considerations
Protecting applicant data is paramount. An ATS holds sensitive personal information, making it a prime target for cyberattacks. Implementing robust security measures is essential to safeguard this data.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data both in transit and at rest is crucial to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. Implementing strong encryption protocols can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches.
- Access Control: Restricting access to sensitive data to authorized personnel is vital. Employing strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access control can enhance security and prevent unauthorized access.
ATS Implementation Roadblocks and Solutions
| Roadblock | Solution |
|—|—|
| Data migration issues | Thorough data mapping, data validation, and potential third-party migration support |
| User resistance to change | Comprehensive training programs, clear communication, and demonstrating benefits |
| Integration problems with existing systems | Careful planning, thorough due diligence, and potential custom integrations |
| Lack of budget | Prioritize essential features, explore phased implementation, and seek funding options |
| Insufficient resources | Employ additional personnel, outsource tasks, and leverage automation tools |
| Inadequate support | Establish a dedicated support team, provide access to online resources, and offer ongoing training |
Future Trends in ATS
Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) are rapidly evolving, driven by the need for more efficient and effective recruitment processes. Emerging technologies are transforming the landscape, particularly the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning. These advancements promise to streamline workflows, enhance candidate experience, and ultimately, improve the overall hiring process.
Emerging Technologies Impacting ATS Development
Advancements in natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms are enabling ATS to analyze unstructured data more effectively. This includes candidate resumes, job descriptions, and even social media profiles. By extracting key information and patterns, ATS can identify suitable candidates more accurately and quickly, reducing the time spent on manual screening. For example, sophisticated NLP can now understand the nuances of language in resumes, recognizing s and skills relevant to specific roles.
Role of AI and Machine Learning in Shaping the Future of Recruitment
AI and machine learning are playing a crucial role in automating various aspects of the recruitment process. These technologies can automate tasks such as screening applications, scheduling interviews, and even generating initial candidate feedback. This not only accelerates the process but also reduces the potential for human bias. For instance, AI can be trained to analyze applicant data objectively, identifying the best-suited candidates without subjective judgment. This leads to a more equitable and efficient hiring process.
Potential Future Functionalities and Capabilities in ATS Systems
Future ATS systems are expected to offer more sophisticated features beyond traditional applicant tracking. These include proactive candidate engagement, predictive analytics for talent acquisition, and intelligent matching algorithms. Proactive candidate engagement features will allow recruiters to nurture potential candidates at various stages of the hiring process. Predictive analytics can forecast talent demand and identify potential candidates before a role is even advertised. Intelligent matching algorithms can dynamically adjust and refine candidate matching based on real-time feedback and market trends.
Ways ATS Might Evolve to Support More Complex Hiring Processes
The evolution of ATS is also moving towards supporting more complex hiring processes, such as those involving niche skills or specialized roles. This includes advanced filtering and searching functionalities, along with the ability to manage complex evaluation criteria. The systems will be able to handle diverse skill sets and experience levels, and also track and evaluate candidate performance throughout the hiring process, from initial application to final onboarding. This data-driven approach will lead to a more holistic understanding of candidate potential and better hiring decisions.
Potential Future ATS Features and Benefits
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Automated Skill Matching | Identify candidates with specific skills and experience faster and more accurately. |
| Predictive Analytics for Talent Acquisition | Forecast talent demand and identify potential candidates proactively. |
| Proactive Candidate Engagement | Nurture potential candidates through personalized communication and feedback. |
| Intelligent Interview Scheduling | Optimize interview schedules based on candidate availability and recruiter workload. |
| Advanced Data Visualization and Reporting | Gain deeper insights into the recruitment process and candidate performance. |
| Integration with Social Media Platforms | Access and analyze candidate profiles from social media, providing a more comprehensive view. |
| Personalized Candidate Experience | Enhance candidate engagement and improve the overall applicant experience. |
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, applicant tracking systems are transforming how organizations approach recruitment. From optimizing the hiring process to improving the candidate experience, ATS platforms are becoming increasingly sophisticated. Understanding the features, benefits, and potential challenges is crucial for organizations looking to leverage these tools effectively. This comprehensive look at ATS will equip readers with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about their implementation and ongoing use.