Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are pivotal for businesses of all sizes, enabling them to streamline operations, enhance customer interactions, and ultimately, drive growth. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of CRM systems, exploring their functionalities, implementation strategies, and future trends. From defining different CRM types to integrating with existing systems, this exploration offers a holistic view of CRM, empowering businesses to make informed decisions about their CRM adoption.
This guide provides a detailed overview of the essential aspects of CRM systems. It covers various facets, from the fundamental concepts of CRM to advanced considerations like security and customization. By examining diverse CRM types and their benefits, readers can determine which best suits their specific needs. The guide concludes with a look into the future of CRM technology and its integration with emerging trends like artificial intelligence.
Defining CRM Systems
A Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is a software application designed to manage and streamline interactions with customers. It acts as a central hub for storing customer data, tracking sales activities, and managing customer service requests. Effective CRM systems improve customer satisfaction and drive business growth by fostering better communication and understanding of customer needs.
CRM systems are essential for businesses of all sizes to organize customer information, automate tasks, and ultimately, enhance the customer experience. They enable businesses to understand their customers better, personalize interactions, and nurture relationships, leading to increased customer loyalty and profitability.
Defining CRM System Functionality
A typical CRM system encompasses several key functionalities. These include contact management, sales force automation, marketing automation, customer support, and analytics. Contact management allows for the organization and categorization of customer data. Sales force automation automates sales processes, such as lead qualification, opportunity tracking, and order management. Marketing automation facilitates targeted marketing campaigns, personalized messaging, and automated email sequences. Customer support modules allow for efficient handling of customer inquiries and complaints. Finally, CRM analytics provide insights into customer behavior and trends, allowing businesses to optimize strategies and improve performance.
Types of CRM Systems
CRM systems are available in various deployment models, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. These models include on-premise, cloud-based, and open-source systems.
On-Premise CRM Systems
On-premise CRM systems are installed and maintained on a company’s own servers. This gives the business complete control over the system’s security and data. However, it often requires significant upfront investment in hardware and software, and ongoing maintenance costs. Furthermore, the need for IT expertise for installation, maintenance, and security can be a significant overhead.
Cloud-Based CRM Systems
Cloud-based CRM systems are hosted on remote servers and accessed through the internet. This model eliminates the need for in-house infrastructure, reducing upfront costs and maintenance expenses. The scalability of cloud-based systems allows businesses to easily adapt to changing needs. However, security concerns regarding data access and potential downtime are important considerations.
Open-Source CRM Systems
Open-source CRM systems are software programs with open-source code, allowing users to modify and adapt the system to their specific needs. These systems offer a high degree of customization and flexibility. However, maintaining and supporting open-source systems often requires internal technical expertise, and updates and security patches may need to be managed independently.
Comparison of CRM System Types
| Feature | On-Premise | Cloud-Based | Open-Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Installed on company servers | Hosted on remote servers | Software with open-source code |
| Scalability | Requires careful planning and potential hardware upgrades | Highly scalable, easily adaptable to growth | Customization allows for flexibility, but scalability might be less predictable |
| Cost | High upfront costs, ongoing maintenance expenses | Lower upfront costs, recurring subscription fees | Potentially lower upfront costs, but ongoing maintenance and support might be significant |
CRM System Implementation
Implementing a CRM system is a significant undertaking that requires careful planning and execution. A poorly implemented system can lead to wasted resources, frustrated users, and ultimately, a failure to achieve the desired outcomes. Conversely, a well-structured implementation process, anchored in thorough planning and best practices, can unlock substantial value for businesses. It’s crucial to recognize that CRM implementation isn’t a one-size-fits-all process; each organization needs a tailored approach to maximize the system’s effectiveness.
Effective CRM implementation hinges on a clear understanding of the system’s potential, aligning it with the company’s specific needs and workflows. This necessitates meticulous planning, involving key stakeholders and considering potential challenges. By proactively addressing these concerns, organizations can minimize disruptions and ensure a smooth transition to the new system.
Planning and Preparation
Thorough planning is the bedrock of a successful CRM implementation. It encompasses a comprehensive assessment of the current business processes, identification of key stakeholders, and a realistic definition of the desired outcomes. Without a robust foundation, the implementation risks becoming a chaotic endeavor. This proactive approach allows businesses to fine-tune the system to their unique operational needs, leading to a more efficient and effective CRM strategy.
Stages of Implementation
The implementation process typically unfolds through distinct stages, each with its own set of tasks and responsibilities. A structured approach helps manage expectations and ensure that each step is completed effectively. These stages are crucial for mitigating risks and ensuring a smooth transition.
- Needs Assessment and System Selection: This crucial stage involves a deep dive into the organization’s specific needs and goals. It encompasses a thorough review of current processes, identification of pain points, and research into available CRM systems. This evaluation should weigh the system’s features against the organization’s requirements to ensure optimal fit.
- Data Migration and Customization: Once the system is chosen, the next phase involves transferring existing data into the new CRM. This often requires careful planning and execution to ensure data integrity and minimize errors. Customization is also vital, ensuring the system aligns with the specific workflows and business processes of the organization.
- Training and User Adoption: A robust training program is essential to ensure users understand how to utilize the system effectively. This program should be tailored to the specific needs of different user roles and responsibilities, facilitating efficient adoption and maximizing user satisfaction. Successful training empowers users to leverage the system’s features for enhanced productivity.
- Testing and Go-Live: Thorough testing of the implemented system, including all functionalities and integrations, is critical to identify and resolve any issues before the official launch. This stage should simulate real-world scenarios to ensure the system operates as expected. A smooth go-live is essential for avoiding disruptions and ensuring a seamless transition to the new system.
- Post-Implementation Support and Monitoring: Ongoing support and monitoring are crucial for ensuring the system remains effective and responsive to evolving business needs. Regular feedback mechanisms and support channels are vital for identifying and addressing potential issues, fostering continuous improvement.
Best Practices for Successful Implementation
Adhering to best practices significantly increases the likelihood of a successful CRM implementation. These best practices ensure that the system effectively supports the organization’s objectives and enhances productivity.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involving key stakeholders throughout the implementation process is crucial. This ensures buy-in and alignment with the overall business strategy. Open communication and collaboration are essential for a successful outcome.
- Realistic Expectations: Setting realistic expectations about the system’s capabilities and limitations is essential. Understanding the time and resources required for implementation is critical for avoiding disappointment and ensuring success.
- Phased Approach: A phased approach to implementation allows for a more controlled rollout. This approach allows for adjustments and fine-tuning, ensuring that the system meets the organization’s evolving needs. It also reduces the risk of overwhelming users with a large-scale change.
- Data Quality Management: Data quality is paramount to the effectiveness of a CRM system. Implementing procedures to ensure data accuracy and completeness throughout the implementation is critical.
Step-by-Step Guide for CRM Implementation
This step-by-step guide provides a structured approach to CRM implementation:
- Assess Needs and Goals: Clearly define the organization’s specific needs and desired outcomes from the CRM system.
- Select a Suitable System: Evaluate various CRM options based on features, pricing, and scalability.
- Plan Data Migration: Develop a comprehensive plan for migrating existing data to the new system.
- Design the System Configuration: Tailor the CRM system to the organization’s specific workflows and processes.
- Implement User Training: Develop and deliver training programs to equip users with the necessary skills.
- Test the System Thoroughly: Conduct rigorous testing to identify and resolve potential issues.
- Go Live and Monitor: Launch the CRM system and track its performance to identify areas for improvement.
CRM System Benefits and Uses
A Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is more than just software; it’s a strategic tool that can transform how businesses interact with customers. By centralizing customer data and streamlining processes, CRM systems empower businesses to foster stronger relationships, increase sales, and enhance overall customer satisfaction. This in turn leads to greater profitability and a competitive edge in the market.
CRM systems offer a wide range of advantages, making them invaluable for businesses of all sizes. These advantages extend across various departments, improving efficiency and effectiveness in sales, marketing, and customer service. A well-implemented CRM system can provide a holistic view of the customer journey, allowing businesses to tailor their interactions and offerings to meet individual needs.
Key Advantages of Using a CRM System
CRM systems provide numerous benefits that contribute to improved business performance. These include enhanced customer relationship management, increased sales productivity, and more effective marketing campaigns. By centralizing customer data, businesses can gain a 360-degree view of their customers, fostering deeper understanding and personalized interactions.
Business Use Cases for CRM Systems
CRM systems are adaptable to various business functions, each benefiting from the unique features of the system. Sales teams can use CRM to manage leads, track sales opportunities, and close deals more effectively. Marketing teams can leverage CRM to segment customers, personalize campaigns, and measure marketing ROI. Customer service teams can use CRM to resolve issues efficiently, track customer interactions, and improve customer satisfaction.
Improving Customer Relationships with CRM
CRM systems enable businesses to personalize interactions with customers. By storing and analyzing customer data, businesses can tailor their communication and offerings to individual preferences. This personalization builds stronger customer relationships, fosters loyalty, and encourages repeat business. A CRM system acts as a centralized repository of customer information, allowing businesses to understand their customers better, anticipate their needs, and provide tailored solutions.
Boosting Sales and Marketing Effectiveness with CRM
A CRM system significantly enhances sales and marketing efforts. By automating tasks, tracking leads, and analyzing customer data, CRM systems empower sales teams to focus on building relationships and closing deals. For marketing teams, CRM helps segment customers, personalize messaging, and measure the effectiveness of marketing campaigns. This leads to higher conversion rates, improved customer engagement, and a better return on investment (ROI).
CRM System Improvements Across Business Functions
| Business Function | CRM System Improvement |
|---|---|
| Sales | Improved lead management, enhanced opportunity tracking, increased sales conversion rates, streamlined sales processes, better forecasting capabilities. |
| Marketing | Targeted marketing campaigns, improved customer segmentation, enhanced campaign analysis, increased ROI on marketing spend, personalized customer communication. |
| Customer Service | Faster issue resolution, improved customer satisfaction, enhanced knowledge sharing, efficient communication channels, reduced customer churn. |
CRM System Selection and Evaluation
Choosing the right Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is crucial for a business’s success. A poorly selected CRM can lead to wasted resources, frustrated users, and ultimately, a diminished return on investment. A well-evaluated and carefully selected system, on the other hand, streamlines processes, enhances customer relationships, and empowers informed decision-making. This process involves a systematic approach that goes beyond simply picking the first system that looks appealing.
A thorough evaluation process for CRM systems is essential for ensuring the selected system aligns perfectly with the business’s unique needs and objectives. This includes careful consideration of various factors, including budget constraints, user experience, and system functionalities. This evaluation must be comprehensive to avoid potential issues down the line and guarantee optimal utilization of the chosen CRM.
Factors to Consider When Evaluating CRM Systems
A comprehensive evaluation process necessitates considering various factors to ensure the chosen system effectively addresses business needs. These include, but are not limited to, the system’s functionality, ease of use, and integration capabilities.
- Functionality: Assess the system’s ability to handle the specific tasks and processes required by your business. Does it offer the necessary features for sales, marketing, and customer service? Consider features like lead management, opportunity tracking, and customer service ticketing. A robust sales pipeline management feature, for example, is crucial for businesses focused on lead conversion. Adequate reporting and analytics are also critical for informed decision-making.
- Ease of Use: A user-friendly interface is vital for adoption and effective utilization. A system that’s too complex or difficult to navigate can lead to frustration and low user engagement. Evaluate the intuitiveness of the system’s design, the clarity of its instructions, and the availability of adequate training materials. Consider how intuitive the user interface is for different roles within the organization. For example, a sales team might need a streamlined interface for lead management, while a customer service team might need a different approach for resolving customer issues.
- Integration Capabilities: Evaluate how well the CRM system integrates with existing software and platforms. Seamless integration with accounting software, email marketing platforms, and other tools used in the business is essential for streamlining workflows. The CRM system must integrate effectively with existing tools, such as email marketing software or accounting systems, to avoid data silos and maintain a unified view of customer interactions. For example, a CRM that integrates with an e-commerce platform can automatically track customer orders and update customer profiles.
Budget Constraints in CRM Selection
Budgetary constraints are a significant factor in CRM selection. Choosing a system that exceeds your allocated budget can lead to financial strain and negatively impact ROI.
- Cost Analysis: Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) of different CRM systems, including licensing fees, implementation costs, maintenance fees, and potential upgrades. This analysis should also consider potential hidden costs like training and support. Compare different pricing models (e.g., per user, per month, or per transaction) to identify the most cost-effective option. Consider the different types of pricing models available and their impact on the overall cost.
- Prioritization: Prioritize the most essential features and functionalities that are crucial for the business. Focusing on core functionalities within a budget-friendly CRM can be more effective than purchasing an expensive system with unnecessary features. By focusing on the core functions that are essential for the business, you can avoid unnecessary costs and ensure a more effective use of the budget.
- Negotiation: Negotiate with vendors to explore potential discounts or bundled packages. Negotiation is crucial to ensuring the chosen CRM system is aligned with the allocated budget. Discuss pricing models and explore potential discounts with the vendor. Consider the potential for volume discounts and negotiate based on the projected usage.
User Experience in CRM Selection
User experience (UX) plays a critical role in the success of a CRM system. A poor UX can lead to user resistance and decreased adoption rates, ultimately hindering the system’s effectiveness.
- User Interface (UI) Design: Evaluate the system’s user interface (UI) design for ease of navigation and intuitive use. A well-designed UI will reduce user frustration and promote better adoption rates. Consider the different roles within the organization and how the UI should be designed for each role.
- User Training and Support: Evaluate the availability of adequate training materials and support resources. Comprehensive training programs and ongoing support are essential for ensuring that users can effectively utilize the CRM system. Assess the quality of the training and support materials available for different user roles.
- User Feedback: Gather user feedback during the evaluation process. Involve potential users in testing and provide opportunities for them to offer input on the system’s design and functionality. This allows for the incorporation of user input and the creation of a system that meets the specific needs of the user.
CRM System Evaluation Checklist
This checklist provides a framework for evaluating different CRM systems based on various criteria.
| Criteria | Rating Scale (1-5, 5 being Excellent) | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Functionality | ||
| Ease of Use | ||
| Integration Capabilities | ||
| Budget | ||
| User Experience | ||
| Customer Support | ||
| Scalability |
CRM System Integration
A CRM system, by itself, is a powerful tool. However, its true potential is unlocked when integrated with other business applications. Integration allows data to flow seamlessly between systems, creating a holistic view of the customer and streamlining business processes. This interconnectedness is crucial for organizations seeking to maximize efficiency and gain a competitive edge.
Importance of CRM Integration
Integrating a CRM system with other applications, such as accounting software, e-commerce platforms, or marketing automation tools, is essential for a complete customer view. This holistic view is achieved by linking customer interactions across various touchpoints. Data from sales, marketing, and service activities is consolidated into a single platform, allowing for a 360-degree view of each customer. This integrated approach improves data accuracy, reduces redundancy, and fosters better decision-making across the organization.
Common Integration Challenges and Solutions
Integrating systems can present various challenges, often stemming from compatibility issues, data discrepancies, and the need for technical expertise. However, these challenges are surmountable with careful planning and the right solutions.
- Compatibility Issues: Different systems may use varying data formats and protocols. Solutions include choosing systems with established API integrations or utilizing middleware to bridge the gap between incompatible systems.
- Data Discrepancies: Data inconsistency between systems can lead to inaccurate reporting and analysis. Addressing this involves data cleansing and standardization procedures to ensure data integrity and consistency across all systems.
- Technical Expertise: Integrating systems often requires specialized technical knowledge. Solutions involve hiring or contracting skilled IT professionals or utilizing cloud-based integration platforms.
Methods for Integrating a CRM System
Several methods exist for integrating a CRM system with other applications. Choosing the right method depends on the specific needs and resources of the organization.
- Application Programming Interfaces (APIs): APIs allow different systems to communicate and exchange data. This is a common and flexible method for integration, often used for real-time data transfer and seamless updates.
- Middleware: Middleware acts as a bridge between different systems, converting data formats and ensuring compatibility. It provides a standardized way to exchange data between systems that might not natively support each other.
- Custom Integrations: Custom integrations are tailored solutions built specifically for the organization’s needs. This is a more complex approach, often requiring significant upfront investment but offering the highest level of customization and control.
Examples of Successful CRM System Integrations
Many businesses have successfully integrated their CRM systems with other applications to enhance customer relationship management and operational efficiency.
- A retail company integrated its CRM with its e-commerce platform. This allowed them to track customer purchasing history, personalize recommendations, and manage customer service requests within the CRM system, leading to improved customer satisfaction and sales.
- A financial institution integrated its CRM with its loan origination system. This streamlined the loan application process, enabling faster loan approvals and improved customer experience.
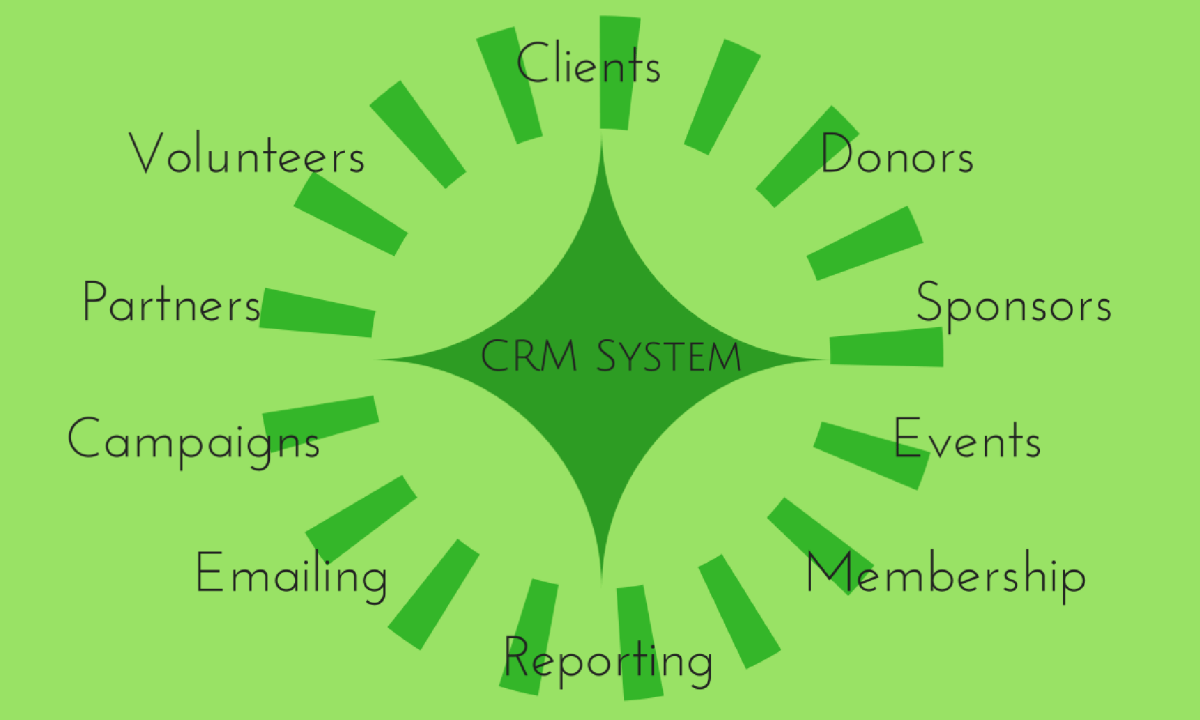
Visual Representation of CRM System Integration
Imagine a central hub representing the CRM system. Connected to this hub are various other systems, each representing different business functions like marketing automation, e-commerce, accounting, and customer support. Lines connecting these systems visually illustrate the flow of data between them. For example, a line connecting the CRM to the marketing automation system signifies the transfer of customer data to personalize marketing campaigns. Similarly, a line connecting the CRM to the accounting system represents the tracking of sales and revenue associated with customer interactions.
CRM System Customization
Off-the-shelf CRM systems provide a solid foundation, but often fall short of perfectly mirroring a company’s unique workflows and data structures. Tailoring a CRM system to match specific business processes unlocks its full potential, allowing for more efficient operations and streamlined interactions with customers. Customization is a key factor in successful CRM implementation.
CRM systems, in their standardized form, are designed to handle common business functions. However, specific business needs often require adjustments to the system’s core features. This customization allows the CRM to adapt to the specific nuances of a company’s operations, optimizing data management and improving efficiency. By tailoring the system, companies can effectively align their CRM with their unique business processes.
Methods for Customizing a CRM System
Customization options range from simple configuration adjustments to more complex integrations and custom development. Companies can leverage these methods to fine-tune the system to their precise needs.
- Configuration: Modifying pre-defined settings within the CRM system’s interface is the most common and straightforward approach. This includes adjusting fields, modifying workflows, and changing report layouts. Configuration tools are typically user-friendly, allowing businesses to alter existing features without extensive programming knowledge.
- Integration: Integrating the CRM with other systems like accounting software, e-commerce platforms, or marketing automation tools allows for seamless data exchange. This is particularly beneficial for businesses with existing systems that need to be connected. Integration enhances the system’s functionality by allowing data to flow effortlessly between different applications.
- Custom Development: For highly specific requirements that cannot be met through configuration or integration, custom development might be necessary. This involves writing specific code to add new features, modify existing functionalities, or create entirely new modules within the CRM. This approach requires technical expertise and a deeper understanding of the CRM’s underlying architecture.
Examples of CRM System Customizations
Customization examples demonstrate the diverse ways CRM systems can be tailored. These examples showcase how CRM systems can be adapted to various business needs.
- Industry-Specific Workflows: A real estate agency might need a custom workflow for property listings, showing different stages of a property’s sale cycle. A legal firm could customize workflows for client intake and case management.
- Unique Reporting Requirements: A company might need specific reports that track customer lifetime value, or those that highlight the performance of particular sales teams. Customizing reporting features allows for tailored insights.
- Data Entry Optimization: Businesses can streamline data entry by creating automated workflows for specific actions. For example, automating the entry of customer details from incoming emails or online forms.
Configuring a CRM System for Specific Workflows
Configuring a CRM system involves tailoring the system to match the specific workflow of a business. This process is crucial for optimizing productivity and efficiency.
- Identify Key Workflows: Begin by identifying the crucial steps in your sales, marketing, or customer service processes. Clearly defining these workflows provides a framework for configuring the CRM.
- Map CRM Features to Workflows: Determine how different CRM features can be used to support each identified workflow. This step ensures the CRM aligns with your business processes.
- Configure CRM Settings: Use the CRM’s configuration tools to set up the identified workflows. This may involve adjusting fields, creating custom reports, or modifying existing processes.
- Test and Refine: Thoroughly test the configured workflows to ensure they function as intended. Refine the configurations based on the results of the testing.
Potential CRM System Customizations
This table Artikels potential customization options for various CRM system features. This demonstrates the broad range of possibilities for tailoring a CRM to specific needs.
| Feature | Customization Options |
|---|---|
| Reporting | Custom report templates, specific metrics, dashboards, real-time updates, sales pipeline visualization, and data visualizations. |
| Workflow | Custom approval processes, automated tasks, lead assignment rules, escalation procedures, and personalized customer journeys. |
| Data Entry | Automated data entry from other systems, custom validation rules, and pre-populated fields. |
CRM System Security

Protecting customer data is paramount in any CRM system. A robust security framework is essential to maintain customer trust and avoid reputational damage. Data breaches can lead to significant financial losses, legal repercussions, and a decline in customer loyalty. Therefore, prioritizing security measures is crucial for the long-term success of any organization utilizing a CRM system.
CRM systems store sensitive customer information, including contact details, financial data, and transaction histories. Compromising this data can have devastating consequences. The increasing reliance on digital platforms and the growing sophistication of cyber threats make robust security protocols more critical than ever. This necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the risks and proactive measures to mitigate them.
Importance of CRM Security
A secure CRM system is vital for maintaining customer trust and preventing financial and reputational damage. Data breaches can lead to legal issues, loss of customer confidence, and significant financial penalties. Organizations must prioritize security measures to safeguard sensitive customer information and ensure the integrity of their CRM system.
Risks Associated with CRM Security Breaches
Security breaches in CRM systems expose sensitive customer data to unauthorized access, potentially leading to identity theft, financial fraud, and reputational harm. Data breaches can result in significant financial losses, legal liabilities, and the erosion of customer trust. These risks underscore the importance of implementing robust security measures to protect customer data. Examples include breaches that expose credit card numbers, social security numbers, or personally identifiable information (PII). These breaches can result in substantial fines under data protection regulations.
Measures to Protect CRM Data
Protecting CRM data from unauthorized access requires a multi-layered approach. Strong passwords, regular security audits, and encryption are crucial components. Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security. Regular software updates and vulnerability assessments are vital to mitigate known security threats. Employing security tools like intrusion detection systems and firewalls strengthens the overall defense. Data encryption, particularly for sensitive data like financial information, is a crucial measure.
Security Protocols for CRM Systems
Implementing robust security protocols is essential to safeguard CRM data. These protocols include using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and regularly updating software. Implementing encryption for sensitive data and employing access controls are crucial measures. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments help identify and address potential weaknesses. Data backups and disaster recovery plans are essential to ensure business continuity in the event of a breach or system failure.
Security Checklist for a CRM System
A comprehensive security checklist for a CRM system should cover various aspects of data protection.
- Password Management: Strong passwords, regular password changes, and password complexity requirements are crucial. Consider using a password manager to securely store and manage passwords.
- Access Controls: Implement role-based access controls to restrict access to sensitive data based on user roles and responsibilities. Regularly review and update access permissions to reflect changes in roles or responsibilities.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest. This protects data from unauthorized access even if the system is compromised.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and address potential security vulnerabilities. Employ penetration testing to simulate real-world attacks and assess the system’s resilience.
- Software Updates: Keep all software components, including the CRM system itself, operating systems, and applications, up-to-date with the latest security patches.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly test an incident response plan to handle security breaches or data compromises effectively. This plan should Artikel procedures for detection, containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident activities.
- Physical Security: Implement physical security measures, such as access controls and security cameras, to protect the physical hardware used for the CRM system.
Future Trends in CRM Systems
CRM systems are evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and changing customer expectations. This evolution is not just about adding new features, but about fundamentally altering how businesses interact with their customers. The future of CRM lies in its ability to anticipate needs, personalize experiences, and ultimately, drive deeper customer loyalty.
Emerging Trends in CRM Technology
The landscape of CRM technology is being reshaped by several key trends. These include the increasing importance of cloud-based solutions, the rise of mobile CRM, and the growing adoption of AI and machine learning capabilities. These trends are converging to create more integrated and user-friendly CRM platforms, enabling businesses to manage customer interactions more effectively.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on CRM Systems
AI is transforming CRM systems by automating tasks, providing intelligent insights, and enabling more personalized interactions. AI-powered chatbots can handle routine customer inquiries, freeing up human agents to address complex issues. AI algorithms can analyze customer data to predict future behaviors and tailor marketing campaigns. This leads to a more proactive and responsive approach to customer management, fostering stronger customer relationships.
Role of Machine Learning in CRM Systems
Machine learning (ML) algorithms are playing a crucial role in enhancing CRM systems. ML models can identify patterns and trends in customer data that might be missed by traditional methods. This allows businesses to segment customers more accurately, personalize recommendations, and predict potential churn. By learning from vast amounts of data, ML empowers CRM systems to provide highly targeted and effective solutions.
Innovative CRM Features
Several innovative CRM features are emerging to enhance customer experiences and business efficiency. These include predictive analytics, which can forecast customer behavior and tailor interactions; personalized recommendations, which suggest products or services based on individual preferences; and proactive support, which anticipates customer needs and provides assistance before issues arise. These features are designed to improve the efficiency of customer interactions and create more engaging experiences.
Future Direction of CRM Systems
CRM systems are evolving towards becoming more integrated, intelligent, and personalized. The future of CRM lies in its ability to anticipate customer needs, adapt to market changes, and provide actionable insights to businesses. As AI and ML become more sophisticated, CRM systems will increasingly automate tasks, provide intelligent recommendations, and personalize interactions. This shift will empower businesses to build stronger relationships with customers, foster loyalty, and drive greater business success.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, CRM systems are powerful tools for businesses seeking to cultivate stronger customer relationships and enhance operational efficiency. The guide highlighted the multifaceted nature of CRM, from defining and selecting the right system to ensuring its successful implementation and ongoing maintenance. Understanding the different types, functionalities, and security considerations is crucial for maximizing the return on investment and achieving strategic business goals. The future of CRM is bright, promising further integration with innovative technologies to optimize business operations and drive customer satisfaction.