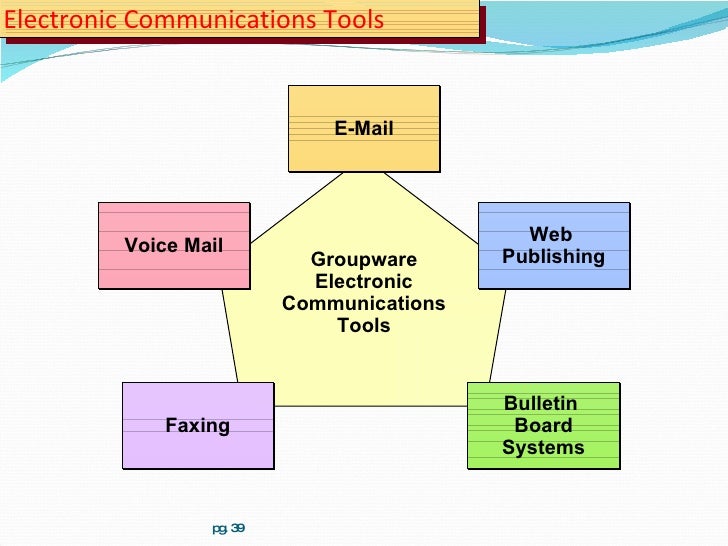
Right, so groupware – it’s basically software designed for teams to work together. Think shared documents, instant messaging, project management – all in one place. It’s been around for a while, but the way we use it is constantly evolving. From simple file-sharing to complex project management systems, groupware is changing how we collaborate and get things done. It’s a game-changer, really.
This Artikel dives deep into the world of groupware, exploring its definition, features, applications across various industries, implementation strategies, security concerns, and future trends. We’ll unpack the different types of groupware, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses. We’ll also look at how groupware can revolutionize collaboration and productivity in everything from education to healthcare to business.
Defining Groupware
Groupware, encompassing a wide array of applications, facilitates collaborative work among individuals and teams. It transcends traditional methods of communication and information sharing, offering streamlined processes and enhanced productivity. Its core functionality lies in enabling collective action and knowledge management within a group setting.
Groupware’s purpose is to create a digital space where individuals can interact, share information, and complete tasks together. This digital environment allows for improved communication, streamlined workflows, and increased efficiency in project execution. It moves beyond individual software tools, focusing on enabling group dynamics and knowledge sharing.
Key Characteristics of Groupware
Groupware possesses several key characteristics that differentiate it from other collaborative tools. These characteristics include: centralized data storage, version control for documents, and support for various communication methods (e.g., email, instant messaging, forums). Groupware also often provides a shared workspace for project management, scheduling, and task assignment. Crucially, it promotes the efficient sharing of information and knowledge across a team.
Evolution of Groupware
The development of groupware has been a gradual process, evolving alongside technological advancements. Early forms of groupware were primarily focused on document sharing and basic communication. As technology progressed, more sophisticated functionalities were added, such as project management tools, calendars, and shared workspaces. The introduction of the internet and networked computers accelerated the growth of groupware, enabling broader access and greater collaboration.
Types of Groupware Applications
Groupware applications are categorized based on their functionalities. These categories include: communication, document sharing, and project management. Each category offers specific features designed to enhance collaboration within a team or organization.
- Communication Groupware: These applications facilitate real-time or asynchronous communication. They enable teams to share information, discuss ideas, and coordinate tasks in a structured manner. Examples include instant messaging platforms and video conferencing tools.
- Document Sharing Groupware: These applications support the creation, editing, and version control of documents. This allows multiple users to work on the same document simultaneously, ensuring everyone has access to the latest version. Document sharing also includes the ability to track changes, facilitating version control and collaboration.
- Project Management Groupware: These applications are designed to help teams manage projects from initiation to completion. They often include features for task assignment, scheduling, progress tracking, and communication between team members.
Prominent Groupware Systems
Several prominent groupware systems have emerged, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. These systems have played a significant role in shaping the landscape of modern collaboration.
- Microsoft Teams: A widely used platform, Microsoft Teams combines communication, file sharing, and project management features. Its strength lies in its integration with other Microsoft products, providing a seamless user experience for those already using the suite. However, its extensive feature set can sometimes be overwhelming for users unfamiliar with the platform.
- Slack: Known for its focused communication features, Slack excels at fostering team discussions and real-time interactions. Its strength is its ability to organize communication into channels, facilitating targeted conversations. However, Slack may not be ideal for complex project management tasks.
- Google Workspace: A suite of collaborative applications, Google Workspace provides document sharing, email, calendar, and video conferencing. Its strength lies in its ease of use and accessibility across different devices. However, its project management capabilities might be less robust than dedicated project management software.
Comparison of Groupware Categories
| Category | Description | Example | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Communication | Facilitates real-time or asynchronous communication | Slack, Microsoft Teams | Enhanced team communication, real-time collaboration | May not be suitable for complex project management tasks |
| Document Sharing | Supports creation, editing, and version control of documents | Google Docs, Microsoft Word Online | Version control, multiple users editing simultaneously | May not include comprehensive project management features |
| Project Management | Manages projects from initiation to completion | Asana, Trello | Task assignment, scheduling, progress tracking | May not offer robust communication features |
Features and Functions
Groupware solutions are crucial for enhancing team collaboration and productivity. Effective groupware goes beyond simple file sharing; it encompasses a suite of features and functions designed to streamline workflows, foster communication, and facilitate knowledge sharing. This section will explore the key features and functions that distinguish successful groupware systems, highlighting their impact on team performance and user experience.
The core of a robust groupware system lies in its ability to support diverse team activities, from project management and communication to document collaboration and knowledge management. These functionalities empower teams to work more efficiently and effectively, ultimately leading to higher output and greater success. The user interface plays a critical role in this process, shaping the overall user experience and impacting the likelihood of adoption.
Essential Features of Effective Groupware
Essential groupware features encompass a broad range of functionalities designed to streamline workflow and enhance communication. These features are vital for supporting team activities and ensuring efficient project management. A comprehensive system should provide tools for managing projects, sharing documents, and facilitating communication among team members.
- Centralized Document Management: This feature allows for secure storage, version control, and easy retrieval of documents. It reduces the risk of losing crucial information and ensures that everyone has access to the latest versions, minimizing confusion and errors. A well-implemented system facilitates version history tracking and access control, ensuring data integrity.
- Integrated Communication Tools: Instant messaging, email, and forums are essential for facilitating real-time communication and discussion. These tools enable quick responses to queries, instant feedback loops, and efficient information exchange within the team. Effective communication tools can significantly reduce response times and increase team coordination.
- Task Management and Scheduling: Groupware should provide tools for assigning tasks, setting deadlines, and tracking progress. This ensures accountability, prevents delays, and helps manage project timelines effectively. Clear task assignment, tracking progress, and providing reminders contribute to higher team efficiency.
- Calendar and Scheduling Integration: Sharing calendars and scheduling meetings seamlessly within the groupware platform facilitates better coordination and reduces the potential for scheduling conflicts. This feature enhances efficiency by enabling teams to plan activities and allocate time effectively.
Key Functions and Impact on Productivity
Key functions of groupware significantly impact team productivity by streamlining workflows and promoting effective collaboration. These functions enhance communication, project management, and knowledge sharing.
- Project Management Tools: These tools facilitate the creation, assignment, and tracking of tasks, enabling better project management and coordination. Features such as task dependencies, milestones, and progress reports improve project visibility and allow for timely interventions in case of delays or roadblocks.
- Document Collaboration: The ability to simultaneously edit documents, track changes, and manage revisions promotes efficient collaboration and ensures everyone has access to the latest version. Features like real-time co-editing and version history contribute to the quality and accuracy of collaborative work.
- Knowledge Management Systems: These systems help capture, store, and disseminate information and expertise within the team. This ensures that team members can readily access relevant knowledge, promoting learning and reducing the need to reinvent the wheel.
User Interface and Usability
The user interface (UI) of groupware plays a crucial role in its adoption and usability. A well-designed UI is intuitive and user-friendly, enabling easy navigation and task completion. Intuitive interfaces encourage more frequent use, leading to improved productivity.
- Intuitive Navigation: A clear and logical structure for accessing features and functions minimizes user confusion and maximizes efficiency. Users should easily find what they need without spending excessive time searching.
- Accessibility and Customization: The UI should accommodate diverse user needs and preferences, including accessibility features for users with disabilities. Customization options allow users to personalize the interface, improving their efficiency and comfort level.
- Responsiveness and Performance: A fast and responsive interface ensures a smooth user experience, reducing frustration and promoting continuous use. The system should perform efficiently even under heavy load.
Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
Groupware facilitates collaboration and knowledge sharing through various mechanisms. These mechanisms support knowledge transfer, communication, and data management within teams.
- Shared Workspaces: These virtual environments allow teams to work together on projects, share documents, and communicate effectively. Shared workspaces provide a central hub for all project-related activities.
- Discussion Forums and Chat Features: These features facilitate communication, provide a platform for questions and answers, and foster a sense of community among team members. Effective communication and knowledge sharing are crucial for successful collaboration.
- Document Version Control: This feature ensures that everyone has access to the latest version of documents, promoting collaboration and preventing inconsistencies. Version control minimizes errors and facilitates easier collaboration.
Groupware Features and Benefits
| Feature | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Centralized Document Management | Secure storage, version control, and easy retrieval of documents | Reduces information loss, ensures everyone has the latest versions, minimizes confusion, and enhances data integrity. |
| Task Management and Scheduling | Assigning tasks, setting deadlines, and tracking progress | Improves accountability, prevents delays, manages project timelines effectively, and enhances team efficiency. |
| Integrated Communication Tools | Instant messaging, email, and forums | Facilitates real-time communication, quick responses, feedback loops, and efficient information exchange, leading to increased team coordination. |
| Calendar and Scheduling Integration | Sharing calendars and scheduling meetings seamlessly | Improves coordination, reduces scheduling conflicts, and enhances efficiency by enabling teams to plan activities and allocate time effectively. |
Groupware in Specific Industries
Groupware solutions are not a one-size-fits-all tool. Their effectiveness hinges on tailoring them to the specific needs and workflows of different industries. This section explores the practical applications of groupware in education, healthcare, and business, highlighting the unique advantages it offers in each sector.
Groupware in Education
Groupware tools significantly enhance the learning and teaching experience in educational settings. They foster collaborative learning environments, allowing students to work together on projects, share resources, and communicate effectively with peers and instructors. This can lead to increased engagement and deeper understanding of subject matter.
Groupware in Healthcare
Groupware plays a critical role in healthcare by streamlining communication and collaboration among various stakeholders. Its use in patient care facilitates interdisciplinary communication, allowing doctors, nurses, therapists, and other healthcare professionals to access and share patient information in real-time. This ensures better coordinated care and reduces the risk of errors.
Groupware in Business
Groupware significantly improves productivity and efficiency in the business sector. It enhances project management by facilitating communication, task delegation, and progress tracking. Moreover, it improves communication across teams, departments, and even geographical locations, ensuring seamless information flow and timely decision-making. Groupware solutions can also automate workflows, reducing manual processes and increasing overall operational efficiency.
Examples of Industry-Specific Groupware Solutions
Several groupware solutions are tailored to address specific industry needs. For example, some solutions are designed with the educational sector in mind, featuring tools for assignment sharing, grading, and student communication. In healthcare, groupware solutions often integrate with electronic health records (EHRs) to facilitate secure data sharing and collaboration among care teams. Similarly, in business, many groupware solutions offer specialized project management tools and dashboards for tracking progress, resource allocation, and budget management.
Table of Groupware Applications Across Industries
| Industry | Groupware Application | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Education | Learning management systems (LMS), collaborative document editors, discussion forums | Improved student engagement, enhanced collaboration, streamlined communication between teachers and students, easy access to resources |
| Healthcare | Electronic health records (EHR) systems with integrated communication tools, patient portals, telehealth platforms | Improved patient care coordination, reduced medical errors, enhanced interdisciplinary communication, increased efficiency in data sharing |
| Business | Project management software, communication platforms, workflow automation tools | Improved project management, enhanced team collaboration, reduced communication delays, streamlined workflows, improved efficiency |
Groupware Implementation and Management
Implementing groupware effectively requires a structured approach that considers various factors from initial selection to ongoing maintenance. A well-implemented system can significantly enhance collaboration and productivity within an organization. Careful planning and user engagement are crucial for successful adoption and long-term sustainability.
Steps in Implementing a Groupware System
A phased approach to implementation ensures a smoother transition and minimizes disruption. The initial stage involves thorough planning and assessment. This includes identifying specific needs, evaluating existing infrastructure, and defining roles and responsibilities. Careful consideration of user input during this phase helps ensure the chosen system aligns with the organization’s workflows and culture. The second stage focuses on system configuration and integration. This includes installing the software, configuring settings, and linking it to relevant systems. Testing is crucial to ensure functionality and identify any potential issues. The final stage involves training users and monitoring the system’s performance. Continuous monitoring and feedback loops are important for identifying and addressing issues promptly.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Groupware Solution
Choosing the right groupware solution is critical for long-term success. Key factors include scalability, security, and integration capabilities. The solution should be able to adapt to the organization’s growth and evolving needs. Security features are paramount to protect sensitive data and comply with regulations. Integration with existing systems, such as email, calendar, and file sharing platforms, ensures a seamless workflow. User-friendliness is also important; a system that is intuitive and easy to navigate promotes user adoption. Vendor reputation and support are important considerations. Thorough evaluation of vendor support and their track record can help mitigate risks.
User Training for Effective Utilization
Training is essential for maximizing the benefits of groupware. Effective training programs should cover the functionality of the system, best practices for collaboration, and troubleshooting techniques. A comprehensive training program should cover the different features of the platform and how to use them effectively. Interactive sessions, practical exercises, and hands-on demonstrations are more effective than passive lectures. This enables users to learn by doing and become comfortable with the platform. Clear documentation and online resources can support ongoing learning and provide supplemental information to the initial training sessions.
Strategies for Maintaining and Upgrading the Groupware System
Maintaining a groupware system involves ongoing support and updates. Regular system backups, security audits, and performance monitoring are critical for minimizing downtime and data loss. A well-defined maintenance schedule ensures the system is kept up-to-date with security patches and bug fixes. Upgrading the system allows for the integration of new features and improvements in functionality. This should be planned and implemented in a way that minimizes disruption to users. Regular communication with users and clear communication about planned upgrades are crucial to maintain user satisfaction and minimize concerns.
Step-by-Step Guide for Implementing a Groupware Solution
- Needs Assessment and Planning: Identify specific needs, evaluate existing infrastructure, define roles and responsibilities. Consider user feedback and organizational culture during this crucial phase.
- Selection and Procurement: Evaluate potential solutions based on scalability, security, integration, user-friendliness, vendor reputation, and support. Obtain necessary approvals and procure the chosen solution.
- System Configuration and Integration: Install the software, configure settings, integrate with relevant systems. Thoroughly test functionality and identify potential issues.
- User Training and Support: Deliver comprehensive training sessions on using the platform. Provide ongoing support and resources to users. Create clear documentation and readily available support channels.
- System Maintenance and Monitoring: Implement a regular maintenance schedule. Monitor system performance, conduct security audits, and perform backups. Regularly update the system with security patches and bug fixes.
Groupware and Security

Groupware systems, while offering enhanced collaboration, introduce unique security challenges. Protecting sensitive data shared within these environments is paramount, demanding robust security measures to mitigate potential risks. This section delves into the critical security considerations for groupware, from data protection and privacy to access controls and preventative measures.
Data Protection and Privacy Concerns
Groupware systems often handle confidential information, necessitating stringent data protection policies. These policies must address data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Privacy concerns arise from the shared nature of groupware, requiring mechanisms to ensure user data is handled responsibly and in compliance with applicable regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA. Protecting sensitive data, like financial records or personal information, is a key aspect of groupware security.
Unauthorized Access Prevention
Preventing unauthorized access to groupware systems is crucial. Implementing strong authentication methods, like multi-factor authentication (MFA), is essential. These methods verify user identity beyond simple passwords, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments help identify and address potential weaknesses in the system.
Access Control Mechanisms
Access control mechanisms are fundamental to secure groupware environments. These mechanisms define who can access specific data, applications, or features within the groupware platform. Role-based access control (RBAC) is a common approach, granting different levels of access based on user roles. Granular control over access privileges allows for targeted security measures, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized individuals.
Security Threats and Risks
Several security threats and risks are inherent in groupware systems. These include malicious software (malware), phishing attacks, and social engineering tactics. Data breaches can result in significant financial and reputational damage. Insider threats, where authorized users misuse their access, are another critical concern. Furthermore, outdated software or inadequate security patches can create vulnerabilities. Understanding these threats is critical for implementing robust security measures.
Security Protocols and Best Practices
| Security Protocol | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Requires multiple forms of authentication to verify user identity (e.g., password, security token, biometric scan). | Increases security by adding an extra layer of protection, making it significantly harder for unauthorized individuals to access accounts. |
| Regular Security Audits | Systematic reviews of the groupware system’s security posture, identifying potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses. | Proactively identifies and addresses security gaps before they can be exploited, enhancing the overall security posture. |
| Strong Password Policies | Enforces complex password requirements, preventing simple and easily guessed passwords. | Reduces the risk of password cracking and unauthorized access to accounts. |
| Data Encryption | Converting data into an unreadable format to protect sensitive information during transmission and storage. | Ensures confidentiality and integrity of data, even if intercepted. |
| Regular Software Updates | Ensuring all software components are up-to-date with the latest security patches. | Addresses known vulnerabilities and enhances overall security, protecting against exploitation by hackers. |
Future Trends in Groupware
Groupware systems are constantly evolving to meet the dynamic needs of modern teams and organizations. The future of groupware promises innovative solutions, leveraging emerging technologies to enhance collaboration, communication, and productivity. This section explores key trends shaping the future of groupware, including the impact of artificial intelligence and machine learning.
Emerging Technologies Impacting Groupware
The integration of cutting-edge technologies like cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and blockchain is reshaping groupware applications. Cloud-based platforms offer scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness, enabling seamless collaboration across geographical boundaries. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are poised to revolutionize how groupware systems analyze user behavior and preferences, proactively suggesting relevant information and streamlining workflows.
Innovative Solutions and Advancements
Several innovative solutions are emerging in the field of groupware. These include intelligent document processing, which leverages AI to automate tasks like data extraction and analysis from documents, reducing manual effort and increasing efficiency. Predictive analytics capabilities are also anticipated to improve team performance by identifying potential bottlenecks and optimizing resource allocation. Further, virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR) technologies are being explored for immersive collaboration experiences, enabling teams to work together in virtual spaces, regardless of their physical locations.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Groupware
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are set to play a crucial role in the future of groupware. AI-powered chatbots can handle routine tasks, answer user queries, and provide real-time support. Machine learning algorithms can analyze user data to personalize the groupware experience, suggesting relevant information and workflows tailored to individual needs. For instance, an AI-powered calendar could automatically suggest meeting times based on user availability and preferences. Furthermore, ML algorithms can analyze communication patterns within teams to identify potential conflicts or misunderstandings, proactively suggesting solutions.
Future Groupware Features and Functionalities
The future of groupware is likely to feature more sophisticated tools for project management, communication, and knowledge sharing. Expect AI-driven project planning tools that automatically assess tasks, allocate resources, and predict potential delays. Advanced communication features will likely incorporate AI-powered summarization and translation tools, enabling seamless collaboration across linguistic barriers. Knowledge management systems will also become more intelligent, automatically organizing and categorizing information, making it easier for users to find what they need.
Summary of Future Trends and Potential Impact
| Trend | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| AI-powered automation | Groupware applications leveraging AI to automate tasks, personalize user experience, and improve decision-making. | Increased efficiency, reduced manual effort, improved accuracy, and enhanced user satisfaction. |
| Intelligent document processing | AI-driven tools for extracting, analyzing, and summarizing information from documents, streamlining workflow. | Improved data management, faster information retrieval, and enhanced collaboration. |
| Predictive analytics | Groupware systems using predictive models to forecast trends, identify potential problems, and optimize resource allocation. | Enhanced decision-making, proactive risk management, and improved team performance. |
| Immersive collaboration | Integration of VR/AR technologies for virtual collaboration experiences. | Improved communication, enhanced team cohesion, and creation of new possibilities for collaborative work. |
Closure
So, groupware is more than just a tool; it’s a way of working. We’ve seen how it shapes collaboration, productivity, and efficiency across industries. From defining its core features to exploring its future, we’ve covered a lot of ground. It’s clear that groupware is here to stay, evolving to meet the ever-changing demands of modern teams.
Ultimately, understanding groupware is key to leveraging its power to streamline operations and boost productivity in any sector. The future looks bright for collaborative tools, and groupware is leading the charge.