Microsoft Project is a powerful project management tool used by professionals across various industries. This guide delves into the core functionalities of MS Project, from its different versions and supported methodologies to advanced features and integration with other applications. Understanding MS Project can significantly enhance project planning, execution, and ultimately, success.
This comprehensive exploration covers everything from basic project setup and task management to resource allocation, budgeting, reporting, and advanced features. It will provide a practical understanding of how MS Project can be used effectively to streamline complex projects and achieve desired outcomes.
Introduction to MS Project
Microsoft Project is a powerful project management software application designed to help users plan, schedule, track, and manage projects effectively. It offers a comprehensive suite of tools for defining project scope, assigning tasks, setting deadlines, and monitoring progress against the schedule. Its user-friendly interface and robust features make it a popular choice for project managers across various industries.
The core functionalities of MS Project encompass the entire project lifecycle, from initiation to closure. It allows users to create detailed work breakdown structures (WBS), define dependencies between tasks, allocate resources to tasks, and generate reports on project progress. These features facilitate proactive risk management, enabling project managers to anticipate potential delays and adjust plans accordingly.
Core Functionalities of MS Project
Microsoft Project empowers project managers with a suite of tools for comprehensive project management. These functionalities include creating work breakdown structures (WBS), assigning tasks and deadlines, allocating resources, and managing dependencies. The software also supports detailed scheduling, resource leveling, and generating various reports to track progress and identify potential issues. A key strength lies in its ability to integrate with other Microsoft Office applications, streamlining workflow and data management.
Different Versions of MS Project
Over the years, Microsoft Project has evolved with new versions offering enhanced functionalities and features. Each version builds upon the previous one, incorporating improvements in usability, reporting, and integration with other applications. Key differences between versions include:
- Project Standard: This version offers basic features for managing projects, ideal for smaller projects and teams. It provides essential tools for planning, scheduling, and tracking progress.
- Project Professional: Designed for larger, more complex projects, this version offers advanced features like resource leveling, collaboration tools, and extensive reporting capabilities. It’s suited for projects involving multiple teams and intricate dependencies.
- Project Online: This cloud-based version facilitates collaboration and remote project management. It allows multiple users to access and work on project plans concurrently, streamlining communication and enhancing teamwork across geographical boundaries.
The choice of version depends on the project’s scale, the team’s size, and the specific needs of the project management process.
Project Management Methodologies Supported
MS Project supports various project management methodologies, enabling users to adapt their project management approach to suit their specific needs. This flexibility is crucial for managing projects in diverse industries and environments. Examples of supported methodologies include:
- Agile: The software’s adaptability allows users to customize the project plan to reflect the iterative nature of Agile projects. This adaptability is essential for managing evolving requirements and responding to changing market dynamics.
- Waterfall: The sequential nature of the Waterfall methodology can be effectively managed using MS Project’s task dependency features. This ensures each stage of the project is completed before the next begins.
- Critical Path Method (CPM): MS Project allows users to identify and analyze the critical path, enabling them to focus resources and time on the most critical tasks to optimize project timelines.
MS Project vs. Other Project Management Software
A comparison of MS Project with other prominent project management software reveals strengths and weaknesses across various aspects.
| Feature | MS Project | Alternative Software (e.g., Asana, Jira) |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | Generally user-friendly, especially for users familiar with Microsoft Office applications. | Often praised for intuitive interfaces, tailored for specific needs. |
| Collaboration | Collaboration features are present, but might not be as robust as dedicated collaboration tools. | Stronger focus on team collaboration and communication. |
| Reporting | Excellent reporting capabilities, producing various visual and detailed reports. | May offer customizable reports, but depth might be less comprehensive. |
| Integration | Excellent integration with other Microsoft Office products. | Often integrate with other project management tools and platforms. |
| Cost | Licenses can vary depending on the version and number of users. | Often subscription-based models, with pricing varying based on features and user counts. |
Choosing the right software depends on the specific requirements of the project and the project team’s familiarity with the tool.
Project Planning with MS Project
Mastering project planning is crucial for success. Microsoft Project offers a robust suite of tools to streamline this process, enabling project managers to visualize, schedule, and track progress effectively. This comprehensive approach allows for proactive identification and mitigation of potential roadblocks. By utilizing MS Project’s features, teams can optimize resource allocation, ensure timely completion, and ultimately, achieve project objectives.
Defining clear project scope and objectives is paramount to successful project planning. Understanding the project’s deliverables, timelines, and resource constraints allows for informed decision-making throughout the project lifecycle. MS Project provides a structured environment for meticulously detailing each stage, enabling project managers to visualize the entire process and allocate resources effectively.
Setting Up a New Project
Establishing a new project in MS Project involves defining its parameters and scope. This includes inputting project details, such as the project name, description, start and end dates, and anticipated duration. The project manager should also specify the project’s objectives and deliverables. Thorough documentation of these elements establishes a solid foundation for subsequent planning and execution. Crucially, this initial setup phase ensures that all project stakeholders are aligned on the project’s core goals.
Defining Tasks and Assigning Resources
Project tasks are the individual components that contribute to the overall project goal. Defining tasks involves breaking down the project into smaller, manageable units. A well-defined task list includes detailed descriptions of the work to be performed, anticipated duration, and associated resources. This granular approach allows for accurate resource allocation. Resource assignment in MS Project involves assigning specific individuals or teams to particular tasks. This crucial step ensures that the required skills and expertise are allocated to the right components of the project. Properly defining tasks and assigning resources minimizes potential conflicts and bottlenecks.
Estimating Durations
Estimating task durations is a critical aspect of project scheduling. Accuracy in these estimations is vital to creating a realistic project schedule. Methods for estimating task durations include expert judgment, historical data analysis, and work breakdown structure (WBS) analysis. Utilizing a combination of these techniques leads to more reliable estimates. An accurate duration estimate is critical for creating a realistic project schedule, enabling effective resource management and timely completion. For instance, if a task requires 10 days of effort and is assigned to a team member with a consistent 8-hour workday, the duration estimate would reflect that reality.
Creating a Project Schedule
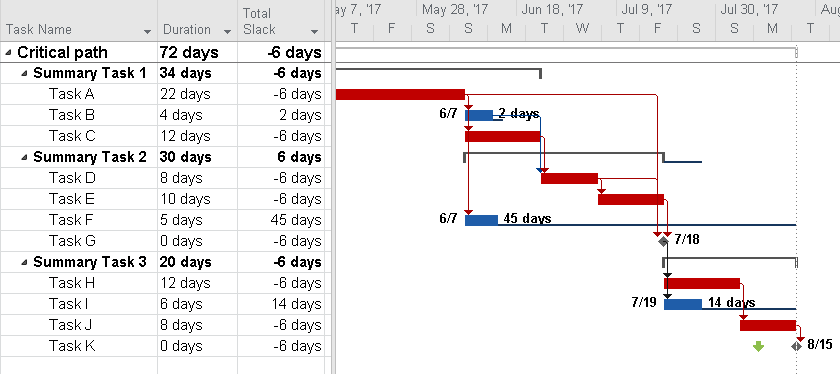
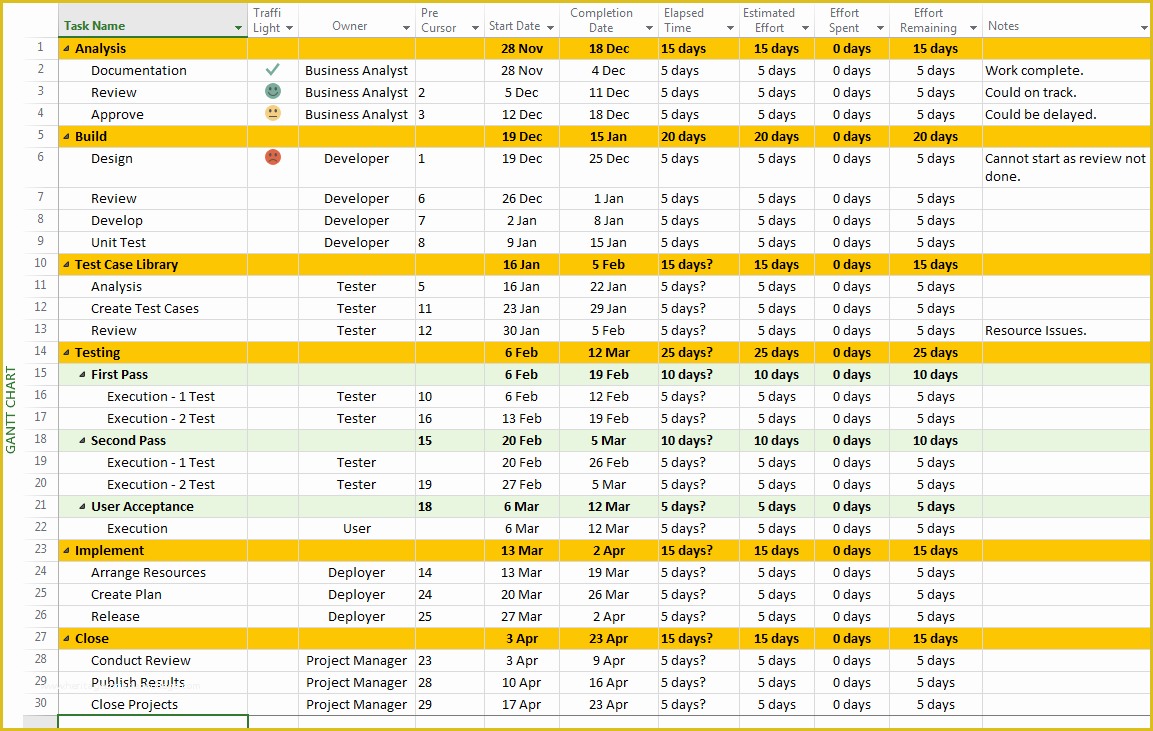
Creating a project schedule in MS Project involves linking tasks together, defining dependencies, and assigning durations. The software allows for visualization of the entire project timeline. A well-organized schedule helps in tracking progress, identifying potential delays, and proactively addressing risks. MS Project’s features allow for the creation of various views, including Gantt charts and network diagrams, facilitating an easy comprehension of the project timeline. This aids in making informed decisions and in identifying potential issues early.
Managing Dependencies Between Tasks
Dependencies between tasks are crucial in project management. Tasks are frequently reliant on others’ completion. MS Project allows for defining these relationships to ensure that tasks are completed in the correct sequence. Understanding these dependencies is critical to preventing delays and ensuring that resources are available when needed. For example, a task to design a website cannot begin until the design brief is finalized, showcasing the linear dependence between these tasks.
Tracking Progress and Identifying Potential Delays
MS Project provides tools to track progress against the planned schedule. By monitoring actual completion dates against planned ones, potential delays can be identified early. Project managers can then take corrective actions to mitigate these risks. The software offers a variety of reporting tools to analyze project progress and identify areas that require attention. This proactive approach helps in preventing project delays. Regular progress reports enable a project manager to identify variances between planned and actual progress.
Task Views in MS Project
MS Project offers various task views to visualize different aspects of the project. Understanding these views allows for a comprehensive perspective of the project’s status. This ability to tailor views is critical for various stakeholder needs.
| Task View | Description |
|---|---|
| Gantt Chart | Visualizes tasks as bars on a timeline, displaying dependencies and durations. |
| Network Diagram | Depicts tasks as nodes and dependencies as arrows, highlighting the logical flow. |
| Resource Sheet | Displays resource allocation across tasks, enabling capacity planning. |
| Task Usage | Demonstrates the allocation of resources to tasks, facilitating resource optimization. |
| Summary Task | Displays high-level project milestones, enabling overall progress monitoring. |
Resource Management in MS Project
Effective project management hinges on efficient resource allocation and control. MS Project provides robust tools for managing resources, enabling project managers to optimize schedules, anticipate potential bottlenecks, and ensure project success. Understanding how to assign resources, manage their availability, and resolve conflicts is crucial for achieving desired outcomes. This section explores these critical aspects within the MS Project environment.
Resource allocation is a cornerstone of successful project completion. By meticulously assigning resources to tasks, project managers can accurately predict project timelines, anticipate resource constraints, and ensure optimal utilization of available personnel and equipment. This section details the process of assigning resources in MS Project, including strategies for managing resource availability and resolving conflicts. It also covers the pivotal role of resource leveling in optimizing project schedules.
Assigning Resources to Tasks
Resource assignment in MS Project involves linking personnel, equipment, or materials to specific tasks. This process allows project managers to track resource utilization, estimate task durations, and proactively address potential resource constraints. Accurate resource assignments are vital for creating realistic project schedules and for informed decision-making throughout the project lifecycle. MS Project provides several methods for assigning resources, including individual assignment and bulk assignment. Individual assignment allows for fine-grained control over resource allocation, while bulk assignment facilitates efficient allocation of resources to multiple tasks simultaneously. Utilizing these assignment options ensures project managers can maintain an accurate overview of resource utilization.
Managing Resource Availability and Constraints
Resource availability is a crucial factor in project scheduling. MS Project allows project managers to define resource calendars that reflect the availability of resources. These calendars account for factors like vacation time, project commitments, and other obligations. Defining these calendars is essential for realistic scheduling and for identifying potential conflicts in resource utilization. Project managers should proactively manage resource constraints to ensure timely completion of tasks. This includes monitoring resource utilization, anticipating potential bottlenecks, and adjusting schedules accordingly. This proactive approach helps in minimizing delays and maximizing project efficiency. Managing constraints includes utilizing MS Project’s features to model and track resource availability, as well as understanding and adjusting for constraints like time-off, overtime policies, and resource-specific skill sets.
Resolving Resource Conflicts
Resource conflicts often arise during project execution, where multiple tasks demand the same resource simultaneously. MS Project provides tools for identifying and resolving these conflicts. Methods for resolving resource conflicts include adjusting task durations, assigning additional resources to a task, rescheduling tasks, and adjusting resource calendars. Proactive conflict resolution can prevent significant delays and maintain project momentum. Understanding the different techniques for conflict resolution is critical for successful project management.
Resource Leveling in MS Project
Resource leveling is a crucial technique for optimizing resource allocation in MS Project. It adjusts task start and finish times to smooth out resource demand, ensuring that resources are not overloaded. Resource leveling helps to create more realistic schedules by avoiding overallocation of resources to tasks. This approach minimizes potential delays caused by resource conflicts and maintains a sustainable pace of work. Resource leveling in MS Project aims to create a more balanced and efficient project schedule.
Resource Allocation Strategies
| Strategy | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Allocation | Assigns specific resources to tasks, without flexibility. | Provides clarity and control over resource usage. | Can lead to resource overallocation or underutilization if not carefully planned. |
| Variable Allocation | Allows resources to be assigned to tasks based on availability and demand. | More flexible and adaptable to changing circumstances. | Requires careful monitoring to prevent resource conflicts. |
| Resource Pooling | Assigns resources to a pool, allowing for dynamic assignment based on task requirements. | Maximizes resource utilization. | Requires sophisticated resource management tools and careful planning. |
Resource allocation strategies influence project timelines and resource utilization. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each approach allows project managers to choose the most suitable strategy for their specific project needs.
Budgeting and Cost Management in MS Project
Effective project management hinges on accurate cost estimations and meticulous tracking. MS Project provides robust tools for budgeting and cost management, allowing project managers to anticipate and mitigate potential cost overruns. This section delves into the functionalities within MS Project for creating, tracking, and analyzing project budgets.
MS Project’s cost management features enable project teams to meticulously monitor expenses against planned budgets, facilitating proactive adjustments and ultimately ensuring project success. This detailed analysis of cost management within MS Project empowers project managers to make data-driven decisions, enabling them to effectively allocate resources and maintain budgetary control throughout the project lifecycle.
Creating and Managing Budgets in MS Project
Project budgets are established by assigning costs to tasks and resources within MS Project. This process involves estimating material costs, labor hours, and other associated expenses. Users can define cost codes to categorize expenses, improving the organization and analysis of project costs. Budgeting in MS Project enables detailed tracking of individual tasks and resources, facilitating a granular understanding of project expenditures. A well-defined budget provides a baseline for evaluating actual costs and identifying potential deviations.
Cost Tracking Methods in MS Project
MS Project supports various cost tracking methods, empowering project managers to monitor expenses effectively. These methods include:
- Actual Cost Tracking: This method involves recording the actual costs incurred for each task or resource. Comparing actual costs against the planned budget helps identify variances and potential issues early on.
- Earned Value Management (EVM): EVM is a comprehensive method for tracking project progress and cost performance. It evaluates the value of completed work against the planned budget, enabling proactive adjustments to address potential overruns or delays.
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Costing: Project costs are broken down by work packages in the WBS, providing a detailed view of costs associated with specific deliverables. This granular approach helps pinpoint areas of high expenditure and potential cost issues.
These methods allow for a multifaceted analysis of cost performance, facilitating timely interventions and improved project outcomes.
Analyzing Cost Variances and Potential Cost Overruns
Identifying cost variances and potential overruns is crucial for effective project management. MS Project’s reporting capabilities facilitate the analysis of cost variances. This process involves comparing planned costs to actual costs. Understanding the reasons behind cost discrepancies is vital for mitigating potential overruns. Tools like cost-performance curves provide visual representations of cost variances, aiding in the identification of problem areas.
By proactively monitoring cost variances, project managers can adjust strategies to stay within budget and avoid significant overruns. Early identification of deviations helps in making informed decisions to rectify potential issues.
Creating Cost Reports in MS Project
MS Project provides a suite of tools for generating comprehensive cost reports. These reports provide insights into project expenditures, facilitating informed decision-making. Different reports can be tailored to specific needs, such as detailed task-level costs or resource-based expense breakdowns. Cost reports are essential for communicating project status to stakeholders and obtaining necessary approvals for budget adjustments. These reports also serve as historical records for future project planning. For example, a cost report might highlight unexpected material costs exceeding the initial budget.
Comparison of Cost Management Features Across MS Project Versions
| Feature | MS Project 2019 | MS Project 2021 | MS Project Online |
|---|---|---|---|
| Budgeting | Supports detailed budget creation and tracking. | Enhanced budgeting features, including integrated cost codes. | Cloud-based budgeting, accessible from anywhere. |
| Cost Tracking | Offers various cost tracking methods. | Improved cost tracking accuracy and reporting. | Real-time cost tracking and visualization. |
| Cost Variance Analysis | Provides tools for cost variance analysis. | Advanced tools for analyzing cost variances and forecasting. | Cloud-based tools for monitoring and forecasting costs. |
| Reporting | Generates various cost reports. | Improved reporting options and visualizations. | Interactive dashboards and reports accessible through web browsers. |
This table summarizes the key cost management features across different MS Project versions. The evolution of MS Project reflects an increasing emphasis on sophisticated tools for project cost control.
Reporting and Visualization in MS Project
MS Project offers a robust suite of reporting and visualization tools, empowering project managers to monitor progress, identify potential issues, and communicate project status effectively. These features are crucial for staying on track, managing resources, and ensuring project success. Comprehensive reporting allows for a deeper understanding of project performance and helps to anticipate and address challenges.
Available Reporting Options
MS Project provides a diverse range of reporting options, ranging from basic summaries to detailed breakdowns. These options cater to different needs and perspectives within a project. The types of reports vary from Gantt charts and task details to resource utilization and cost breakdowns. Selecting the right report type is critical to effectively communicating project information.
Generating Customized Reports
Customization options within MS Project enable the creation of tailored reports that address specific needs. Project managers can filter data based on criteria like task status, resource allocation, or cost categories. This level of granularity is crucial for identifying trends, pinpointing potential bottlenecks, and making data-driven decisions. For example, a project manager might want to see a report specifically on tasks assigned to a particular team member, allowing them to assess individual performance and resource allocation efficiency. Furthermore, users can modify the appearance of the report, such as the colors, fonts, and layouts.
Creating Visual Representations of Project Data
Visual representations are essential for understanding project data quickly and effectively. MS Project’s graphical tools enable users to convert numerical and textual data into charts and graphs. This enhances the comprehension of project performance and enables more insightful analysis. By using visual representations, project managers can easily identify trends, potential issues, and the overall project health at a glance.
Using Charts and Graphs to Display Project Progress
Visualizations, such as Gantt charts, are integral to tracking project progress. These charts visually represent tasks, dependencies, and deadlines, enabling project managers to see the overall project schedule and potential delays or conflicts. Bar charts can also be used to illustrate progress against milestones and deliverables. These graphs allow project managers to quickly assess the project’s progress and identify potential roadblocks. For example, a Gantt chart can display the sequence of tasks, durations, and dependencies, making it easy to identify potential delays and adjust the project plan accordingly.
Types of Project Reports
| Report Type | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Gantt Chart | Visually displays project schedule, tasks, dependencies, and deadlines. | Provides a comprehensive overview of the project timeline and task relationships. |
| Task Usage Report | Details the allocated resources and their work hours. | Tracks resource utilization, identifying potential over-allocation or under-utilization. |
| Resource Allocation Report | Displays the assignment of resources to tasks. | Manages resource availability and ensures efficient task distribution. |
| Cost Report | Provides a breakdown of project costs, including labor, materials, and expenses. | Monitors project budget, identifies cost overruns, and helps in cost control. |
| Earned Value Report | Measures project performance against the baseline plan. | Provides an objective evaluation of project progress, cost, and schedule performance. |
This table provides a concise overview of different report types available in MS Project, highlighting their key features and applications. Choosing the right report type allows project managers to focus on the most pertinent information.
Advanced Features of MS Project
Microsoft Project, while a powerful tool for basic project planning, unlocks even greater potential with its advanced features. These features extend beyond the core functionalities, empowering project managers to handle complex projects with enhanced precision, risk mitigation, and collaboration. Leveraging these advanced capabilities can significantly improve project outcomes, leading to higher success rates and more efficient resource allocation.
Advanced features in MS Project provide tools to go beyond basic scheduling and resource allocation, allowing for a more comprehensive and strategic approach to project management. This encompasses factors like risk assessment, collaboration, and detailed cost analysis, enabling managers to proactively address potential challenges and make data-driven decisions.
Scheduling Tools
Sophisticated scheduling tools in MS Project go beyond simple Gantt charts. These tools allow for more granular control over task dependencies, resource allocation, and critical path identification. They include features for handling complex dependencies, resource constraints, and schedule compression techniques. This precise control enables project managers to identify potential bottlenecks and proactively adjust the schedule to maintain on-time project delivery. For instance, MS Project’s network diagrams visually depict the logical relationships between tasks, making it easier to understand the overall project flow and identify critical path dependencies. This visualization allows project managers to understand the impact of delays in one task on the entire project schedule. Further, the tool can simulate different scenarios to evaluate the project’s resilience to unexpected events.
Risk Management Tools
MS Project’s risk management tools facilitate proactive identification and mitigation of potential project risks. These tools enable the definition of potential risks, their associated probabilities, and the impact they might have on the project schedule or budget. Project managers can then develop mitigation strategies to address these risks. For example, if a key resource is identified as a potential risk due to potential unavailability, the tool can be used to analyze the impact of their absence on the project schedule and identify backup resources. Using these features, project managers can gain a more comprehensive view of potential project roadblocks and create contingency plans to address them effectively. This proactive approach to risk management can minimize the chances of project delays or cost overruns.
Collaboration Tools
MS Project’s collaboration features enable seamless communication and information sharing among project stakeholders. These tools provide mechanisms for sharing project plans, updates, and progress reports with team members and clients. This collaborative environment fosters better communication and reduces potential misunderstandings. For instance, the ability to assign tasks and track progress to individual team members allows for real-time visibility into the project status, enabling stakeholders to understand the progress and potential roadblocks. The integrated communication features facilitate quick feedback loops, ensuring everyone is on the same page and aligned with the project goals.
Custom Fields and Views
Custom fields and views allow project managers to tailor MS Project to their specific project needs. This enhancement enables project managers to collect and analyze relevant data not included in the standard MS Project fields. For example, a construction project might need custom fields for material costs, equipment usage, or weather conditions. Creating custom views allows the user to display the information in a way that best suits their needs. This level of customization is particularly useful for industries with unique project requirements.
Industry Specific Examples
- Construction: MS Project can manage complex construction projects by tracking material deliveries, equipment usage, and labor hours, enabling better cost control and scheduling. Detailed project plans, with milestones for each stage, help ensure the project stays on track.
- Software Development: MS Project is valuable for managing software development projects. Task dependencies can be mapped out, and timelines for each phase of the project, from design to testing, can be visualized. This helps track the progress of each module and ensure the final product meets the requirements.
Advantages of Advanced Features
| Feature | Key Advantages |
|---|---|
| Scheduling Tools | Improved accuracy, enhanced control over dependencies, identification of bottlenecks, proactive schedule adjustments. |
| Risk Management Tools | Proactive risk identification, mitigation strategies, contingency planning, minimized project delays/cost overruns. |
| Collaboration Tools | Seamless communication, improved information sharing, reduced misunderstandings, better stakeholder alignment. |
| Custom Fields and Views | Tailored data collection and analysis, enhanced project visualization, better understanding of project specifics, improved decision-making. |
Integration with Other Tools
Microsoft Project’s power extends beyond its own features by seamlessly integrating with other Microsoft applications and project management software. This integration streamlines workflows, enhances data sharing, and promotes a holistic project management approach. Leveraging these connections allows users to avoid data silos and maintain a unified view of project progress.
Integration with Microsoft Applications
Microsoft Project integrates deeply with other Microsoft Office applications, particularly Excel and SharePoint. This integration facilitates the exchange of data and enhances project management efficiency. Project data can be imported and exported in various formats, enabling the creation of reports, charts, and dashboards that enhance project visibility.
Importing and Exporting Data
Data exchange between MS Project and other applications is crucial for effective project management. Import capabilities allow users to pull data from external sources, such as Excel spreadsheets containing resource assignments or task durations, into MS Project. Conversely, export functions enable users to extract project data, such as schedules or budgets, and share it with other stakeholders. This flexibility enables project managers to leverage the strengths of different applications within the Microsoft ecosystem.
Benefits of Integration with Other Project Management Software
Integration with other project management software provides numerous benefits. For example, data consistency and accuracy are maintained across different project management tools. This reduces errors and allows for better collaboration between team members. Furthermore, the seamless transfer of project data can streamline project reporting and analysis. The ability to share data with other project management tools can help manage multiple projects or workstreams concurrently.
Examples of Integration
A common example of integration is importing resource availability data from an Excel spreadsheet into MS Project. This allows project managers to account for the time constraints of individual team members. Another example involves using SharePoint to store project documents and collaborate on tasks. This facilitates easy access to project-related files and encourages team communication.
Data Format Table for Integration
| Application | Common Data Formats | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Excel | CSV, XLSX, XLS | These formats allow for the import and export of data such as task details, resource assignments, and costs. |
| Microsoft SharePoint | Lists, Libraries | SharePoint allows for storing project documents and facilitating collaboration on tasks, effectively supporting the integration. |
| Other Project Management Software (e.g., Asana, Trello) | CSV, APIs | APIs and CSV files facilitate data exchange between different project management tools. This is becoming increasingly common, but the specific format varies by the third-party software. |
Best Practices for MS Project
Mastering MS Project requires adherence to best practices that streamline project planning, scheduling, and execution. These practices ensure projects stay on track, within budget, and deliver desired outcomes. Effective use of MS Project, coupled with sound project management principles, is crucial for successful project completion.
Optimizing MS Project implementation necessitates understanding and applying key best practices. These strategies focus on efficient planning, meticulous scheduling, and proactive communication throughout the project lifecycle. This includes maintaining clear documentation, fostering open communication, and remaining organized within the MS Project environment. By incorporating these practices, project managers can effectively leverage MS Project’s capabilities to achieve their objectives.
Project Planning Best Practices
Effective project planning in MS Project involves a systematic approach to defining project scope, objectives, and deliverables. This includes developing detailed work breakdown structures (WBS) to break down large projects into manageable tasks. Defining clear success criteria and assigning realistic timelines are also vital for successful project outcomes. Furthermore, a well-defined communication plan should be integrated into the project plan.
- Establish Clear Scope and Objectives: Clearly defining project scope, deliverables, and acceptance criteria from the outset minimizes ambiguity and prevents scope creep. A detailed scope statement, accessible to all stakeholders, ensures everyone understands the project’s boundaries and expected outcomes.
- Develop a Comprehensive WBS: Breaking down complex projects into smaller, manageable tasks using a WBS facilitates better task organization, estimation, and scheduling within MS Project. This ensures a structured approach to planning and execution.
- Set Realistic Timelines and Milestones: Defining realistic timelines for tasks and milestones helps in creating a project schedule that is achievable and avoids unrealistic expectations. Consider historical data and resource availability when estimating task durations.
Scheduling Best Practices
Effective scheduling within MS Project is critical for project success. This involves creating a detailed schedule that considers task dependencies, resource availability, and potential risks. Ensuring the project schedule is regularly reviewed and updated is crucial to maintaining alignment with project objectives.
- Define Task Dependencies: Identifying and documenting task dependencies is crucial for creating a logical and accurate project schedule. MS Project’s features allow for visual representation of these dependencies, helping to avoid conflicts and ensure smooth task sequencing.
- Utilize Resource Allocation Effectively: Efficient resource allocation is key to managing project timelines. MS Project allows for assigning resources to tasks, considering their availability and workload. Over-allocation of resources can lead to delays, and careful planning is needed.
- Establish Realistic Task Durations: Accurately estimating task durations based on historical data or expert judgment is essential for creating a reliable project schedule. Avoid over-optimistic estimates that can lead to schedule slippage.
Execution Best Practices
Monitoring and controlling project execution in MS Project is vital for staying on track. This involves regularly tracking progress against the schedule, identifying and addressing issues promptly, and adapting to changing circumstances.
- Track Progress Regularly: Regular progress tracking allows for early identification of potential delays or deviations from the project plan. MS Project’s reporting features provide valuable insights into project status.
- Address Issues Promptly: Identifying and addressing issues early on can prevent them from escalating and impacting the project schedule and budget. MS Project provides tools for documenting and tracking issues.
- Adapt to Changes Proactively: Project environments are dynamic; therefore, the project plan must adapt to changing requirements. Using MS Project’s features to modify the schedule and resources in response to changes is essential.
Documentation and Communication Best Practices
Effective project documentation and communication are essential for transparency and accountability. Clear communication and well-maintained documentation reduce misunderstandings and ensure everyone is on the same page.
- Maintain Comprehensive Documentation: Maintaining detailed project documentation, including meeting minutes, change requests, and risk logs, ensures that all project information is readily available and accessible to stakeholders.
- Establish Clear Communication Channels: Establishing clear communication channels and procedures ensures that information flows smoothly throughout the project lifecycle. This includes regular status meetings and updates.
- Use MS Project for Reporting: MS Project’s built-in reporting tools generate reports on project status, resource utilization, and budget. Leveraging these reports enhances transparency and promotes accountability.
Staying Organized in MS Project
Staying organized in MS Project is essential for efficient project management. This involves using MS Project’s features to create a clear and logical project structure.
- Utilize MS Project’s Features Effectively: MS Project provides various features to aid in project organization, such as views, filters, and custom fields. Maximizing these features is essential for effective project management.
- Maintain a Clean and Consistent Project Structure: A clear and consistent project structure in MS Project helps maintain order and clarity throughout the project lifecycle. This includes naming conventions for tasks, resources, and other project elements.
Key Project Management Best Practices Summary
| Best Practice Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Project Planning | Define clear scope, objectives, and deliverables; Develop comprehensive WBS; Set realistic timelines and milestones. |
| Scheduling | Define task dependencies; Utilize resource allocation effectively; Establish realistic task durations. |
| Execution | Track progress regularly; Address issues promptly; Adapt to changes proactively. |
| Documentation & Communication | Maintain comprehensive documentation; Establish clear communication channels; Use MS Project for reporting. |
| Organization | Utilize MS Project’s features effectively; Maintain a clean and consistent project structure. |
End of Discussion
In conclusion, this guide has explored the multifaceted capabilities of MS Project, providing a detailed overview of its functionalities and best practices. From foundational concepts to advanced techniques, we’ve examined how MS Project can streamline project management processes across diverse industries. By understanding and effectively utilizing the tools and techniques presented, project managers can leverage MS Project to enhance efficiency, improve outcomes, and ultimately achieve project success.