Photoshop software has revolutionized image editing, evolving from a niche tool to a cornerstone of graphic design, web design, and digital art. This guide delves into its history, core features, advanced techniques, and practical applications, providing a comprehensive overview for both beginners and seasoned users.
From fundamental image manipulation to complex compositing, color grading, and special effects, this exploration of Photoshop covers everything you need to know. We’ll trace its development, highlight key milestones, and examine the strengths and weaknesses of various versions. Learning resources and industry trends are also included, ensuring you’re well-equipped to navigate the ever-changing landscape of image editing.
Introduction to Photoshop Software
Adobe Photoshop, a cornerstone of digital image editing, has revolutionized how professionals and hobbyists alike manipulate and enhance visual content. Its evolution reflects a continuous pursuit of more sophisticated tools and features, enabling users to achieve increasingly complex and creative results. From basic image adjustments to intricate photo compositing and graphic design, Photoshop has become an indispensable tool in diverse fields.
History of Photoshop’s Evolution
Photoshop’s journey began in the early 1980s, with the initial focus on raster graphics editing. Early versions were primarily used for image retouching and basic enhancements. Key milestones marked significant leaps in functionality, leading to the powerful software we know today. The software has undergone numerous iterations, each incorporating advancements in processing power, user interface design, and a wider range of tools.
Key Milestones in Photoshop’s Development
Several pivotal moments shaped Photoshop’s trajectory. The introduction of layer-based editing, for instance, allowed for non-destructive manipulation of images, a revolutionary concept. Further enhancements included the inclusion of advanced filters and adjustments, empowering users to create unique visual effects and achieve specific artistic goals. The incorporation of sophisticated selection tools also played a crucial role in enabling precision in image manipulation.
Fundamental Concepts of Image Editing
The core concepts behind image editing in Photoshop revolve around manipulation of pixels. Pixel-based editing involves altering individual colored dots that form the image. Various tools allow for adjustments to color, brightness, contrast, and other visual properties. Selection tools isolate specific areas of the image, enabling targeted editing.
Image Formats Supported by Photoshop
Photoshop supports a wide array of image formats, including but not limited to: JPEG, PNG, TIFF, GIF, PSD. JPEG, commonly used for web images, is highly compressed but may result in some loss of quality. PNG offers lossless compression, maintaining image quality but often resulting in larger file sizes. TIFF, known for its versatility and high quality, is often preferred for professional-grade images. GIF is suitable for simple animations, while PSD is Photoshop’s native format, allowing for complete preservation of layers and adjustments. The selection of the appropriate format depends on the intended use and desired quality of the output.
Versions of Photoshop Software and Their Features
Photoshop has been released in various versions, each iteration introducing new features and enhancements. Early versions primarily focused on image editing, while later versions incorporated advanced tools for graphic design and compositing. The evolution has been continuous, with new features and capabilities being introduced in each new release. Some notable features include advanced selection tools, 3D tools, and innovative editing capabilities, making each version a valuable asset for various tasks.
Core Features and Tools
Photoshop boasts a comprehensive suite of tools for image manipulation, catering to diverse needs from basic enhancements to complex transformations. Its intuitive interface and powerful features empower users to achieve remarkable results, whether it’s correcting flaws, enhancing visual appeal, or creating entirely new artistic pieces.
Understanding the core tools and their functionalities is essential for navigating Photoshop effectively. Layers, masks, and selection tools are fundamental components, enabling precise control over various image elements. Mastering color correction and adjustment techniques allows for subtle or dramatic alterations to the overall visual impact of an image. These tools, when used effectively, elevate the image from a simple snapshot to a meticulously crafted piece of digital art.
Essential Image Manipulation Tools
Photoshop’s arsenal of tools facilitates diverse image manipulation tasks. These tools provide precision and flexibility, ranging from basic adjustments to advanced transformations. A robust selection of tools allows for precise control over specific areas of an image, opening up a world of possibilities for manipulation and enhancement.
- Selection Tools: Precise selection tools like the Lasso, Magic Wand, and Pen tools allow for intricate control over specific areas within an image. These tools are crucial for isolating elements for editing, resizing, or removing them entirely. The flexibility of these tools is evident in their use for complex selections, such as extracting objects from a background or creating intricate shapes for artistic effects.
- Retouching Tools: Photoshop provides a range of tools for retouching images, including blemish removal, skin smoothing, and other enhancements. These tools allow for the correction of imperfections and enhancement of visual appeal. Effective retouching techniques involve understanding the context and desired effect, avoiding overly processed or unnatural results.
- Drawing and Painting Tools: These tools allow for the creation of custom elements within an image. Brushes, pencils, and other drawing tools offer precise control for creating intricate details or adding artistic elements. The ability to customize brush settings and blending modes gives users a high level of control over the application of these tools.
Layers and Masks
Layers and masks are fundamental to Photoshop’s non-destructive editing approach. They enable the separation of different image elements, allowing for independent manipulation and modification without affecting the overall image.
- Layers: Photoshop’s layers system allows users to treat different image elements as independent components. This is crucial for editing, enhancing, or modifying parts of an image without affecting other parts. This non-destructive approach ensures that the original image data is preserved.
- Masks: Masks provide a way to selectively apply or hide effects to specific areas of an image. This precise control allows for subtle adjustments to the image, such as selective blending or removal of portions of an image. This non-destructive approach enables the user to experiment with different effects without permanently altering the original image data.
Color Correction and Adjustment
Color correction and adjustment tools are integral to achieving a visually appealing and accurate representation of the subject. These tools offer various options for modifying color tones, contrast, and other aspects of the image.
- Color Balance: This tool allows for the adjustment of red, green, and blue color channels within an image. Precise control over these channels enables a wide range of color correction possibilities, such as balancing out a skewed color palette or correcting inaccurate color representations. Color balance is vital in ensuring the accuracy and aesthetic appeal of the final image.
- Curves: Curves provide a more advanced method for adjusting color tones and contrast. This tool allows for non-linear adjustments, enabling users to achieve more nuanced and precise control over the image’s tonal range. This level of control is particularly valuable for achieving a specific look or feel.
- Levels: Levels provides another advanced tool for adjusting tonal values within an image. It allows for the adjustment of the image’s black point, white point, and mid-tones, leading to a more consistent and well-balanced tonal range.
Advanced Techniques
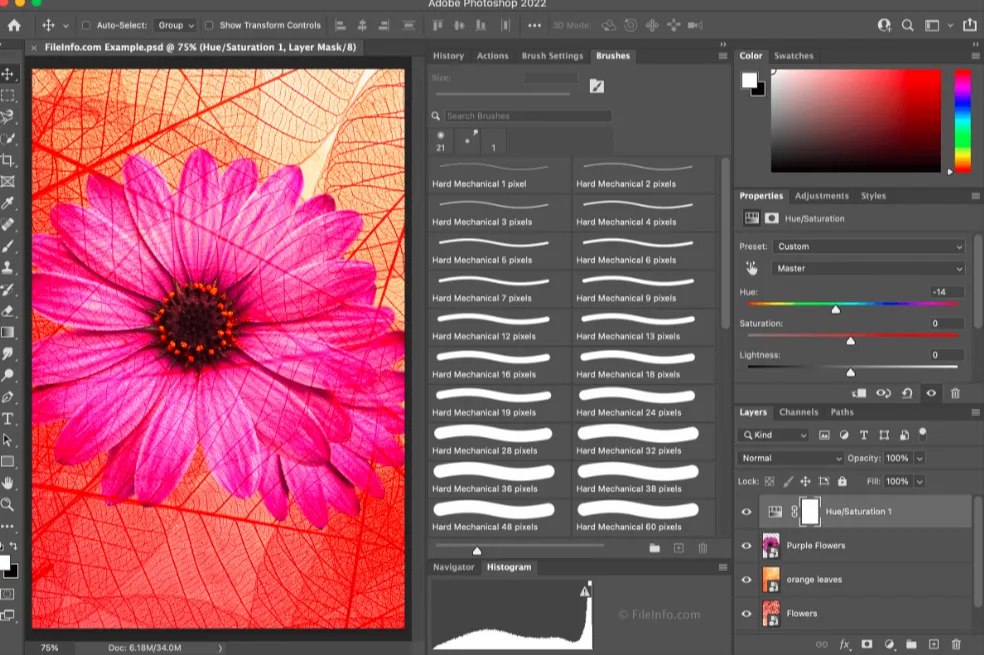
Photoshop’s advanced techniques unlock a world of creative possibilities beyond basic image editing. These methods allow for complex manipulations, intricate effects, and professional-grade image enhancements. Mastering these techniques elevates your image editing from simple adjustments to sophisticated transformations.
Compositing Images
Compositing involves merging multiple images into a single cohesive image. This process allows for seamless integration of elements from different sources, creating realistic or stylized scenes. Sophisticated compositing techniques often involve masking, blending modes, and layer adjustments to achieve a believable result. A common use case is combining a foreground subject with a background scene for a more dramatic or dynamic effect.
- Layer Masking: Precisely defining areas of an image to be affected by edits is crucial. Layer masks allow you to control the transparency of layers, creating a smooth transition between elements. A photographer might use layer masks to remove a distracting object from a background image or integrate a subject into a different backdrop.
- Blending Modes: Blending modes control how pixels from different layers interact. Choosing the correct blending mode can significantly alter the visual impact of a composite image. For instance, using “Multiply” can darken the foreground while retaining the background’s color information, while “Screen” lightens it.
- Smart Objects: Smart objects allow for non-destructive edits to layers. This means that you can modify the original source image without affecting other layers in the composite, allowing for iterative refinements without compromising the quality or integrity of the other elements.
Advanced Color Grading and Blending Modes
Advanced color grading goes beyond simple adjustments, employing techniques to create specific moods and visual styles. Blending modes are essential tools for achieving sophisticated color combinations. Understanding these techniques allows for a more nuanced and controlled color manipulation process, giving images a professional and polished look.
- Color Correction Curves: Curves offer precise control over color channels, enabling adjustments to tones and contrast. This precision is essential in achieving a desired color palette or correcting color casts in an image. Using curves allows a more nuanced approach to color correction compared to basic sliders, enabling photographers to adjust hues and saturation with a greater degree of accuracy.
- Selective Color Adjustments: These tools enable targeted adjustments to specific colors within an image. A user might want to increase the saturation of a particular color without affecting others, or potentially reduce the intensity of a specific shade, such as skin tones, to create a more balanced composition.
- Channel Mixer: This tool allows for advanced color adjustments by manipulating the RGB channels independently. It allows for creative color transformations and effects, including desaturating an image while retaining specific color information, or converting a color image into a monochrome image with subtle tonal variations.
Techniques for Creating Special Effects
Photoshop offers various tools to create special effects, ranging from subtle enhancements to dramatic transformations. Understanding these tools enables users to add unique visual flair to their images. These techniques can significantly enhance the impact and artistry of images, from stylized portraits to abstract creations.
- Filters: Photoshop’s built-in filters provide a wide array of special effects. They range from artistic effects like the “Grunge” filter to more realistic ones like “Lens Blur”.
- Layer Styles: Layer styles can add effects to entire layers, such as drop shadows, glows, or bevels, without significantly altering the original image. This enables the user to quickly add a range of stylistic enhancements without significant image manipulation. It is a time-efficient method for adding artistic flair.
- 3D Tools: Photoshop’s 3D tools enable the creation and manipulation of 3D objects, which can then be integrated into images. For instance, a photographer might create a 3D model of a product and integrate it into a studio scene, or an artist might create a 3D object and integrate it into a photorealistic image.
Workflow for Complex Image Editing Projects
A well-defined workflow is crucial for handling complex image editing projects. It streamlines the process, ensuring that all steps are executed efficiently and effectively. It also minimizes the risk of errors and ensures consistency throughout the editing process.
- Project Organization: Creating well-organized folders and naming conventions for files is essential. This aids in the seamless management of various aspects of the project, ensuring that all related files are easily accessible.
- Version Control: Regularly saving versions of your work is crucial for handling complex edits. This safeguards against potential data loss and allows for easy reversion to previous states if needed.
- Batch Processing: For repetitive tasks, utilizing Photoshop’s batch processing capabilities can significantly save time and effort. This is especially beneficial when dealing with large numbers of similar images that require identical edits.
Optimizing Image Quality
Optimizing image quality is crucial for achieving the desired output for various purposes. Strategies for optimizing image quality depend on the intended use and the characteristics of the image. Understanding these considerations is essential to achieve optimal results.
- File Formats: Selecting the appropriate file format is essential. JPEG is suitable for web images, while TIFF is preferable for high-resolution prints. This ensures that the image retains its quality for its intended purpose.
- Image Resolution: The resolution of an image is critical for its intended use. Images intended for print need a higher resolution than images for the web. This ensures that the image retains sufficient detail for its intended purpose.
- Compression Techniques: Appropriate compression techniques can significantly reduce file size without sacrificing image quality. Understanding these techniques allows the user to optimize file size for the intended purpose.
Practical Applications
Photoshop’s versatility extends far beyond basic image editing. Its robust toolset empowers professionals across diverse creative fields, from graphic design to digital art and photography. This section delves into the practical applications of Photoshop, showcasing its use in various creative domains.
Photoshop offers a wide array of features that enable users to manipulate images and create compelling visual content. Its extensive library of tools, coupled with its intuitive interface, makes it a powerful asset for designers and artists of all levels.
Graphic Design Applications
Photoshop is an essential tool for graphic designers. Its precision tools allow for intricate image manipulation, logo design, and creating marketing materials. Examples include designing posters, flyers, brochures, and advertisements. The ability to seamlessly combine text and images with various effects and adjustments elevates the visual impact of these designs. Users can create compelling visuals that effectively communicate brand messages and engage target audiences.
Web Design and Digital Art
Photoshop is a crucial element in web design, enabling the creation of high-quality graphics for websites. It allows for the design of banners, buttons, icons, and other interactive elements. This ensures a consistent visual identity across the website and enhances user experience. In digital art, Photoshop plays a pivotal role in creating illustrations, digital paintings, and concept art. Artists utilize its powerful tools to bring their visions to life, manipulating colors, textures, and details with remarkable precision.
Photography and Photo Editing
Photoshop is indispensable for photographers seeking to enhance their images. It facilitates a range of photo editing tasks, from basic adjustments to complex retouching. Examples include color correction, exposure adjustments, and removing imperfections. Furthermore, advanced techniques like compositing and special effects can transform images, creating unique and artistic outputs. Photographers use Photoshop to polish their work, ensuring a polished presentation and conveying a specific aesthetic.
Comparison with Other Image Editing Software
Various image editing software exists, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. While Photoshop is renowned for its extensive features, other applications offer specialized functionalities or simpler interfaces. A comprehensive comparison is essential to identify the best fit for a specific user’s needs. Factors such as the specific needs, desired level of detail, and price point influence the selection process.
Photoshop Versions Comparison
| Feature | Photoshop CS6 | Photoshop CC 2023 |
|---|---|---|
| Layer Styles | Basic | Advanced |
| Performance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Price | Lower | Higher |
| Features | Limited | Extensive |
The table above presents a concise comparison of Photoshop CS6 and Photoshop CC 2023. Key differences highlight the advancements in features, performance, and overall functionality introduced with newer versions. The choice between versions often depends on the specific needs and budget of the user. The inclusion of more advanced features in newer versions is crucial for handling intricate tasks.
Learning Resources
Mastering Photoshop requires dedicated learning and exploration. A variety of resources, from online tutorials to comprehensive courses, are available to cater to diverse learning styles and skill levels. Effective learning involves actively practicing techniques and applying knowledge to real-world projects.
A wide array of online resources empowers users to acquire Photoshop skills at their own pace. These resources include video tutorials, interactive exercises, and comprehensive courses, offering diverse perspectives and approaches to learning.
Reputable Online Tutorials
Numerous websites and channels provide high-quality Photoshop tutorials. These resources often cover a broad spectrum of topics, from basic editing to advanced techniques. Seeking out tutorials from recognized experts and reputable sources guarantees a structured and reliable learning path. Examples include Adobe’s official tutorials, which offer a wealth of detailed information and exercises, and popular YouTube channels dedicated to Photoshop. These channels provide practical demonstrations and explanations, facilitating a hands-on learning experience.
Educational Platforms
Several platforms specialize in providing structured learning experiences in Photoshop. These platforms often include comprehensive courses, interactive exercises, and assessments to gauge understanding. Platforms like Skillshare, Udemy, and Coursera offer a variety of Photoshop courses, allowing users to explore different skill levels and approaches. They provide access to a diverse range of instructors and course structures, offering flexible learning options.
Learning Resources for Diverse Skill Levels
Learning resources cater to various skill levels. Beginners can benefit from introductory tutorials and basic editing exercises. Intermediate learners can explore advanced techniques and specialized tools. Experienced users can find resources for advanced techniques, creative applications, and specific workflows. These tailored resources are crucial for a comprehensive learning experience. This diversity of learning resources ensures that individuals at every skill level can find suitable material to advance their Photoshop proficiency.
Strategies for Learning Photoshop Effectively
Effective learning strategies are essential for achieving mastery in Photoshop. Consistent practice is crucial, whether it involves replicating tutorials or creating personal projects. Breaking down complex tasks into smaller, manageable steps aids understanding and prevents frustration. Active experimentation and exploration of different tools and techniques are equally important. This active learning approach allows for a deeper comprehension of the software and its capabilities. Regular review of learned concepts and techniques reinforces retention and fosters mastery.
Comparison of Online Courses
This table provides a comparative overview of several online Photoshop courses.
| Course | Price | Duration | Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| Online Course A | $50 | 2 weeks | Beginner to Advanced |
| Online Course B | Free | 4 weeks | Beginner to Intermediate |
Course A, priced at $50, offers a comprehensive two-week program covering beginner to advanced techniques. Course B, accessible for free, provides a four-week curriculum focusing on beginner to intermediate skills. The differing price points and durations reflect the breadth and depth of content offered in each course.
Industry Trends
Photoshop, a cornerstone of digital image editing, is constantly evolving to meet the demands of a rapidly changing creative landscape. Its future direction is heavily influenced by emerging technologies, particularly artificial intelligence and machine learning, as well as the constant advancement of hardware capabilities. Understanding these trends is crucial for both professional and amateur users to effectively leverage the software’s capabilities and stay competitive.
Future Direction of Photoshop
Adobe Photoshop is anticipated to continue its evolution towards more intuitive and automated workflows. This includes streamlined tools for image manipulation, more sophisticated AI-powered features, and greater integration with other creative applications. The software’s focus on providing comprehensive tools for professionals and ease of use for beginners will likely remain a key aspect of its future development.
Emerging Trends and Technologies
Several key trends are shaping the future of image editing. The rise of high-resolution displays and advanced cameras necessitates tools capable of handling increasingly complex imagery. Furthermore, the growing popularity of virtual reality and augmented reality applications will likely lead to a demand for tools that seamlessly integrate with these immersive technologies.
Influence of AI and Machine Learning on Image Editing
AI and machine learning are already transforming image editing by automating repetitive tasks and enhancing creative possibilities. AI-powered tools can automatically correct color balance, remove blemishes, and even generate new imagery based on existing content. In the future, we can expect more sophisticated AI algorithms to further refine these capabilities, enabling more precise and creative manipulation of images. For instance, tools for object removal or background replacement are becoming increasingly automated and accurate.
Impact of New Hardware on Photoshop Usage
The development of faster processors, more extensive RAM, and high-performance graphics cards directly impacts the performance of Photoshop. Users will experience smoother workflows and reduced processing times, allowing them to work with larger files and more complex edits. High-resolution displays also enhance the precision and detail achievable in image editing.
Comparison of Latest Photoshop Versions
Comparing the latest versions of Photoshop reveals significant advancements in features and performance. New versions often incorporate enhanced AI tools, improved user interface elements, and better integration with other Adobe products. For example, recent versions feature enhanced content-aware fill tools, automated adjustments, and sophisticated smart object handling. This allows for greater precision and efficiency in editing tasks. Users should carefully consider the specific needs and requirements of their workflow to select the most appropriate version for their needs.
Illustrative Examples
A deep dive into Photoshop’s capabilities involves exploring practical workflows. This section demonstrates how to transform raw images into compelling graphics using various tools and techniques, from basic adjustments to complex compositing. We’ll explore specific examples, highlighting the power of Photoshop for diverse applications, including print and web design.
Complex Image Editing Workflow
A comprehensive image editing workflow involves several crucial steps. First, assess the image’s initial state, identifying areas requiring adjustment or enhancement. Next, utilize tools like the Healing Brush and Spot Healing Brush for blemish removal and retouching. Cropping and resizing are critical for optimizing the image’s aspect ratio for different applications. Color adjustments, including levels and curves, fine-tune the overall color balance and contrast. Finally, add special effects and filters for a personalized touch.
Transforming a Raw Photo to a Finished Graphic
This process typically begins with a raw photograph. Initial steps involve basic adjustments like exposure, contrast, and white balance to establish a solid foundation. Using the clone stamp tool and the healing brush, imperfections are meticulously removed. Color grading, utilizing curves and color balance tools, brings the image’s color palette to life. Sharpness and noise reduction are crucial steps to improve the image’s clarity. Adding textures and filters, or applying specific effects, further elevates the image to a finished graphic.
Creating a Realistic Image of a Person
Creating a realistic portrait in Photoshop involves meticulous attention to detail. Start by selecting a high-resolution reference image. Using the Clone Stamp tool, carefully copy details from the reference image to the canvas, paying close attention to skin tones, texture, and lighting. Layer masks can be employed to isolate adjustments to specific areas. Using the Liquify filter, subtle refinements can be made to enhance realism, like shaping the face and body. Precise color adjustments, blending modes, and shadow/highlight techniques complete the process, creating a photorealistic image.
Creating a Stylized Image
Stylizing an image in Photoshop involves manipulating its appearance to achieve a unique aesthetic. This often begins with selecting a reference image and creating a base layer. Specific effects, such as applying a unique color palette using color adjustments, can dramatically alter the image’s mood. Applying artistic filters, textures, and shapes can create an entirely new visual style. Using blending modes, the interplay of layers can be controlled, creating a personalized aesthetic. For example, applying a vibrant color scheme to a portrait, creating a graphic illustration, or adding a stylized grunge effect.
Editing an Image for Print or Web Use
Optimizing images for print or web use involves different considerations. For print, higher resolution images are necessary, often in CMYK color mode. Image compression should be minimal to maintain quality. Web images, on the other hand, require smaller file sizes for faster loading times. Using appropriate compression methods and JPEG or PNG formats, the file size can be optimized. Color mode conversions are crucial to ensure the image appears accurately across various devices. For example, converting a photo to CMYK for print and reducing the resolution to a web-friendly size for online use.
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, Photoshop software remains a powerful tool, constantly evolving with emerging trends and technologies. This guide has provided a deep dive into its history, features, and applications, from basic manipulation to advanced techniques. Whether you’re a budding graphic designer or a seasoned professional, this exploration equips you with the knowledge to excel in the digital realm of image editing. The wealth of resources and illustrative examples will further enhance your understanding and practical application of Photoshop.