POS system, it’s like the secret weapon for any business, big or small. Imagine seamless transactions, super-efficient inventory management, and crystal-clear reporting – all rolled into one. This guide dives deep into the world of POS, covering everything from the basics to the cutting-edge tech shaping the future.
From choosing the right POS system for your needs to understanding the security and user experience aspects, we’ve got you covered. This is your one-stop shop for all things POS, so get ready to level up your business game!
Introduction to Point of Sale (POS) Systems

A Point of Sale (POS) system is a software and hardware solution used in businesses to manage transactions and track inventory. It’s the heart of retail operations, facilitating sales, customer service, and data analysis. From small shops to large corporations, POS systems have become indispensable tools for efficient business management.
POS systems streamline the sales process, providing a centralized platform for handling transactions, recording sales data, and managing inventory. This efficiency translates into reduced errors, improved customer service, and increased profitability. Modern POS systems are capable of integrating with various other business applications, providing a comprehensive view of operations.
Core Functionalities of a POS System
POS systems offer a range of functionalities designed to optimize business operations. These functionalities typically include processing transactions, managing inventory, generating reports, and providing customer support.
- Transaction Processing: POS systems handle the entire transaction process, from accepting payment methods (cash, credit, debit) to generating receipts and recording sales details.
- Inventory Management: POS systems track stock levels, allowing businesses to monitor inventory in real-time. This real-time view helps prevent stockouts and overstocking, leading to optimized inventory levels and reduced costs.
- Reporting and Analytics: POS systems generate various reports, such as sales reports, inventory reports, and customer purchase history. These reports provide valuable insights into business performance, enabling data-driven decision-making.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Some advanced POS systems integrate CRM features, enabling businesses to store and manage customer data, track interactions, and personalize service.
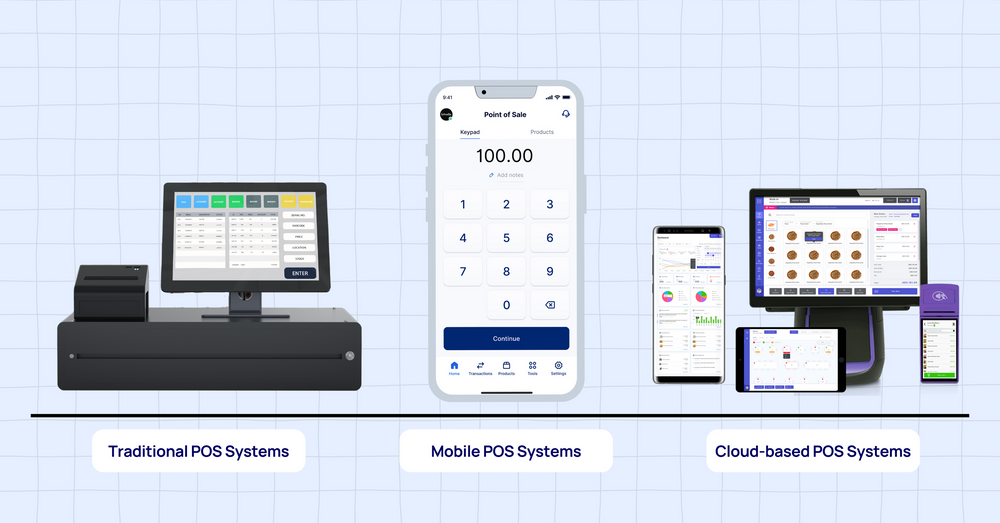
Types of POS Systems
POS systems come in various forms, catering to different business needs and sizes.
- Countertop POS Systems: These are traditional POS systems, typically housed on a countertop with a cash drawer and a display screen. They offer a familiar interface for many businesses, and often come with a variety of hardware options.
- Tablet-Based POS Systems: These systems use tablets as the primary interface, offering mobility and flexibility. Tablet-based POS systems are excellent for businesses that need to move around, like food trucks or mobile retailers. They often offer greater ease of use than countertop systems.
- Cloud-Based POS Systems: These systems are hosted on a cloud platform, eliminating the need for expensive hardware installations. Cloud-based systems often provide greater scalability and flexibility than on-site systems, allowing businesses to easily adapt to changing needs. Remote access is typically a key feature.
Components of a POS System
A POS system comprises various hardware and software components that work together to facilitate transactions.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Point of Sale Terminal | The main interface for processing transactions, often including a touchscreen, keyboard, and barcode scanner. |
| Cash Drawer | Securely stores cash and receipts, typically automatically opening with each transaction. |
| Printer | Prints receipts and transaction records, enabling immediate confirmation for both the customer and the business. |
| Barcode Scanner | Quickly scans barcodes on products to automatically identify items during checkout, reducing manual input errors. |
| Software Application | The software that manages the entire POS system, handling transactions, inventory, reporting, and customer information. |
POS System Features and Benefits
Point of Sale (POS) systems have evolved significantly, moving beyond basic transaction processing to encompass a wide range of functionalities that streamline operations and enhance business efficiency. These systems now provide comprehensive tools for inventory management, customer relationship management (CRM), and reporting, making them indispensable for businesses of all sizes. Modern POS systems offer a dynamic platform for managing various aspects of a business, from sales to customer service.
The core benefit of implementing a POS system lies in its ability to automate and optimize critical business processes. By integrating various functions, POS systems reduce manual errors, free up staff for more productive tasks, and offer valuable insights into business performance. This automation directly translates to improved efficiency and profitability for businesses of all sizes.
Key Features of Modern POS Systems
Modern POS systems offer a wide array of features beyond simple transaction processing. These features are crucial for enhancing operational efficiency and providing valuable business insights. Key functionalities include robust inventory management capabilities, customer relationship management (CRM) tools, and comprehensive reporting tools.
- Inventory Management: Accurate and real-time inventory tracking is a critical function. POS systems allow businesses to monitor stock levels, track sales, and predict future needs. This functionality helps prevent stockouts and overstocking, optimizing inventory levels and reducing waste. For example, a restaurant using a POS system can track the sales of each dish and adjust inventory levels accordingly, minimizing food waste and ensuring ingredients are available when needed.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Modern POS systems integrate customer data, enabling businesses to build stronger customer relationships. These systems can track customer preferences, purchase history, and contact information, enabling targeted marketing campaigns and personalized service. For example, a retail store can use customer purchase history to recommend related products or offer targeted promotions, enhancing customer loyalty and repeat business.
- Reporting and Analytics: Comprehensive reporting tools provide valuable insights into business performance. POS systems generate reports on sales trends, customer demographics, and inventory turnover. These reports are instrumental in identifying areas for improvement and making data-driven decisions. A coffee shop can use sales reports to analyze peak hours and adjust staffing accordingly, optimizing labor costs and maximizing sales.
- Payment Processing: POS systems facilitate secure and efficient payment processing. They support various payment methods, including credit cards, debit cards, and mobile payments. This ensures a smooth transaction process and reduces the risk of errors. A grocery store can accept multiple payment methods, streamlining checkout and improving customer satisfaction.
- Employee Management: Some advanced POS systems integrate employee management tools. These tools allow businesses to track employee hours, manage payroll, and access employee performance data. This can help to optimize labor costs and improve overall efficiency.
Benefits of Implementing a POS System for Different Business Sizes
Implementing a POS system offers significant advantages for businesses of varying sizes. The benefits are substantial and directly impact profitability and operational efficiency.
- Small Businesses: POS systems provide small businesses with a streamlined approach to managing transactions and inventory. These systems offer affordability and accessibility, providing tools to grow and scale operations. For example, a small bakery can use a POS system to track ingredient usage, manage orders, and generate sales reports, allowing for better inventory management and improved profit margins.
- Medium-Sized Businesses: Medium-sized businesses benefit from increased efficiency and better control over their operations. POS systems can manage large volumes of transactions, track inventory across multiple locations, and provide detailed reports on performance, leading to significant operational improvements. A clothing retailer with multiple stores can use a POS system to monitor sales and inventory levels across all locations, optimizing stock distribution and ensuring consistent product availability.
- Large Businesses: Large businesses can utilize POS systems to manage complex operations and maintain consistent performance across multiple locations. POS systems facilitate real-time data analysis, leading to data-driven decisions and improved profitability. A large retail chain can use a POS system to track sales trends across various locations, identify high-performing products, and optimize pricing strategies.
Comparison of POS System Providers
Numerous POS providers cater to diverse business needs. Choosing the right provider is critical to maximizing the benefits of a POS system. Different providers offer varying features and pricing models.
| POS System Provider | Key Features | Pricing | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provider A | Robust inventory management, comprehensive reporting, mobile-friendly interface | Tiered pricing based on transaction volume | Excellent customer support, adaptable to diverse business needs | Slightly higher pricing compared to other providers |
| Provider B | User-friendly interface, quick setup, basic reporting | Flat rate pricing | Affordable, suitable for smaller businesses | Limited advanced features, potentially less scalable |
| Provider C | Advanced CRM integration, cloud-based platform, multiple payment options | Per-transaction fee | Enhanced customer relationship management, data accessibility | Higher per-transaction fees can increase costs |
POS System Implementation and Integration
Implementing a new Point of Sale (POS) system is a significant undertaking for any business. Careful planning and execution are crucial to ensure a smooth transition and maximize the system’s benefits. This process involves not only selecting the right system but also integrating it seamlessly with existing business operations. Successful integration minimizes disruption and maximizes return on investment.
Steps in Implementing a New POS System
A well-structured implementation plan is essential for a successful POS system deployment. The process typically involves several key steps. These steps are often iterative, requiring revisiting and adjustments as the project progresses.
- Needs Assessment and System Selection: Thorough evaluation of current business processes and future needs is paramount. This includes analyzing existing workflows, identifying pain points, and determining the specific features required in a new POS system. A well-defined selection criteria is crucial to narrow down choices and choose a solution that aligns with the business’s specific requirements. This often involves a detailed comparison of different POS systems based on cost, functionality, and scalability.
- System Configuration and Customization: Once the POS system is chosen, configuration and customization are necessary to adapt it to the specific business needs. This might involve configuring settings, adding or modifying user roles, and creating custom reports. Thorough training for staff is vital to ensure efficient use of the new system.
- Data Migration and Testing: Migrating existing data to the new POS system is critical. This step requires careful planning and execution to ensure data accuracy and minimize errors. Comprehensive testing is essential to identify and fix potential issues before the system goes live. Test scenarios should mirror real-world transactions to identify any discrepancies or limitations.
- Training and Staff Support: Providing adequate training to staff on using the new POS system is essential for a smooth transition. Hands-on training sessions and ongoing support are crucial for staff to become proficient in the system’s functions. Documentation, FAQs, and readily accessible support channels are important components of this phase.
- Go-Live and Post-Implementation Review: The system is deployed and transactions are processed. Continuous monitoring of system performance and user feedback is necessary to identify areas for improvement. Post-implementation reviews should assess system efficiency, identify any challenges, and suggest adjustments for optimization.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integration with existing business systems, such as inventory management and accounting software, is crucial for a comprehensive solution. Proper integration ensures data consistency and reduces manual data entry.
- Inventory Management Integration: A seamless integration between the POS system and inventory management software ensures real-time inventory tracking. This allows for automatic updates on stock levels, preventing overselling and facilitating accurate inventory reports. Real-time stock updates are crucial for businesses with high-volume transactions.
- Accounting Software Integration: Integration with accounting software allows for automatic transfer of sales data, eliminating manual data entry and reducing errors. This integration streamlines financial reporting and improves overall financial management. A key aspect is ensuring accurate transaction matching between the POS and accounting software to avoid discrepancies.
- Example: A restaurant using a POS system can automatically update its inventory database when a customer orders a dish. This ensures that the kitchen staff can track ingredient consumption and the inventory system is kept up-to-date. Similarly, the accounting system can automatically record sales transactions, eliminating manual data entry and reducing errors.
Common Challenges During POS System Implementation
Implementing a new POS system can present various challenges. Understanding these challenges is vital for mitigating their impact.
- Data Migration Issues: Errors during data migration can disrupt operations. This highlights the importance of rigorous testing and backup plans.
- Staff Resistance to Change: Resistance from staff to adopting a new system can hinder its effectiveness. Comprehensive training and clear communication about the benefits of the system can overcome this.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating the POS system with existing systems can be complex. Choosing a system with a well-documented API and skilled implementation partners can mitigate this risk.
Checklist for POS System Selection
A structured checklist is helpful in evaluating and selecting the appropriate POS system.
| Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
| Functionality | Check if the system meets the specific business needs. |
| Scalability | Evaluate the system’s ability to adapt to future growth. |
| Cost | Compare the total cost of ownership, including hardware, software, and support. |
| Security | Assess the system’s security features and data protection measures. |
| Integration | Ensure compatibility with existing business systems. |
POS System Security and Data Management

Point of Sale (POS) systems handle sensitive financial and customer data, making robust security crucial. Compromised systems can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. Effective security measures are paramount for protecting both the business and its customers.
Importance of Security Measures
Robust security measures in POS systems are essential to safeguard financial transactions, prevent fraudulent activities, and protect sensitive customer data. Comprehensive security protocols are critical to mitigating risks associated with data breaches and unauthorized access. Security measures also enhance customer trust and confidence in the system. A secure POS system demonstrates a commitment to protecting customer information, which can foster long-term customer loyalty and positive brand perception.
Data Protection and Privacy Regulations
Various data protection and privacy regulations govern the handling of customer data in POS systems. These regulations, such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), and others, mandate specific requirements for data collection, storage, and use. Compliance with these regulations is critical to avoid penalties and maintain the trust of customers. Businesses must implement appropriate security measures to ensure that customer data is handled in accordance with these legal frameworks.
Methods to Protect Customer Data in a POS System
Several methods can be implemented to safeguard customer data within a POS system. These include strong password policies, multi-factor authentication, regular security audits, encryption of data at rest and in transit, and secure data storage practices. These proactive measures can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and protect customer information.
Security Protocols and Effectiveness
Implementing various security protocols is crucial to mitigate the risk of data breaches. A robust security framework must incorporate multiple layers of protection. The effectiveness of these protocols depends on the specific implementation and ongoing maintenance.
| Security Protocol | Description | Effectiveness | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strong Password Policies | Enforce complex password requirements, regular password changes, and password reuse prevention. | High. Strong passwords are a fundamental first line of defense. | Require passwords with a minimum length, including uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Add an extra layer of security by requiring multiple verification steps beyond a password. | High. MFA makes it significantly harder for unauthorized users to access accounts. | Using a security token or biometric scan in addition to a password. |
| Data Encryption | Converting data into an unreadable format during storage and transmission. | Very High. Encryption renders data unusable to unauthorized individuals. | Using encryption protocols like TLS/SSL for online transactions. |
| Regular Security Audits | Conducting periodic assessments of the system’s security posture. | High. Regular audits identify vulnerabilities and allow for proactive remediation. | Penetration testing to simulate attacks and identify weaknesses. |
| Firewall and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) | Protecting the network from unauthorized access and malicious activity. | High. These systems act as a barrier against external threats. | Using a firewall to block unauthorized network connections and an IDS to detect suspicious activity. |
POS System Customization and Reporting

Point of Sale (POS) systems are not one-size-fits-all solutions. Businesses with unique needs often require customization to tailor the system to their specific workflow and reporting requirements. This customization can range from altering the user interface to integrating with existing inventory management or accounting software. Effective reporting is equally critical for analyzing sales trends, identifying profitable products, and optimizing inventory levels.
Customization Options
POS systems offer various customization options to accommodate diverse business models. These include adjusting product categories and descriptions, creating custom sales order types, and modifying pricing strategies. For example, a restaurant might need custom options for specific dish preparations, while a retail store might require dedicated sections for different product lines. These modifications ensure the POS system reflects the unique aspects of the business. Moreover, integrations with other business software systems, such as accounting software, further enhance the system’s functionality. This streamlined data flow simplifies record-keeping and allows for comprehensive analysis.
Reporting Options
POS systems provide a suite of reporting options that empower businesses to gain insights into their operations. Commonly available reports include sales reports, inventory reports, customer reports, and employee performance reports. These reports can be filtered and sorted based on various criteria, such as date range, product type, or sales representative.
Generating Custom Reports
Generating custom reports often involves utilizing the POS system’s built-in reporting tools or utilizing external reporting software integrated with the POS system. Custom reports allow for in-depth analysis by focusing on specific metrics, providing a tailored view of the business’s performance. For instance, a retailer might want a report showing sales of specific products during a promotional period, or a restaurant might need a report detailing the profitability of particular menu items. This ability to generate specific reports gives businesses the power to examine crucial data in the context of their own needs.
Sales Report Types
POS systems can generate various sales reports, each serving a specific purpose. A well-structured POS system will facilitate the creation of the following reports.
| Report Type | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Daily Sales Report | Summarizes sales transactions for a single day. | Tracking daily revenue, identifying peak sales hours. |
| Weekly Sales Report | Provides a summary of sales transactions for a week. | Analyzing weekly sales trends, comparing performance against targets. |
| Monthly Sales Report | Details sales transactions for a given month. | Identifying monthly sales patterns, comparing against previous months. |
| Sales by Product Report | Highlights sales figures for specific products. | Identifying top-selling items, understanding product performance. |
| Sales by Customer Report | Summarizes sales transactions for particular customers. | Analyzing customer purchase patterns, identifying loyal customers. |
| Sales by Employee Report | Details sales figures for individual employees. | Evaluating employee performance, identifying top performers. |
POS System User Experience (UX)
A positive user experience (UX) is crucial for both staff and customers in a Point of Sale (POS) system. A user-friendly interface reduces errors, increases efficiency, and fosters a more pleasant transaction process. Effective design considerations minimize frustration and maximize satisfaction for all users.
Importance of User-Friendly POS Systems
A well-designed POS system streamlines operations for staff, allowing them to complete transactions quickly and accurately. This efficiency translates into higher productivity and reduced staff training time. Moreover, a user-friendly interface minimizes errors, leading to fewer returns and improved accuracy in financial records. For customers, a smooth and intuitive POS experience enhances satisfaction and encourages repeat business. A positive UX fosters a positive perception of the entire business.
Examples of Effective User Interface Design in POS Systems
Effective POS systems utilize intuitive layouts, clear visual cues, and straightforward navigation. For example, well-organized screens with logically grouped buttons and fields allow staff to quickly access necessary information. Clear visual indicators, such as progress bars or confirmation messages, provide immediate feedback on actions. Visual hierarchy, such as using larger fonts for important information or highlighting key fields, further enhances usability. Modern POS systems often employ icons and graphics that are both aesthetically pleasing and highly functional, improving both staff and customer experience.
Improving POS System Usability for Staff and Customers
Improving POS system usability requires a multi-faceted approach. For staff, training should be comprehensive and include practical exercises. User manuals should be clear and easily accessible, with detailed explanations and visual aids. Regular feedback sessions with staff allow for identification and resolution of any issues encountered during the implementation and use of the system. For customers, clear signage and prompts guiding them through the checkout process improve the experience. Intuitive layouts with clear labels for products and services ensure a smooth transaction process. Providing options for different payment methods, including digital wallets, can also enhance customer satisfaction.
Comparing POS System UX
| POS System | Staff UX (Ease of Use) | Staff UX (Error Rate) | Customer UX (Speed) | Customer UX (Clarity) | Customization Options |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| System A | Excellent – intuitive interface, clear navigation | Low – minimal errors due to well-designed prompts | Good – fast transaction process, clear displays | Good – straightforward process, clear product descriptions | Moderate – limited customization options |
| System B | Very Good – customizable interface, good training resources | Low – well-structured data entry, prompts for validation | Excellent – quick checkout process, easy product browsing | Excellent – clear product information, multiple view options | High – extensive customization, API integration |
| System C | Good – user-friendly interface, some learning curve | Moderate – some potential for errors if not used correctly | Fair – average transaction speed, limited product information | Fair – product descriptions can be confusing | Low – limited customization, basic reporting |
This table provides a comparative overview of three hypothetical POS systems. Different criteria are considered, including ease of use for staff, error rates, speed of checkout for customers, and the clarity of the product information presented to customers. Customization options are also evaluated, which can influence the long-term effectiveness and adaptability of the POS system.
Future Trends in POS Systems
Point of Sale (POS) systems are constantly evolving to meet the demands of a dynamic retail environment. Emerging technologies are reshaping the way businesses interact with customers and manage transactions. This section explores the future trends in POS systems, focusing on the impact of advancements in AI, mobile payments, and other technologies.
Emerging Technologies Impacting POS Systems
Modern POS systems are integrating cutting-edge technologies to enhance efficiency, security, and customer experience. Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming various aspects of POS operations, from personalized recommendations to automated customer service. Mobile payments, cloud-based solutions, and biometrics are also playing crucial roles in shaping the future of retail transactions.
Potential Future Developments in POS System Design
Future POS systems will likely feature a more seamless and integrated user experience. Intuitive interfaces, enhanced security measures, and real-time data analysis will become standard features. Expect greater emphasis on personalization and customer engagement, driving customer loyalty and satisfaction. Advanced analytics will provide businesses with valuable insights into customer behavior and market trends.
How Emerging Technologies are Shaping the Future of POS Systems
AI-powered POS systems can offer predictive analytics to optimize inventory management, forecast sales, and personalize customer experiences. Real-time data insights will enable businesses to respond dynamically to changing market conditions. Mobile payment integrations will facilitate contactless transactions, improve customer convenience, and reduce transaction times. Cloud-based solutions will offer greater scalability, accessibility, and data security.
Different POS System Technologies Used Across the World
Various POS technologies are adopted globally, with adaptations based on local needs and regulations. Examples include QR code payment systems prevalent in Asian markets, and biometric authentication gaining traction in Europe. Cloud-based solutions are becoming increasingly popular globally, offering scalable and secure transaction processing. The adoption of these technologies varies based on factors such as technological infrastructure, regulatory environments, and cultural preferences.
| Technology | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| AI-powered POS | Leverages AI for tasks like inventory management, sales forecasting, and customer service. | Increased efficiency, personalized customer experiences, optimized resource allocation. |
| Mobile Payments | Enable contactless transactions through smartphones and tablets. | Enhanced customer convenience, reduced transaction times, improved security. |
| Cloud-based POS | Stores and processes data remotely, offering greater scalability and accessibility. | Improved data security, flexible deployment options, cost-effective solutions. |
| Biometric Authentication | Utilizes unique biological characteristics for secure identification. | Enhanced security, reduced fraud risk, convenient login processes. |
Ending Remarks
So, there you have it – a comprehensive look at POS systems. From their core functionalities to the future trends shaping the industry, we’ve explored it all. By understanding the nuances of POS systems, businesses can unlock efficiency, enhance customer experiences, and ultimately, thrive in today’s competitive market. Ready to take your business to the next level? The choice is yours!