Sales CRM systems are rapidly transforming how businesses manage customer interactions and drive sales. From streamlining lead generation to enhancing customer relationships, these tools offer significant advantages in today’s competitive market. This guide explores the intricacies of Sales CRM, covering everything from core functionalities and implementation strategies to emerging trends and integration possibilities.
This comprehensive overview delves into the critical aspects of sales CRM systems, examining their benefits, features, and implementation strategies to provide a practical guide for businesses seeking to optimize their sales processes.
Introduction to Sales CRM
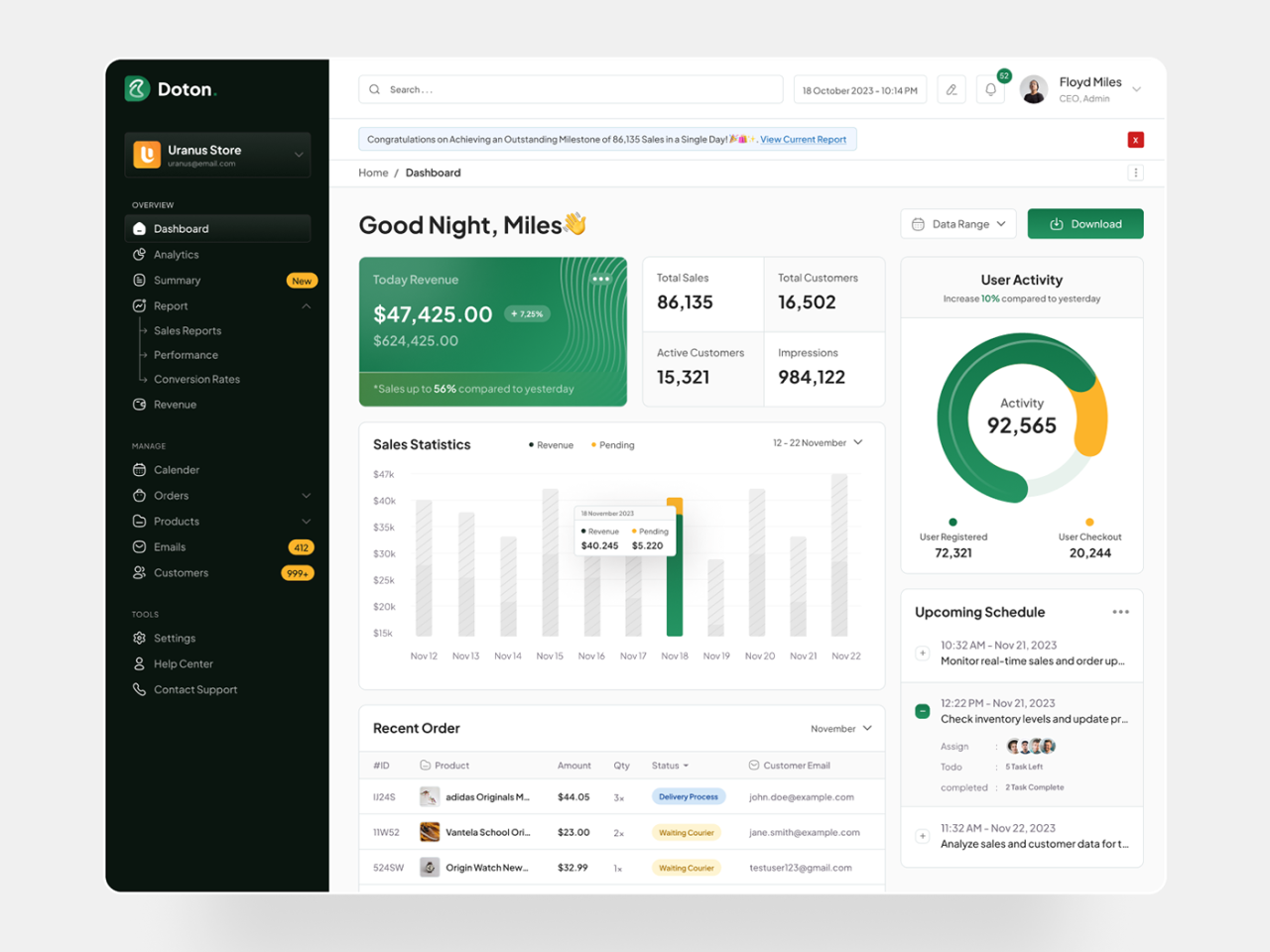
A Sales CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system is a software application designed to manage and streamline interactions with potential and existing customers. It centralizes customer data, sales activities, and marketing efforts, enabling businesses to effectively track leads, manage sales pipelines, and nurture customer relationships. This comprehensive approach fosters a more organized and efficient sales process.
Core functionalities of a Sales CRM encompass various aspects of the sales cycle, including lead generation, opportunity tracking, contact management, sales forecasting, and reporting. These tools allow businesses to analyze sales performance, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions to optimize their sales strategies. Efficiently managing customer interactions through CRM systems often leads to higher conversion rates and improved customer satisfaction.
Core Functionalities of a Sales CRM
A Sales CRM system provides a centralized platform for managing various aspects of the sales process. Key functionalities include lead tracking, contact management, opportunity management, sales forecasting, and reporting. Each function contributes to a more organized and efficient sales process.
- Lead Tracking: A CRM system allows businesses to capture and track potential customers. This includes recording contact information, initial interactions, and any follow-up actions. This crucial function helps businesses prioritize leads and allocate resources effectively.
- Contact Management: A well-maintained contact database is essential for a successful sales strategy. CRMs allow businesses to store comprehensive customer information, including contact details, purchase history, and interaction logs. This detailed view of the customer helps tailor interactions and personalize the sales approach.
- Opportunity Management: CRM systems facilitate the tracking of potential sales opportunities. These opportunities are often categorized by stage, allowing sales teams to visualize their pipeline and manage progress effectively. This feature helps in allocating resources and optimizing the sales process.
- Sales Forecasting: By tracking sales data and identifying patterns, CRM systems can provide insights into potential future sales. This predictive capability empowers businesses to make informed decisions about resource allocation and sales targets.
- Reporting and Analytics: Sales CRM systems generate reports and provide valuable insights into sales performance. This data-driven approach helps businesses understand their strengths and weaknesses, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions to optimize sales strategies.
Benefits of Implementing a Sales CRM
Implementing a Sales CRM offers significant advantages for businesses of all sizes. Improved efficiency, increased sales, and enhanced customer relationships are just some of the benefits. This centralized system streamlines processes, leading to more effective and targeted sales strategies.
- Improved Sales Efficiency: A CRM system automates many repetitive tasks, freeing up sales representatives to focus on building relationships and closing deals. This increased efficiency often translates into faster sales cycles and higher conversion rates.
- Enhanced Customer Relationships: By centralizing customer data, a CRM enables businesses to understand their customers better. This knowledge allows for personalized interactions, leading to stronger customer relationships and increased customer loyalty.
- Increased Sales: Better lead management, streamlined sales processes, and improved customer relationships can directly lead to higher sales figures. The improved efficiency and accuracy in tracking opportunities often results in increased revenue.
Types of Sales CRM Software
Various types of CRM software cater to different business needs and budgets. Common types include cloud-based and on-premises solutions.
- Cloud-based CRM: Cloud-based CRM systems are hosted on remote servers, accessible via the internet. This eliminates the need for on-site infrastructure, offering greater flexibility and scalability.
- On-premises CRM: On-premises CRM systems are installed and maintained on the company’s own servers. This provides greater control over data and security, but requires a dedicated IT infrastructure.
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premises CRM Comparison
| Feature | Cloud-based | On-premises |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Remote access | On-site installation |
| Cost | Typically lower upfront cost | Higher upfront cost |
| Scalability | Easier to scale | More complex to scale |
| Maintenance | Vendor manages | Internal IT team manages |
Key Features and Benefits

Sales CRM systems are crucial for modern businesses seeking to optimize sales processes and enhance customer relationships. These systems consolidate data, automate tasks, and provide valuable insights into sales performance. By centralizing customer interactions, lead management, and sales data, businesses can streamline operations and boost overall efficiency.
Effective CRM systems are no longer a luxury but a necessity in today’s competitive landscape. They provide a comprehensive view of the sales pipeline, enabling businesses to track leads, forecast sales, and make data-driven decisions. This holistic approach improves customer satisfaction and boosts profitability.
Contact Management
A robust contact management system is fundamental to any successful CRM. It allows businesses to store, organize, and access detailed information about individual contacts. This includes contact details, communication history, purchase history, and other relevant data. This centralized repository enables sales teams to quickly access critical information, personalize interactions, and nurture leads effectively. For example, a sales representative can quickly see a customer’s past purchases, identify their needs, and tailor their sales pitch accordingly, fostering stronger customer relationships.
Lead Tracking
Lead tracking is an integral component of a sales CRM. It involves capturing, organizing, and progressing leads through the sales pipeline. This process allows businesses to identify potential customers, nurture their interest, and move them towards a conversion. A well-structured lead tracking system helps prioritize leads based on various factors such as potential value and engagement level. This targeted approach increases conversion rates and maximizes sales opportunities.
Sales Forecasting
Accurate sales forecasting is essential for effective financial planning and resource allocation. CRM systems provide tools to analyze sales data, identify trends, and predict future sales performance. By analyzing historical sales figures, current market conditions, and sales pipeline data, businesses can gain valuable insights into future revenue potential. This allows for proactive planning and resource allocation, ensuring that the company is well-positioned to achieve its targets. For example, a business might predict a 15% increase in sales in the next quarter based on current sales figures and market analysis, allowing them to adjust staffing and inventory levels accordingly.
Reporting and Analytics
Comprehensive reporting and analytics are critical for evaluating sales performance and identifying areas for improvement. CRM systems provide various reports on sales activities, customer interactions, and overall sales performance. These reports can be customized to provide specific insights into key performance indicators (KPIs). For example, businesses can generate reports on sales by region, product, or sales representative, helping identify top performers and areas where sales are lagging. This data-driven approach enables businesses to make informed decisions and optimize their sales strategies.
Automation
Automation plays a crucial role in streamlining sales processes and increasing efficiency. CRM systems automate repetitive tasks such as email marketing, lead nurturing, and appointment scheduling. This frees up sales representatives to focus on high-value activities such as building relationships and closing deals. By automating these tasks, businesses can improve response times, increase productivity, and reduce errors.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
A CRM system significantly improves customer relationship management by centralizing customer interactions. This allows businesses to maintain a comprehensive view of each customer’s history, preferences, and interactions. This detailed information enables businesses to personalize their interactions and tailor their offerings to individual customer needs, fostering loyalty and repeat business. Businesses can also anticipate customer needs and proactively address issues, further strengthening relationships.
Metrics for Tracking
- Sales Cycle Length: The time it takes to convert a lead into a customer.
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of leads that convert into customers.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): The total revenue a customer is expected to generate throughout their relationship with the business.
- Average Sales Value: The average revenue generated per sale.
- Sales by Region/Territory: Performance comparison across different regions or sales teams.
- Lead Source Analysis: Determining the most effective channels for generating leads.
- Customer Churn Rate: The percentage of customers who stop doing business with the company.
These metrics provide a clear picture of sales performance, enabling businesses to identify areas for improvement and optimize their strategies.
Implementation Strategies

A robust Sales CRM implementation is not just about acquiring the software; it’s a strategic process requiring careful planning and execution. Successful implementation hinges on a clear understanding of the system’s capabilities, the organization’s specific needs, and a commitment to employee training and data management. This process ensures the CRM system effectively integrates into existing workflows and yields a measurable return on investment.
Implementing a Sales CRM is more than simply installing software. It’s a multifaceted process requiring meticulous planning and execution. A successful implementation ensures the CRM system seamlessly integrates into existing workflows, maximizing its value and delivering a positive return on investment.
Step-by-Step Implementation Procedure
A structured approach to implementation is crucial for minimizing disruption and maximizing the system’s adoption. A phased rollout, starting with a pilot group and gradually expanding to the entire sales team, allows for early identification and resolution of potential issues. Documentation of each step, including timelines and responsibilities, is essential for tracking progress and maintaining accountability.
- Assessment and Planning: Thorough analysis of current sales processes and identification of specific CRM needs is critical. This stage involves defining key performance indicators (KPIs) and establishing clear objectives for the CRM system.
- Data Migration: Careful planning is essential to ensure a smooth transfer of data from existing systems. This includes data cleansing, validation, and transformation to ensure data integrity in the new CRM system.
- Customization and Configuration: The CRM system should be tailored to meet the specific requirements of the business. Customization may include creating custom fields, workflows, and reports. This stage ensures the CRM aligns perfectly with the sales team’s unique processes.
- Pilot Testing: A pilot group tests the system and provides valuable feedback for adjustments before full implementation. This ensures the system is user-friendly and addresses potential issues proactively.
- Training and Support: Comprehensive training programs for all users are crucial for effective CRM utilization. Continuous support and mentorship are equally important to address questions and encourage adoption.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Post-implementation, the system should be monitored to track its effectiveness in achieving business goals. Regular analysis and adjustments are necessary to optimize performance.
Importance of Employee Training
Effective employee training is fundamental to the successful adoption and utilization of a Sales CRM system. Training should go beyond basic software operation; it should focus on the strategic benefits and how the CRM can enhance their daily tasks. A clear understanding of the system’s features and functionalities empowers employees to leverage its full potential, leading to improved efficiency and productivity.
- Comprehensive Training Modules: Training materials should encompass practical exercises, real-world scenarios, and hands-on demonstrations to reinforce learning and build confidence in utilizing the system.
- Hands-on Workshops: Workshops should provide opportunities for interactive learning and practical application of CRM features. This fosters a deeper understanding of how the system integrates with existing workflows.
- Mentorship and Support: Assign experienced mentors to guide new users, address questions, and provide ongoing support. This personalized approach ensures a smoother transition and fosters user confidence.
Data Migration Plan
A well-defined data migration plan ensures a smooth transition of existing sales data into the new CRM system. This plan should Artikel the steps involved in extracting, transforming, and loading (ETL) data from the old system to the new. The plan should include a data quality check to identify and correct any inconsistencies or errors.
- Data Extraction: Identify the data points to be migrated, ensuring completeness and accuracy.
- Data Transformation: Adjust data formats and structures to align with the new CRM system’s requirements.
- Data Loading: Migrate the data to the new CRM system in a secure and efficient manner.
Role of Data Quality in CRM Success
High-quality data is the cornerstone of any successful CRM system. Accurate and consistent data enables reliable reporting, insightful analysis, and effective decision-making. Maintaining data quality throughout the implementation process ensures that the CRM system provides valuable insights.
Data quality directly impacts the effectiveness of a Sales CRM system. Inaccurate or incomplete data leads to unreliable reports, flawed analysis, and ultimately, poor business decisions.
Choosing the Right CRM System
Selecting a CRM system that aligns with specific business needs is paramount. This involves carefully evaluating the system’s features, functionalities, and scalability to ensure it can accommodate future growth and evolving requirements. The system should integrate seamlessly with existing software and provide adequate support for the business.
- Consider Business Requirements: Assess the current sales processes and identify areas where the CRM can improve efficiency.
- Evaluate Scalability: Ensure the system can adapt to the evolving needs of the business as it grows.
- Analyze Integration Capabilities: Confirm compatibility with existing software applications to minimize disruption during implementation.
Potential Challenges in Sales CRM Implementation
Implementing a Sales CRM system can present various challenges. Addressing these challenges proactively can minimize disruptions and ensure a smoother transition.
| Challenge | Potential Solution |
|---|---|
| Data Migration Issues | Develop a robust data migration plan, including data validation and cleansing procedures. |
| User Resistance | Provide comprehensive training and support, addressing user concerns and emphasizing the benefits of the system. |
| Integration Difficulties | Select a CRM with compatible APIs or utilize integration tools to ensure seamless data flow. |
Case Studies
Implementing a Sales CRM is not a one-size-fits-all endeavor. Success hinges on understanding the specific needs and challenges of individual businesses. Real-world case studies provide valuable insights, demonstrating how different companies have leveraged Sales CRMs to enhance their sales processes and achieve tangible results. These examples showcase not only the positive impacts but also the critical lessons learned along the way.
Successful CRM Implementations
Businesses across various sectors have benefited from Sales CRM implementations. A common thread is the improvement in sales efficiency and effectiveness, leading to increased revenue and profitability. For example, a retail company might see a surge in sales conversions due to enhanced lead management and customer relationship nurturing. Likewise, a software company might witness a significant reduction in sales cycle length, thanks to streamlined workflows and improved communication.
Impact on Sales Processes
Sales CRM systems can revolutionize sales processes in numerous ways. Automated tasks like lead qualification and follow-ups free up sales representatives to focus on higher-value activities, leading to improved productivity and conversion rates. Data analysis capabilities allow for a deeper understanding of customer behavior, enabling businesses to personalize their interactions and tailor their offerings accordingly. Furthermore, centralized data repositories provide a holistic view of the sales pipeline, enabling more informed decision-making and improved forecasting.
Key Lessons Learned
Successful CRM implementations often hinge on a few key factors. Firstly, thorough planning and alignment with business objectives are crucial. Secondly, comprehensive training for sales teams is essential to ensure effective adoption and usage. Finally, ongoing monitoring and refinement of the CRM system are vital for maximizing its long-term benefits. In short, a successful implementation is a journey, not a destination, requiring constant adaptation and optimization.
Case Study: XYZ Manufacturing
XYZ Manufacturing, a mid-sized producer of industrial machinery, faced the challenge of managing a growing sales pipeline with limited internal resources. Their existing manual processes were inefficient, leading to delays in communication and lost opportunities. They implemented a Sales CRM to centralize customer data, automate tasks, and track sales progress. The implementation included training sessions for sales representatives, and dedicated support staff for the CRM.
- Challenges: Inefficient manual processes, lack of centralized customer data, difficulty in tracking sales progress, and inadequate communication across departments.
- Solutions Implemented: A cloud-based Sales CRM solution, comprehensive training programs for sales teams, and dedicated CRM support staff. The system allowed for streamlined communication, automated tasks, and comprehensive data analysis.
- Positive Impacts: A 20% reduction in sales cycle time, a 15% increase in sales conversions, and a 10% improvement in customer satisfaction. This resulted in increased revenue and profitability.
Future Trends in Sales CRM

Sales CRM systems are continuously evolving, driven by technological advancements and shifting business needs. The future of sales hinges on the ability to anticipate customer behavior, personalize interactions, and optimize processes for efficiency. This evolution demands a deeper understanding of emerging technologies and their impact on the sales landscape.
The landscape of sales is undergoing a rapid transformation, moving from traditional methods to data-driven, AI-powered approaches. This shift is fueled by the growing importance of customer experience, the need for automation, and the desire for greater personalization. Businesses that effectively leverage these advancements will gain a significant competitive edge.
Emerging Technologies Impacting Sales CRM
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is revolutionizing sales CRM. These technologies are enabling sales teams to automate tasks, personalize interactions, and gain deeper insights into customer behavior. AI-powered chatbots, for example, can handle routine inquiries, freeing up sales representatives to focus on more complex interactions.
AI in Sales CRM
AI is being deployed in various ways within sales CRM platforms. Predictive analytics, powered by machine learning, can forecast sales performance, identify potential leads, and optimize sales strategies. AI-driven lead scoring helps prioritize high-potential leads, maximizing sales efforts. Furthermore, AI-enabled chatbots are increasingly used to handle customer inquiries, provide product information, and even schedule appointments. These functionalities enhance customer experience and streamline sales processes.
Personalized Customer Experiences
Personalized customer experiences are paramount in the future of sales. AI-driven systems can analyze customer data to tailor interactions, offering products or services that resonate with individual needs. This leads to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty. For example, a retailer could use CRM data to recommend products based on past purchases, browsing history, and even social media activity.
Evolution of Sales Processes
Sales processes will evolve towards greater automation and efficiency. AI-powered tools can automate tasks such as data entry, lead qualification, and email marketing. This frees up sales representatives to focus on building relationships and closing deals. Furthermore, the use of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) could revolutionize product demonstrations and customer interactions, providing a more immersive and engaging experience.
Future of Data Security in Sales CRM
Data security is crucial in sales CRM, given the sensitive nature of customer data. Enhanced security measures, including robust encryption and access controls, are essential to safeguard information. Furthermore, organizations should adhere to strict data privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR) and implement data breach prevention strategies.
Impact of Mobile Sales on Sales CRM
Mobile sales represent a significant trend, with sales representatives increasingly relying on mobile devices for communication and data access. Sales CRM platforms must be mobile-friendly, enabling sales representatives to access critical information and update records on the go. This mobile accessibility is critical for responsiveness and real-time decision-making.
Final Wrap-Up

In conclusion, a well-implemented Sales CRM system can significantly boost sales efficiency and customer satisfaction. Careful consideration of features, integration capabilities, and implementation strategies is paramount to achieving desired outcomes. The future of Sales CRM lies in leveraging emerging technologies like AI and machine learning to create even more personalized and efficient customer experiences.