Unlock the power of statistical analysis with SPSS software for free! This comprehensive guide navigates the world of free SPSS downloads, offering a detailed overview of available options, installation procedures, and practical usage examples. Discover how to access and utilize this powerful tool without breaking the bank, whether you’re a student, researcher, or professional seeking to analyze data effectively.
From identifying free download platforms and evaluating their limitations to mastering installation and exploring various usage scenarios, this guide provides a complete resource for anyone interested in harnessing the capabilities of SPSS software without incurring licensing fees. Learn about system requirements, common pitfalls, and alternative software comparisons, enabling informed decision-making in your data analysis journey.
Introduction to SPSS Software
SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences) is a widely used software package for statistical analysis. It’s a powerful tool for researchers, academics, and professionals across various disciplines, including social sciences, market research, and business analytics. SPSS facilitates data manipulation, analysis, and interpretation, allowing users to uncover meaningful insights from their data. Its user-friendly interface and comprehensive statistical procedures make it accessible to both novice and experienced users.
SPSS excels at handling various types of data, from simple surveys to complex experiments. It offers a wide range of statistical techniques, from descriptive statistics to advanced modeling methods. This versatility makes SPSS a valuable asset for researchers needing to analyze a wide range of data types and gain meaningful insights.
Key Features and Functionalities of SPSS
SPSS offers a diverse range of functionalities, enabling users to perform various statistical analyses. Its primary strength lies in its comprehensive suite of statistical procedures, covering a broad spectrum of techniques. This includes descriptive statistics (such as calculating means, standard deviations, and frequencies), inferential statistics (such as hypothesis testing and regression analysis), and advanced statistical modeling (including logistic regression, ANOVA, and more).
- Data Management: SPSS provides robust tools for data entry, cleaning, transformation, and manipulation. This allows users to organize, validate, and prepare their data for analysis. Data import/export capabilities are also essential for seamless integration with other systems.
- Statistical Analysis: SPSS offers a wide array of statistical tests, including t-tests, ANOVA, regression analysis, correlation analysis, and non-parametric tests. This allows users to test hypotheses, examine relationships between variables, and make informed decisions based on their data.
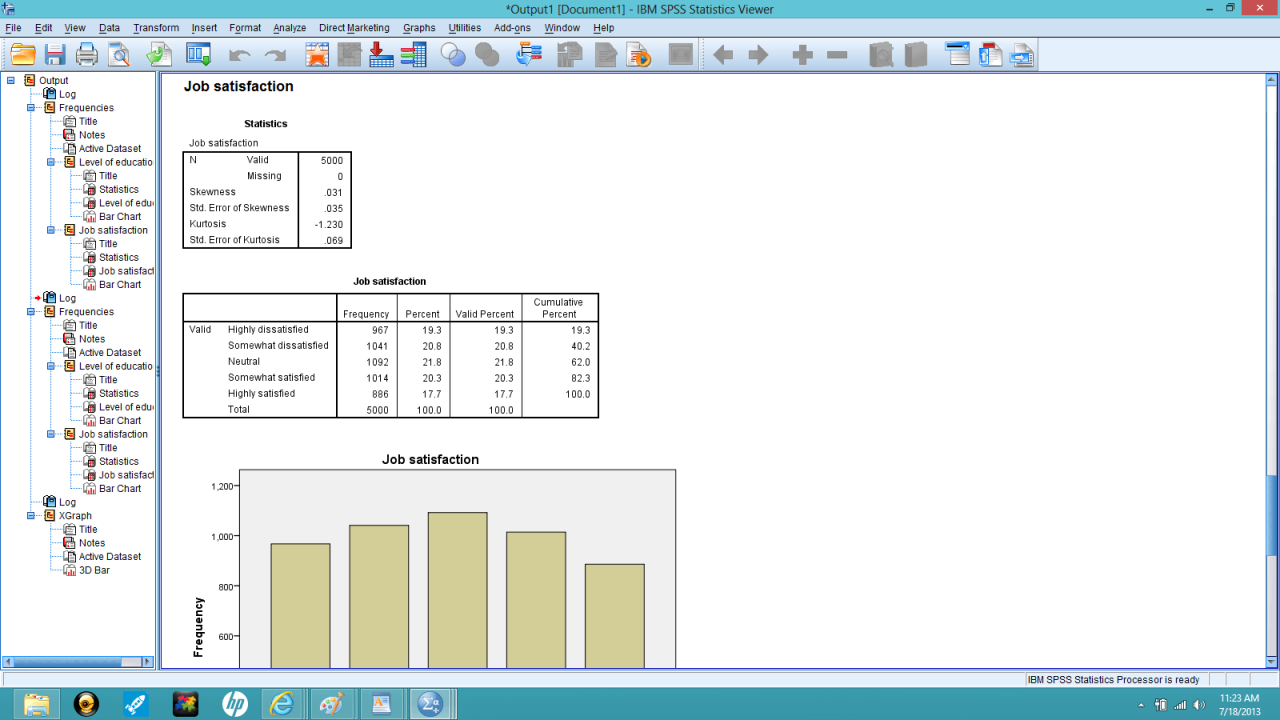
- Data Visualization: SPSS generates various charts and graphs to visually represent data and facilitate the interpretation of results. These visualizations are crucial for understanding trends, patterns, and outliers within the data.
- Reporting and Output: SPSS generates comprehensive reports and outputs, including tables, charts, and statistical summaries. This feature streamlines the presentation of results and allows for clear communication of findings.
Different Versions of SPSS Software
Different versions of SPSS cater to diverse needs and functionalities. This section provides an overview of the commonly used versions, highlighting their distinctions.
| Version | Key Features | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| SPSS Statistics | General statistical analysis, data management, and visualization. Offers a wide range of procedures for various statistical analyses. | Academic research, market research, social science studies, and business analytics. |
| SPSS Modeler | Predictive modeling, data mining, and machine learning tasks. Focuses on building predictive models from data. | Predictive modeling, customer segmentation, fraud detection, and risk assessment. |
Free Download Options
Finding free SPSS software can be tricky, as full versions aren’t typically offered for free. However, several avenues provide access to the software for various purposes. This section explores the different ways to obtain free SPSS access, including limitations and restrictions.
Obtaining free or trial versions of SPSS software often comes with conditions and restrictions. Understanding these terms and conditions is essential to avoid unexpected costs or limitations. Educational institutions, for instance, often have special arrangements for students and faculty, but these may be tied to specific requirements or timeframes. Knowing these details is critical for ensuring the free access aligns with your needs.
Free Download Platforms
Various platforms offer free SPSS software downloads, often with specific limitations. These options include educational institutions, limited-time trials, and specific academic programs. The availability of free trials varies widely.
Educational Institutions
Many universities and colleges provide free or discounted access to SPSS software for students and faculty. This access is often part of a larger academic package, and the terms of use may vary based on the institution’s specific policies.
Trial Versions
Trial versions are another common way to experience SPSS software without immediate purchase. These trials usually have time limits and feature restrictions, but they offer a valuable opportunity to evaluate the software before committing to a full purchase.
Limited-Time Offers
Some software vendors may offer free or discounted SPSS downloads for limited periods. These promotional periods might be tied to specific events, holidays, or special campaigns. These opportunities can be helpful for those looking to try the software without a long-term commitment.
Terms and Conditions
Free downloads of SPSS software often come with terms and conditions. These conditions Artikel limitations, restrictions, and the scope of use for the free software. Important aspects to consider include:
- Duration of Access: Free trials typically have a limited time frame for use.
- Feature Limitations: Trial versions might restrict access to certain features or functions of the software.
- Data Handling Restrictions: Some free trials may have limits on the size or type of data that can be processed.
- User Restrictions: Free downloads might be restricted to individual users or academic institutions.
These limitations need careful consideration before committing to a free download. Understanding the terms and conditions ensures a smooth and productive experience.
Comparison Table of Free Download Options
The following table summarizes different free download options, including links (if available), system requirements, and user reviews (where applicable). Note that links to user reviews or download sites are not provided in this example.
| Option | Download Link | System Requirements | User Reviews |
|---|---|---|---|
| Educational Institution Access | (varies) | (varies) | (varies) |
| Trial Version | (varies) | (varies) | (varies) |
| Limited-Time Offer | (varies) | (varies) | (varies) |
Obtaining a Free SPSS Trial Download
The process for obtaining a free SPSS trial download varies depending on the vendor. Generally, it involves visiting the vendor’s website, navigating to the download section, and selecting the trial option. Following the instructions provided by the vendor will guide you through the download and installation process. A typical process might involve providing personal or institutional information.
Evaluating Free Versions
Free SPSS alternatives can be a valuable resource for students and researchers with limited budgets. However, understanding their limitations is crucial for making informed decisions. These versions often come with restrictions on features and data size, significantly impacting their usability for complex analyses. Knowing these constraints beforehand can prevent frustration and wasted time.
Limitations of Free SPSS Software
Free versions of statistical software often have restricted functionalities compared to their paid counterparts. These limitations frequently involve the types of analyses possible, the amount of data that can be processed, and the availability of advanced features. Careful consideration of these limitations is necessary to avoid encountering unforeseen problems during your analysis.
- Feature Restrictions: Free versions typically omit certain statistical procedures or advanced options found in paid versions. For example, some free software might lack specific regression models, specialized clustering techniques, or advanced graphical options. This can significantly limit the scope of analyses you can perform.
- Data Limits: Many free SPSS alternatives impose restrictions on the size of datasets that can be analyzed. This limitation arises from the software’s processing capabilities and available memory. Beyond the imposed data size, other limitations include the type of data the free software supports.
- Technical Support: The level of technical support for free versions often differs significantly from paid versions. This may result in a lack of assistance when encountering problems or needing clarification on functionalities. While online forums and communities can provide support, they may not always offer the same level of personalized assistance as paid versions.
Comparison with Paid Versions
A crucial aspect of evaluating free SPSS alternatives is comparing them to paid versions. This comparison highlights the trade-offs between functionality and cost. It’s essential to understand what features are sacrificed in the free version to understand the limitations.
| Feature | Free Version | Paid Version |
|---|---|---|
| Statistical Tests | Basic descriptive statistics, t-tests, ANOVA | Wide range of tests, including advanced regressions, non-parametric tests, multivariate analyses |
| Data Handling | Limited data import/export options | Comprehensive data management tools, flexible data manipulation |
| Graphics | Basic charts and graphs | Advanced and customizable graphs, statistical plots |
| Support | Limited or no dedicated support | Technical support, documentation, FAQs |
Evaluating for Specific Needs
Choosing the right free SPSS alternative requires careful consideration of your specific needs. Before downloading any software, assess your analysis requirements and identify the necessary features. This detailed evaluation will guide you toward software that aligns with your project goals.
- Define Your Analysis Goals: Clearly Artikel the specific statistical analyses you need to perform. This will help you narrow down the options and identify software capable of handling your requirements.
- Assess Data Characteristics: Evaluate the size and complexity of your dataset. Free software may not be suitable for extremely large datasets or intricate data structures. Determine the data type and format to ensure compatibility.
- Consider Software Functionality: Evaluate the statistical tests, data management tools, and graphical capabilities offered by the free software. Compare these features to the requirements of your analysis.
- Explore User Reviews and Documentation: Look for user reviews and documentation to gain insights into the software’s usability, ease of use, and common issues. This will provide practical knowledge of the software’s strengths and weaknesses.
Key Factors in Choosing a Free Download
Several key factors influence the decision of selecting a free SPSS alternative. These factors help guide your decision-making process and ensure you choose the right software for your needs.
- Functionality: Ensure the software supports the specific statistical analyses you require. A strong emphasis on the core functions of the software is critical.
- Data Capacity: Evaluate the software’s limitations regarding data size and type. This is crucial to prevent issues with processing large datasets.
- User Friendliness: A user-friendly interface and clear documentation contribute to a positive user experience.
- Support Availability: Consider the availability of support resources, such as online forums or documentation, to assist you when needed.
System Requirements for Free Downloads
Before diving into the exciting world of free SPSS downloads, understanding the technical prerequisites is crucial. Compatibility issues can lead to frustrating errors and wasted time. Knowing your system’s capabilities ensures a smooth installation and optimal performance. This section Artikels the system requirements for various free SPSS versions, helping you determine if your computer meets the minimum standards.
Minimum System Requirements
To avoid installation or performance problems, it’s essential to verify your system’s compatibility with the specific SPSS version you’re considering. Different versions may have varying requirements, so meticulous checking is vital. Meeting the minimum requirements guarantees a functional download and installation process.
Operating System Compatibility
Different free SPSS versions support various operating systems. This section provides a comprehensive table outlining the compatibility of each free download with different OS versions.
| SPSS Version | Supported Operating Systems |
|---|---|
| SPSS Statistics Free Trial | Windows 10, Windows 11, macOS 10.15 or higher |
| SPSS Modeler Free Trial | Windows 10, Windows 11, macOS 10.15 or higher |
| Other Free SPSS Alternatives (e.g., PSPP) | Windows, macOS, Linux |
This table illustrates the operating systems supported by different free SPSS versions. Note that compatibility can vary, and it’s always advisable to check the official documentation of the specific free version you are interested in.
Verifying System Specifications
To ensure your system meets the technical specifications, there are several ways to determine the compatibility.
- Check your operating system’s version and architecture. This information is usually accessible through the system settings or properties of your computer. Verify if it aligns with the supported OS versions in the table above.
- Assess your processor speed. Most free SPSS versions require a minimum processor speed. Check the specifications of your CPU to confirm its capabilities.
- Evaluate your RAM capacity. Free SPSS versions typically require a minimum amount of RAM. Verify your system’s RAM capacity to ensure it meets the minimum requirements.
- Inspect your hard drive space. The installation process requires sufficient hard drive space. Ensure there’s enough free space available on your hard drive to accommodate the installation.
By following these steps, you can accurately determine if your system is capable of running the free SPSS software. This proactive approach prevents installation failures and ensures a smooth experience.
Installation and Setup Procedures
Getting SPSS up and running smoothly involves careful attention to detail during both installation and initial setup. This section will provide a step-by-step guide, including pre-installation checks and troubleshooting common issues, ensuring a seamless transition from download to fully functional software. A well-executed installation minimizes frustration and maximizes your use of SPSS.
Pre-Installation Checks
Before initiating the installation process, it’s crucial to verify your system meets the minimum requirements Artikeld in the free download documentation. This proactive step prevents potential installation problems down the line. Incorrect system configurations can lead to installation failures or software instability. Ensure sufficient hard drive space is available, and that necessary drivers are already installed on your system.
- Verify System Requirements: Double-check that your computer’s processor, RAM, operating system, and available hard drive space meet the minimum specifications Artikeld for the free SPSS version you’ve chosen. Discrepancies can lead to installation errors.
- Antivirus Software: Temporarily disable your antivirus program during the installation process. Sometimes antivirus software can interfere with the installation procedure, blocking essential files from being copied or causing conflicts. Resume antivirus protection after the installation is complete.
- Administrator Privileges: Ensure you have administrator privileges on your computer. This is crucial for the installation program to access and modify system files.
- Sufficient Disk Space: Verify that there’s enough available hard drive space to accommodate the entire SPSS installation package. Insufficient space can halt the installation.
- Download Integrity: Before initiating the installation, verify the integrity of the downloaded file. Use a checksum verification tool to ensure the downloaded file hasn’t been corrupted during the transfer.
Installation Procedures
This section details the steps to install the free SPSS software. Follow the on-screen instructions meticulously for a smooth installation.
- Run the Installer: Locate the downloaded SPSS installation file and run it. The installation wizard will guide you through the process. Carefully review the prompts and options presented.
- Accept the License Agreement: Read and accept the software license agreement. Failing to do so will prevent the installation from proceeding.
- Select Installation Directory: Choose a location on your hard drive where you want to install the software. A default location is often provided, but you can customize it.
- Specify Components (if applicable): Some free versions may allow you to select specific components for installation. Choose the components you need to save space or enhance functionality later.
- Installation Progress: Monitor the installation progress. The installation wizard will display progress updates. Do not interrupt the process unless prompted.
- Complete Installation: Once the installation is complete, the installer will typically prompt you to restart your computer. Follow this step for proper software initialization.
Troubleshooting Installation Issues
This section addresses common problems that might occur during the installation process.
- Installation Errors: If an error message appears, carefully review the error code and associated description. Online resources may provide solutions to specific errors.
- Missing Files: If the installation process reports missing files, ensure the download was complete and verify the integrity of the downloaded file. Redownload the file if necessary.
- Insufficient Space: If the installation fails due to insufficient space, free up disk space on your hard drive before attempting the installation again. Delete unnecessary files or programs to free up the required space.
- Compatibility Issues: If the installation fails due to incompatibility with your system, verify that your system meets the minimum specifications required for the free SPSS version you are installing. If not, consider using a different version or upgrading your system.
Setup Procedures
Once installation is complete, the setup process involves configuring the software to suit your needs.
- Software Initialization: Locate the SPSS application and run it. This step initializes the software for use.
- Data Import: Familiarize yourself with the various data import options provided by SPSS. This allows you to load and work with your data efficiently.
- Basic Operations: Practice performing basic operations, such as data entry, manipulation, and analysis, to become proficient in using SPSS.
- User Interface Customization: Customize the user interface to your preferences by adjusting settings or using the options available. This enhances your workflow efficiency.
Common Usage Examples
SPSS, a powerful statistical software, provides a versatile platform for analyzing diverse datasets. Its user-friendly interface and robust analytical tools make it an essential tool for researchers, students, and professionals across various fields. This section delves into practical examples of using SPSS for data analysis, highlighting the steps involved in conducting simple analyses, importing and exporting data, and manipulating datasets within the software.
Practical Example of Data Analysis with SPSS
This example demonstrates how to analyze customer satisfaction data. Imagine a company wants to understand the factors influencing customer satisfaction with their new product. They collect data from a survey, including questions about product features, pricing, and customer service. Using SPSS, they can analyze this data to identify correlations between different variables and determine which factors have the most significant impact on customer satisfaction.
Steps Involved in Performing a Simple Analysis
To perform a simple analysis, such as determining if there’s a relationship between product features and customer satisfaction, follow these steps:
- Data Entry and Import: Input the collected data into SPSS or import it from other sources (e.g., Excel spreadsheets).
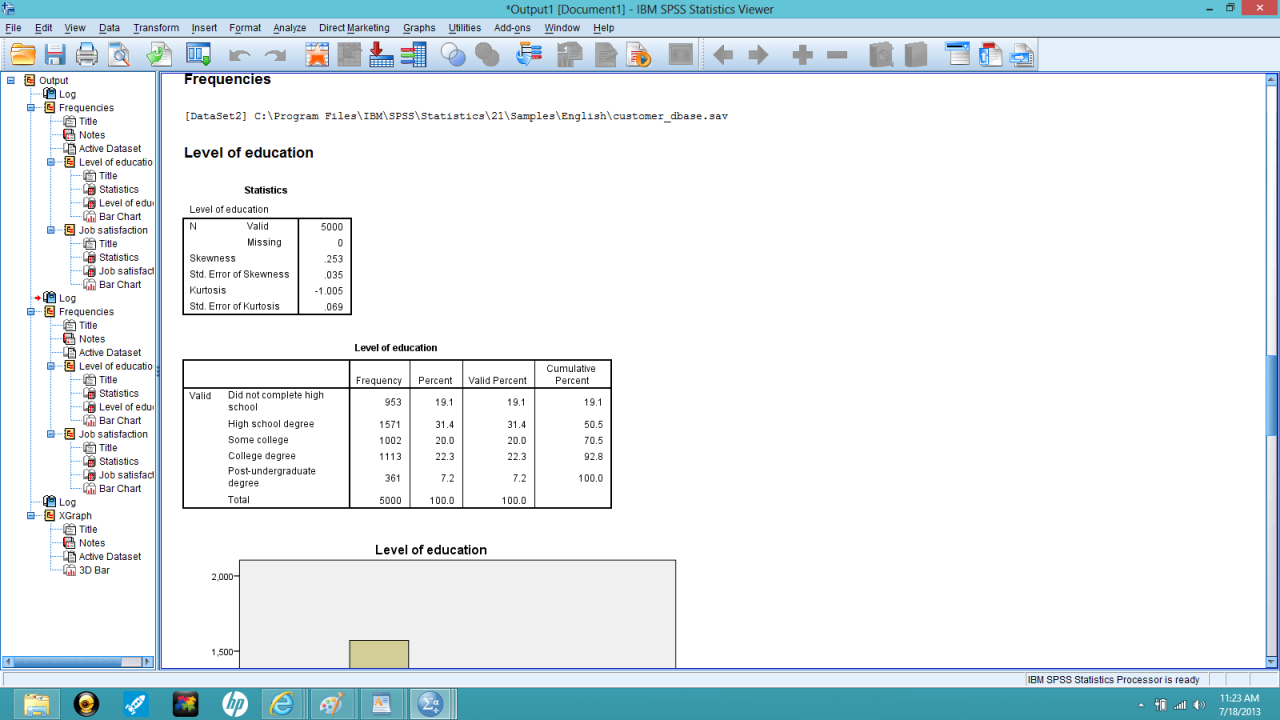
- Data Exploration: Examine the data to understand its characteristics, identify potential outliers, and assess the distribution of variables. Descriptive statistics like means, standard deviations, and frequencies can be used.
- Variable Selection: Identify the key variables for the analysis, such as the satisfaction rating and the features of the product. Ensure that these variables are suitable for the chosen statistical test.
- Analysis Selection: Choose an appropriate statistical test. For example, a correlation analysis might be used to identify relationships between product features and satisfaction ratings. SPSS offers a variety of tests for different types of data.
- Running the Analysis: Execute the selected analysis using the SPSS software. This generates results in tabular or graphical formats.
- Interpretation of Results: Analyze the results obtained from the analysis. Determine if the results support the initial hypothesis or if further investigation is required. Look for patterns, trends, and correlations in the data.
Data Import and Export in SPSS
Data import and export are fundamental functionalities in SPSS. This section Artikels the common ways to import data into SPSS and export results for further use or sharing.
- Importing Data: SPSS supports importing data from various formats like CSV, Excel spreadsheets, and other delimited text files. The import wizard guides users through the process, allowing specification of delimiters, variable types, and other necessary details.
- Exporting Data: SPSS enables exporting analyzed data and results into different formats. Results can be exported as tables, graphs, or reports, facilitating data sharing and collaboration. The flexibility in export options allows for seamless integration with other applications.
Data Manipulation Using SPSS
Data manipulation is crucial for preparing data for analysis in SPSS. This section highlights techniques for transforming data within the software.
- Recoding Variables: SPSS allows recoding existing variables into new ones based on specified criteria. This helps in grouping or categorizing data for analysis.
- Creating New Variables: SPSS allows the creation of new variables based on existing variables through calculations and transformations. This can involve combining existing variables or performing mathematical operations.
- Filtering Data: SPSS allows filtering data based on specific criteria, enabling the analysis of subsets of the data that meet specific conditions. This can involve selecting specific values or ranges for certain variables.
Comparison with Alternative Software
Choosing the right statistical software can significantly impact your analysis. While SPSS offers a user-friendly interface and a comprehensive suite of tools, understanding its strengths and weaknesses relative to other options is crucial. This section compares SPSS with popular alternatives like R and SAS, highlighting their respective advantages and disadvantages.
SPSS, while powerful, is often a paid software. This often presents a barrier for researchers and students on tighter budgets. R, a free and open-source language, provides unparalleled flexibility and customizability. SAS, another industry-standard software, is known for its sophisticated modeling capabilities but often comes with a hefty price tag. Understanding the trade-offs between these choices is essential for making an informed decision.
Comparison of Key Features
SPSS is known for its ease of use and intuitive graphical interface, making it ideal for beginners and those needing a straightforward approach to statistical analysis. R, on the other hand, offers unparalleled flexibility and customizability, making it a powerful tool for advanced users. SAS is generally known for its scalability and ability to handle complex, large-scale datasets, often used in enterprise-level research.
Advantages of SPSS
- SPSS provides a user-friendly interface, making it easier to learn and use compared to some alternatives. This intuitive design helps to avoid complex syntax or coding requirements.
- SPSS offers a comprehensive set of pre-built statistical procedures, simplifying common tasks such as t-tests, ANOVAs, and regression analysis. The streamlined procedures enable quick analysis without needing to write extensive code.
- The extensive library of pre-built templates and reports in SPSS can save significant time and effort. This helps users to focus on data interpretation rather than report creation.
Disadvantages of SPSS
- SPSS is a proprietary software, which often comes with a price tag that can be a barrier for some users. This limits accessibility for individuals and institutions with constrained budgets.
- The pre-built procedures in SPSS can sometimes limit flexibility, particularly for highly customized analyses. The user might need to use alternative tools for analyses that are not readily available within the software.
- The closed-source nature of SPSS can hinder customization options compared to open-source alternatives like R. This might be a drawback for users needing complete control over their analysis workflows.
Advantages of R
- R is a free and open-source software, making it accessible to a wide range of users. This makes it a cost-effective option for students, researchers, and institutions on a budget.
- R offers unparalleled flexibility and customizability. Users can write their own functions and scripts, enabling them to create analyses tailored to specific needs and research questions. This flexibility allows for a more personalized and in-depth approach.
- R has a vast and active community, providing extensive support, tutorials, and packages. This support network allows users to address issues and expand their skills.
Advantages of SAS
- SAS is known for its ability to handle large datasets efficiently, making it suitable for enterprise-level research. This scalability makes it an appropriate choice for institutions and organizations dealing with massive datasets.
- SAS offers advanced modeling capabilities, which are beneficial for intricate analyses. The modeling capabilities enable the creation of complex statistical models, ideal for complex research scenarios.
- SAS is widely used in industry, which provides a substantial user community and extensive documentation. This extensive resource base provides ample assistance to users.
Comparison Table
| Feature | SPSS | R | SAS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Paid | Free | Paid |
| Ease of Use | High | Medium-High (with learning curve) | Medium-Low |
| Flexibility | Medium | High | High |
| Scalability | Medium | Medium | High |
| Community Support | Medium | High | High |
Resources for Learning SPSS
Spss, a powerful statistical software, can seem daunting at first. However, numerous resources are available to guide you through its intricacies. These resources, ranging from online tutorials to comprehensive documentation, make learning SPSS a more accessible and enjoyable experience.
Learning SPSS effectively involves leveraging a variety of resources, each catering to different learning styles and needs. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each resource will help you tailor your learning journey for optimal results. This section details various learning paths, emphasizing practical application and engagement with the software.
Online Learning Platforms
Online platforms offer a wealth of resources for learning SPSS, often providing structured courses and interactive tutorials. This accessibility makes it easier for individuals to learn at their own pace and in a flexible manner.
- Dedicated SPSS Learning Websites: Many websites are dedicated to providing tutorials, examples, and exercises on using SPSS. These platforms often include downloadable practice datasets and detailed explanations of various statistical procedures. These websites allow for a structured approach to learning, often providing quizzes or assessments to gauge understanding.
- YouTube Channels: Numerous YouTube channels feature SPSS tutorials, offering visual demonstrations and step-by-step instructions. These videos can be particularly helpful for those who learn visually or prefer a more dynamic learning environment. Look for channels with clear explanations and practical examples.
- Online Courses (Platforms like Coursera, edX, Udemy): These platforms offer structured courses on statistical analysis, often including SPSS as a key component. These courses typically combine theoretical knowledge with practical application, providing a comprehensive learning experience. Look for courses tailored to your specific needs and skill level.
Tutorials and Documentation
Tutorials and documentation provide valuable insights into specific SPSS functions and procedures. They often include examples, screenshots, and detailed explanations. They can be used as a reference material for particular tasks.
- Official SPSS Documentation: The official SPSS documentation, usually accessible through IBM’s website, offers detailed information on the software’s features, functions, and syntax. This resource is highly recommended for comprehensive understanding.
- User-Generated Tutorials: Numerous online communities and forums offer user-generated tutorials, covering specific analyses or tasks. These tutorials often offer practical solutions to common problems, providing valuable insight and alternative approaches to complex tasks.
Learning Paths for Beginners
A structured approach to learning SPSS is key for beginners. This involves starting with the fundamentals and progressively building upon your knowledge.
- Begin with the Basics: Focus on fundamental concepts of data input, variable manipulation, and basic statistical analyses. Mastering these foundational aspects will lay a solid groundwork for more complex procedures.
- Learn Specific Analyses: Select specific statistical procedures relevant to your field or interests. Learn to use SPSS for these analyses by practicing with datasets. Explore various methods like regression, t-tests, or ANOVA.
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice with SPSS is crucial for solidifying your understanding. Work through examples, create your own datasets, and try to solve different statistical problems using the software.
Accessing and Utilizing SPSS Tutorials
Effectively utilizing online SPSS tutorials involves a systematic approach. This will maximize learning and minimize confusion.
- Search Effectively: Use precise s when searching for tutorials. Specify the type of analysis or function you need assistance with.
- Review Multiple Sources: Compare information from different tutorials to gain a deeper understanding of the concepts and techniques. Look for consistency and clarity in explanations.
- Practice and Experiment: Follow the instructions carefully and experiment with the provided datasets. Actively engage with the software by trying different scenarios and adapting the examples to your needs.
Epilogue
In conclusion, accessing SPSS software for free opens a world of statistical possibilities. This guide has presented a thorough exploration of available options, installation procedures, and practical examples. By understanding the limitations of free versions and comparing them to paid alternatives, you can make informed decisions tailored to your specific needs. Furthermore, this guide has offered a wealth of resources for learning SPSS, empowering users with the knowledge to effectively utilize this powerful tool in their data analysis endeavors.





